文献精选
第十一章 老年糖尿病的急性并发症

低血糖 、高血糖高渗状态(hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state,HHS)和糖尿病酮症酸中毒 (diabetic ketoacidosis,DKA)是糖尿病的严重急性并发症,需要迅速识别、及时诊断并积极治疗。低血糖是降糖治疗过程中的不良反应,可导致短期或长期不良临床结局并增加死亡率。老年糖尿病患者较非老年患者更易发生低血糖,低血糖导致的死亡风险也更高,临床医师应充分重视。DKA 和HHS 的特征是胰岛素缺乏和严重的高血糖,临床上,这两种情况仅在脱水程度和代谢性酸中毒的严重程度上有所不同。DKA或HHS患者的预后和结局取决于年龄、脱水的严重程度、合并症及治疗是否及时规范。老年糖尿病患者发生DKA和HHS的预后和结局通常较非老年糖尿病患者更差。
一、低血糖
在老年糖尿病患者中,低血糖是常见的急性并发症之一,可导致心律不齐、心肌梗死、跌倒,甚至昏迷、死亡等不良事件,反复发生严重低血糖会导致老年糖尿病患者的认知功能下降甚至痴呆[201] 。
1. 定义和标准:国内外指南目前推荐的低血糖定义和分级标准如下:接受药物治疗的糖尿病患者只要血糖<3.9 mmol/L 就属于低血糖。(1)1 级低血糖:血糖<3.9 mmol/L 且≥3.0 mmol/L;(2)2 级低血糖:血糖<3.0 mmol/L;(3)3 级低血糖:需要他人帮助治疗的严重事件,伴有意识和(或)躯体改变,但没有特定血糖界限[202] 。由于老年人群的异质性强,缺乏该人群的低血糖研究,且不同研究中低血糖的诊断标准尚未统一,我国缺乏大型的流行病学调查资料,目前我国老年糖尿病患者低血糖发生率情况不详。
2. 危险因素:年龄是低血糖发生的危险因素之一[203] ,老年糖尿病患者较非老年糖尿病患者的低血糖风险更高[204] 。除年龄因素以外,糖调节能力减弱、合并多种疾病(如 CKD、心血管疾病、肝功能不全等)、多重用药、合并自主神经病变等均是老年糖尿病患者发生低血糖的危险因素[205] 。老年糖尿病患者认知功能下降也是导致严重低血糖风险增加的重要原因[206] 。空腹饮酒、过度限制碳水化合物、进餐不规律、大量运动前未加餐等不良生活习惯是导致低血糖的常见诱因。
3. 临床表现:典型低血糖症状包括出汗、心慌、手抖等交感兴奋症状和脑功能受损症状。但老年糖尿病患者低血糖临床表现有极大的异质性,出现低血糖时常不表现为交感兴奋症状[207] ,而表现为头晕、视物模糊、意识障碍等脑功能受损症状,夜间低血糖可表现为睡眠质量下降、噩梦等。临床上对老年糖尿病患者的不典型低血糖症状应高度警惕。老年糖尿病患者由于神经反应性减弱,对低血糖的反应阈值下降,极易出现严重低血糖。无症状性低血糖发生风险较非老年糖尿病患者更高,而存在无症状性低血糖的老年糖尿病患者发生严重低血糖甚至死亡的风险高[208] 。反复发生低血糖可能进一步减弱神经反应性[209] ,患者甚至在不出现交感兴奋症状的情况下直接昏迷[210] ,如夜间发生上述情况,由于难以被发现和得到及时救治,极为凶险。
4. 预防和治疗:需要特别强调的是,胰岛素和促泌剂使用不当是糖尿病患者发生低血糖的重要原因[211] 。因此,胰岛素、磺脲类促泌剂、格列奈类促泌剂等低血糖风险较高的降糖药物需谨慎选用,使用时应加强血糖监测,必要时可应用 CGM 系统[212] 。单药应用二甲双胍、DPP‑4i、α‑糖苷酶抑制剂、GLP‑1RA、SGLT2i 等低血糖风险较低[213] ,但由于老年糖尿病患者常合并多种疾病,使用前述药物时仍应警惕与其他药物相互作用而导致的低血糖风险增加[214] 。低血糖风险增加与严格的血糖控制有关[215] ,因此,在老年糖尿病患者中针对患者个体情况设定合理的 HbA1c目标,对于减少低血糖发生至关重要。在设定个体化 HbA1c目标时,需仔细考量以下几个问题:糖尿病病程、患者的预期寿命、是否应用胰岛素和促泌剂、是否曾发生严重低血糖、是否合并存在其他情况(如共存疾病多、认知障碍、多重用药)等[216] 。老年T1DM患者的严重低血糖发生率高,尤其是长病程的患者[217] 。随机对照试验研究结果显示,佩戴 CGM 系统可能有助于降低老年T1DM患者低血糖发生风险[218] ,有条件的患者需要时可考虑使用。
二、高血糖危象
高血糖危象主要包括HHS和DKA。HHS是糖尿病的严重急性并发症之一,临床以严重高血糖、血浆渗透压升高、脱水和意识障碍为主要表现,通常无明显的酮症和代谢性酸中毒。老年糖尿病患者是HHS的最主要人群。HHS比DKA的病死率更高,约为 DKA 病死率的 10 倍[219],需引起临床医师的高度重视。感染是 HHS 的主要诱因,其次是胰岛素等降糖药物的不恰当停用,或患者存在心肌梗死、脑血管事件和创伤等其他伴随疾病[220] 。HHS起病隐匿,30%~40% 的 HHS 患者此前未诊断为糖尿病。HHS的临床表现包括高血糖症状、脱水症状以及神经系统症状,患者表现为烦渴、多饮、淡漠、嗜睡,甚至出现幻觉、癫痫样发作、昏迷等表现。由于老年人皮肤弹性较差,脱水的识别更加困难。HHS 的 诊 断 标 准 包 括 :血 浆 葡 萄 糖 水 平 ≥33.3 mmol/L,有效血浆渗透压≥320 mOsm/L,无明显的代谢性酸中毒和无严重酮症。治疗上,补液是至关重要的首要步骤,有助于恢复血容量和肾脏灌注、改善外周循环,并降低血糖水平。对于老年糖尿病患者,补液过慢过少更易出现低血压、肾前性肾功能不全,而补液过量过快则可能出现肺水肿、心功能不全。因此,补液速度需根据患者的血压、肾功能、心功能情况进行个体化调整。连续静脉注射胰岛素,积极补钾,并注意监测血钾,避免低钾血症导致恶性心律失常。
尽管老年糖尿病患者中的 DKA 并不常见,但一旦出现,老年糖尿病患者较非老年糖尿病患者更可能出现各种并发症、合并症,导致器官系统功能损害,最终导致不良结局[221] 。值得注意的是,DKA与 HHS并存并不少见。近年来随着免疫检查点抑制剂的使用,免疫检查点抑制剂使用后出现的糖尿病多以DKA起病[222] ,也可以同时合并HHS[223] 。因此,对于使用免疫检查点抑制剂的老年糖尿病患者应警惕 DKA 和 HHS。应用 SGLT2i的老年糖尿病患者也需警惕DKA发生的可能[224] 。腹痛、恶心、呕吐是 DKA 的常见临床表现,老年糖尿病患者出现DKA 时神经系统表现可能更为突出,而胃肠道表现不明显。诊断要点包括:血糖升高,血酮体和(或)尿酮体升高,血 pH 值和(或)二氧化碳结合力降低。无论是DKA还是HHS,或是两者并存,治疗均遵循下列原则:尽快补液恢复血容量、降低血糖、纠正电解质及酸碱失衡,同时积极寻找并去除诱因、防治并发症、降低病死率。
三、乳酸酸中毒
乳酸酸中毒罕有发生,但死亡率高,极其凶险。当糖尿病患者肾功能不全时,有可能造成双胍类药物在体内蓄积,增加乳酸酸中毒风险。肝肾功能不全的老年糖尿病患者应用双胍类药物时应警惕乳酸酸中毒。
第十二章 老年糖尿病的共患疾病

一、心力衰竭
年龄和糖尿病均是 HF 的危险因素,老年糖尿病患者中 HF 患病率高达 22.3%[225] ,近年来国外单中心研究显示,住院老年糖尿病 HF 患病率甚至高达 56%[226] 。由于老年糖尿病患者中射血分数保留的 HF 较常见,因此,老年糖尿病患者的 HF 易被漏诊。研究显示,老年糖尿病患者中 HF 漏诊率高达27.7%[227] 。HF与心血管死亡和住院风险独立相关[228]。尽管老年糖尿病中HF常见,但却缺乏制定最佳治疗策略所需的临床证据。胰岛素可能导致水钠潴留而加重HF,在合并HF的老年糖尿病患者中应慎用。美国纽约心脏病协会心功能Ⅲ级及以上的老年糖尿病患者禁用TZD 类降糖药 。 在SAVOR研究中,相较于安慰剂组,作为次要终点组分之一的HF住院率在沙格列汀治疗组中升高[229] ,合并 HF的老年糖尿病患者选择 DPP‑4i时,慎重选用沙格列汀。二甲双胍对糖尿病合并HF的患者安全有益[230‑231] ,如无禁忌证或不耐受,二甲双胍应保留在治疗方案中。SGLT2i能降低 HF住院风险,老年糖尿病人群与总体人群相似[73] 。合并HF的老年糖尿病患者,应优先选择该类药物[232] 。队列研究显示,相较于 DPP‑4i,GLP‑住院风险在内的复合终点[233 1 ] RA 也能改善包括 HF。
二、骨质疏松

骨质疏松是一种与增龄相关的疾病,60 岁以上人群骨质疏松患病率明显增高,80 岁以上女性椎体骨折患病率可高达 36.6%[234]。糖尿病患者的骨折风险明显超过非糖尿病人群[235]。北京地区的数据显示,2016 至 2018 年糖尿病合并骨质疏松的患病率为13.4%~14.8%,老年糖尿病患者的骨质疏松患病率高于年轻糖尿病患者[236] 。因此,老年糖尿病患者是骨质疏松性骨折的高危人群,老年糖尿病患者一旦出现骨折,严重影响生活质量,致残率、致死率高。跌倒史、骨折史、握力低和HbA1c升高是老年 T2DM 患者骨折的危险因素[237] 。双能 X 线骨密度仪测定骨密度和骨折风险评估工具 FRAX 可用于评估糖尿病患者的骨折风险。但双能 X 线骨密度仪测得的骨密度会低估糖尿病患者的骨折风险,相同骨密度下,T2DM 较非糖尿病人群更易发生骨折[238] 。骨折风险评估工具 FRAX 也同样会低估糖尿病患者的骨折风险[239] 。应加强老年糖尿病患者骨质疏松防治知识的教育,积极进行骨折风险的评估,并早期干预。合并骨质疏松的老年糖尿病患者应慎重使用可能增加骨质疏松或骨折风险的降糖药物。Meta分析发现,老年T2DM患者使用磺脲类药物可能增加骨折风险,与其引发低血糖可能相关[240] 。中国专家共识建议,糖尿病合并骨质疏松的治疗参照非糖尿病患者[241] 。在骨质疏松药物选择上需考虑多病共存、多重用药等情况,全面评估、权衡利弊进行后个体化用药并进行监测。
三、肌少症与衰弱

老年综合征是老年人中普遍存在的一种多种异常状态的群集,严重影响老年人的生活质量,导致不良的临床结局。亚太地区共识认为老年综合征应包含阿尔茨海默病、压疮、听力下降、视力下降、肌少症、衰弱和跌倒等[242] 。与非糖尿病老年人相比,老年糖尿病患者中老年综合征的患病率更高。
肌少症是一种增龄性疾病,中国老年糖尿病患者肌少症患病率14.8%[243] 。T2DM与肌肉力量下降和肌肉质量差有关,加剧了与年龄有关的肌少症[244] 。T1DM 患者也可出现肌少症[245] ,其发生机制与自身免疫性损害有关[246] 。合并肌少症的糖尿病患者糖代谢异常更加严重、营养状态更差,也更易合并骨质疏松、跌倒[247] 。肌少症使老年糖尿病患者的血糖更加难以控制,日常生活活动能力下降,并增加死亡率[248] 。因此,老年糖尿病中的肌少症问题应得到重视。由于增龄所带来的身体成分改变,老年糖尿病患者可同时出现肥胖和肌少症,即肌少性肥胖[249] 。肌少性肥胖的发生率随年龄增长而增加,在80岁以上的人群中,女性和男性分别达到 48.0% 和 27.5%[250] 。不应忽视肥胖的老年糖尿病患者中的肌少症,避免盲目减重,避免用药导致的体重过低。建议依据亚洲肌少症工作组的筛查与诊断标准在老年糖尿病患者中进行肌少症的评估[251] 。对于社区基层医疗机构,可以通过量表(简易五项评分问卷量表或简易五项评分问卷+小腿围量表)进行筛查,并对肌肉力量和躯体功能进行评估,考虑“肌少症可能”即进行生活方式干预。除上述筛查和评估的手段外,在医疗机构或临床研究中心还可以进一步通过测定四肢骨骼肌的含量来明确肌少症的诊断。
衰弱是指随着年龄的增长,机体退行性改变、生理储备功能下降以及多种慢性疾病引起的机体易损性增加,无法抵抗身体或心理应激,是一种残疾前状态。因此,与残疾、共病不同,导致衰弱的病因在一定程度上尚可逆转,早期识别并干预衰弱的老年人有助于改善预后。在老年人中,糖尿病使衰弱的风险增加 5 倍[252] ,导致患者活动能力下降、血糖监测和管理难度增加,影响患者的预后。Meta分析显示,社区患糖尿病的老年人中,衰弱和衰弱前期的患病率分别为 20.1% 和 49.1%[253] 。在制定血糖控制目标时,需考虑患者的虚弱程度,对于合并虚弱的老年糖尿病患者,可能需要简化、转换或降级治疗方案,尤其应考虑减少可能诱发低血糖的治疗,例如磺脲类药物和胰岛素[254] 。
关注老年糖尿病患者的肌少症和衰弱问题,对老年糖尿病患者进行肌少症和衰弱的评估,并给予适当干预有助于改善老年糖尿病患者的预后并减少医疗支出[255‑256] 。
四、跌倒

跌倒是我国老年人创伤性骨折、因伤致死的主要原因。随着年龄的增长,老年人的各项生理功能减退,包括维持肌肉骨骼运动系统功能减退造成的步态协调性下降、平衡能力降低,以及视觉、听觉、前庭功能、本体感觉下降,均增加了跌倒的风险。糖尿病增加老年人的跌倒风险,尤其是使用胰岛素的老年糖尿病患者,跌倒风险较非糖尿病老年人增加 94%[257] 。老年糖尿病患者跌倒虽然高发,但也是可以预防的。所有老年糖尿病患者都需要进行跌倒风险的评估,包括既往病史、躯体功能状态、环境、心理评估等。老年糖尿病患者跌倒的主要危险因素包括低血糖与血糖波动、中枢及外周神经病变、血管因素、体位性低血压、餐后低血压、糖尿病眼部病变、药物(降压药、利尿剂、镇静催眠药等)、肌少症与衰弱等。对于存在上述情况的老年糖尿病患者应积极干预,并寻求相关科室协助,以降低患者发生骨折和骨折相关并发症的风险。谨防合并骨质疏松的老年糖尿病患者跌倒。
五、认知障碍

中国老年糖尿病患者中认知障碍的发生率为48%,在女性、年龄较大、教育水平较低、收入较低、无配偶和独居的人群中发生率更高[258] 。认知障碍与低血糖风险之间存在双向关系[259‑260] 。低血糖增加痴呆发生风险,包括血管性痴呆和阿尔茨海默病。另一方面,有认知障碍的糖尿病患者易发生低血糖。认知障碍使老年糖尿病患者很难执行复杂的自我管理任务[261] ,例如监测血糖和调整胰岛素剂量,也影响患者进食时间及用餐合理性。及早识别认知障碍对老年糖尿病管理具有重要意义。推荐老年糖尿病患者每年进行一次筛查,以便早期发现轻度认知障碍或痴呆。可选用简单易行的评估工具筛查认知障碍,如MMSE[262] 和MoCA[263] 。调整认知障碍的糖尿病患者的治疗方案,选用低血糖风险低的药物,同时尽可能简化治疗方案、“去强化治疗”,放宽血糖控制目标,避免低血糖和高血糖危象。二甲双胍和 GLP‑1RA 可能有助于改善认知功能。回顾性研究显示,老年 T2DM患者使用二甲双胍与痴呆风险降低显著相关,且呈现出剂量依赖效应[264] 。GLP‑1RA的使用与老年患者阿尔茨海默病发病率降低有关[265] 。磺脲类、TZD 类、DPP‑4i以及SGLT2i对认知功能的影响尚不明确[266] 。运动也有助于改善认知功能,一项随机临床试验发现太极拳比健身步行更有效地改善我国老年 T2DM 患者的认知功能[267] 。
六、精神疾病

老年糖尿病患者发生抑郁的风险高于非糖尿病的老年人[268] ,但易被忽视。抑郁和焦虑情绪可能导致老年糖尿病患者依从性降低[269] ,血糖不易得到有效控制。应关注老年糖尿病患者的精神状态,尽早识别精神疾病并干预。可采用老年抑郁量表等简化筛查工具进行早期识别。建立和完善多学科团队协同照料模式,改善患者抑郁、焦虑症状,不但有助于提高生活质量,也有助于控制血糖。老年人群常出现谵妄[270] ,若老年糖尿病患者出现谵妄,应及时识别并去除诱因,积极鼓励家属参与非药物治疗的过程,提供护理支持,预防和治疗谵妄相关并发症。
七、低血压

增龄导致心血管结构和功能发生改变,因此,老年人易出现体位性低血压和餐后低血压[271] 。低血压增加跌倒风险[272] ,甚至增加心血管事件和死亡的风险[273‑274] 。老年糖尿病患者体位性低血压风险较非糖尿病老年人更高,40%的体位性低血压患者合并糖尿病[275] 。合并高血压的老年糖尿病患者可同时存在体位性低血压,因此,该类患者应优先选择ARB类或钙通道阻滞剂[276‑277] ,避免坦索罗辛、卡维地洛等可能恶化体位性低血压的降压药物。在老年人中摄入碳水化合物含量高的热食和直立姿势均与症状性餐后低血压有关[278] 。在老年糖尿病患者中应关注头晕、晕厥等症状与进食和体位变化的关系。调整生活方式可能有助于减少老年糖尿病患者症状性低血压的发生。此外,α‑糖苷酶抑制剂有助于改善老年糖尿病患者的餐后低血压 症 状[50,279],选 用 降 糖 药 物 时 可 予 以 考 虑 。SGLT2i 有轻度降低血压的作用,应关注应用该类降糖药物患者的血压。
八、肿瘤
糖尿病患者肿瘤风险增加,包括肝细胞癌、肝胆管癌、胰腺癌、乳腺癌、卵巢癌、子宫内膜癌和胃肠道恶性肿瘤等多种癌症[280‑281] 。建议老年糖尿病患者接受与其年龄和性别匹配的肿瘤筛查。血糖升高有时是胰腺癌的首发临床表现[17] ,新发老年糖尿病患者应筛查排除胰腺癌可能。部分降糖药可DPP‑4i [283] 等。

九、阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征

阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征(obstructive sleepapnea syndrome,OSAS)是常见的睡眠障碍类型之一,属于片段化睡眠,是导致糖代谢异常、继发性高血压及多器官损害的睡眠呼吸疾病。OSAS导致多种应激激素分泌增加、血糖波动加剧、血糖控制的难度增加。OSAS 的患病率随着年龄增长而增加[284] ,肥胖也是OSAS的重要危险因素。合并糖尿病者 OSAS 常更严重[285] ,OSAS也与糖尿病并发症的发生和进展密切相关。男性OSAS的发生率高于女性,绝经后女性 OSAS 发生率明显高于绝经前女性。建议老年糖尿病患者,尤其是肥胖者进行OSAS筛查。
对合并 OSAS 的老年糖尿病患者,应积极进行生活方式干预减重、戒烟、限酒,避免浓茶和咖啡以及日间过度劳累和兴奋而影响睡眠[286] 。持续气道正压是治疗 OSAS 的有效方法,可显著改善糖尿病患者血糖水平及胰岛素抵抗[287‑288] 。避免选用导致体重增加的药物,严重低氧血症的患者应慎用或禁用双胍类药物。此外,需注意排查并治疗引起或加重 OSAS 的基础疾病,如甲状腺功能减退等[289] 。
十、睡眠障碍
除 OSAS 外,老年糖尿病患者还可能存在多种形式的睡眠障碍。本节内容讨论非OSAS所致的睡眠障碍。老年人存在脑功能生理性退化、易出现焦虑情绪、心理承受能力较弱等特点,是睡眠障碍的高发人群[290] 。糖尿病患者夜尿增多、痛性神经病变、躯体症状和精神障碍等均可能导致睡眠障碍。老年糖尿病患者睡眠障碍发生风险高,影响血糖控制和生活质量,应予以关注。对存在睡眠障碍的老年糖尿病患者积极进行健康教育与干预,有助于提高睡眠及生活质量,同时改善血糖[291] 。

十一、口腔疾病

随着年龄的增长,口腔疾病的风险增加。口干、口腔运动功能下降、口腔卫生管理能力下降等多种原因均可导致老年人出现口腔疾病。糖尿病患者口腔疾病的患病率、病程和严重程度均较非糖尿病人群明显增加[292] 。牙周炎是糖尿病的常见合并症之一,糖尿病是牙周炎的重要危险因素,糖尿病患者与非糖尿病人群相比,牙周炎的发生风险增加近3倍。与非老年糖尿病患者相比,老年患者面临更普遍、更严重的口腔问题,如龋齿、口腔干燥症、牙周疾病等。良好的血糖控制有利于患者牙周炎等口腔病变的治疗,而针对牙周炎等口腔病变的治疗有利于改善血糖的控制[293‑295] 。鼓励老年糖尿病患者养成良好的卫生习惯,坚持每天有效刷牙,去除牙石、食物嵌顿等局部刺激因素,保持口腔环境清洁,定期进行口腔检查和牙周洁治。
十二、皮肤病变
糖尿病患者可以出现多种皮肤病变,包括:
(1)皮肤感染:细菌、真菌或病毒感染;
(2)与糖尿病
(3)糖尿病慢性并发症的皮肤表现:如糖尿病足所致皮肤溃疡,甚至坏疽;(4)糖尿病治疗所致皮肤改变:如注射胰岛素后所致皮下脂肪增生、皮下脂肪减少等。皮肤瘙痒是糖尿病患者常见症状,12.7% 的T2DM 患者出现皮肤瘙痒,合并糖尿病周围神经病变的T2DM中皮肤瘙痒发生率更高(20.5%)[296] 。高龄、长病程也是糖尿病患者皮肤瘙痒的危险因素[297] ,因此,老年糖尿病患者皮肤瘙痒发生率高,皮肤瘙痒严重影响老年糖尿病患者的生活质量。减少洗澡次数和涂抹润肤霜可以改善皮肤干燥,可能有助于缓解皮肤瘙痒。糖尿病患者血糖控制不佳可导致皮肤病变风险增加,皮肤感染等皮肤病变也可导致血糖升高。内分泌专科医师应关注老年糖尿病患者的皮肤情况,进行积极的处理,必要时转诊至皮肤专科进一步诊治。直接相关的皮肤病:糖尿病性大疱、黑棘皮病等;

第十三章 老年糖尿病的多重用药

多重用药是指患者同时使用≥5种药物。老年糖尿病患者多合并高血压、冠心病、脑卒中及慢性呼吸系统疾病等,多重用药在老年糖尿病患者中较为普遍且难以避免。多重用药会增加药物相互作用的风险,不仅可能影响老年糖尿病患者的降糖疗效,还可能增加低血糖风险。磺脲类药物主要经肝脏 CYP2C9 酶代谢,老年患者合用氟康唑、西咪替丁等 CYP2C9 抑制剂时,会减慢磺脲类药物代谢,增加低血糖风险。阿卡波糖与华法林合用会使凝血酶原国际标准化比值升高,增加出血风险,需要及时调整剂量。瑞格列奈主要通过 CYP2C8 和CYP3A4酶代谢,与氯吡格雷、酮康唑、ACEI及单胺氧化酶抑制剂等药物合用时,可能增强和(或)延长瑞格列奈的降糖作用,增加低血糖风险。沙格列汀经 CYP3A4 代谢,与酮康唑、伊曲康唑、阿扎那韦、利托那韦、克拉霉素和泰利霉素等 CYP3A4的强抑制剂合用时,显著升高血药浓度,应减量使用;而与卡马西平合用会加快其代谢,显著降低降糖效果[298] ;维格列汀与肿风险[299] 。罗格列酮 ACEI 、吡格列酮经 合用会增加血管神经性水CYP2C8 代谢,吉非罗齐、氯吡格雷减缓其代谢,升高血药浓度[300] ;CYP2C8 诱导剂利福平等加快其代谢,降低降糖疗效。因此,在制定药物治疗方案时需考虑老年患者的药物使用情况,对于多重用药的患者,尽可能选择药物相互作用较少的降糖药物,避免不良的药物‑药物相互作用。
第十四章 老年糖尿病的特殊情况

一、老年糖尿病的医院管理
老年糖尿病患者常因各种非糖尿病相关的问题住院,如心血管疾病、呼吸困难、感染等,内分泌科医师需与其他专科医师进行团队合作对患者的血糖进行管理。住院患者的情况可能会在短时间发生变化,要求医师及时识别并调整治疗方案。应用糖皮质激素治疗、鼻饲、全肠外营养、透析等可能引起患者血糖变化的情况出现时,应及时再次评估降糖方案。临床医师应该始终将患者的年龄、预期寿命、整体的健康状态、功能状态、认知能力等纳入考量,在血糖控制与不良反应之间权衡。患者在非内分泌科专科住院期间,制定清晰的血糖控制目标有利于血糖管理[301] 。参照《中国住院患者血糖管理专家共识》的建议[302],健康状态分级为良好(Group 1)和中等(Group 2)的住院老年糖尿病患者采取一般的血糖控制目标:空腹血糖控制在 6.1~8mmol/L,餐后2 h血糖或随机血糖控制在7.8~10.0mmol/L,可根据患者的个体情况,对于低血糖风险高、预期寿命短、健康状态分级为差(Group 3)的老年糖尿病患者,适当放宽目标至空腹血糖7.8~10.0 mmol/L,餐 后 2 h 血 糖 或 随 机 血 糖 7.8~13.9 mmol/L,同时应避免高血糖危象发生。
二、老年糖尿病的养老机构管理
随着我国老龄化社会进程加快,养老机构老年糖尿病患者的健康管理越来越重要。对有专业医护人员的养老机构,可参照前述老年糖尿病的医院管理进行处理。但目前我国养老机构主要提供基本生活照料,缺少糖尿病等慢性疾病的健康管理服务,应加强对照护人员的糖尿病教育[136] 。过于严格的饮食控制对老年糖尿病患者血糖控制获益有限[303] ,还可能增加其发生营养不良的风险。在设定血糖管理目标时,充分考虑老年人并发症及合并症情况、功能状态及预期寿命[304] ,根据不同的组别、血糖控制及并发症情况等情况制定相应的饮食、运动方案。目前养老机构常用血糖仪进行指尖血糖监测,有条件的养老机构可根据需要检测HbA1c 和进行持续葡萄糖监测(continuous glucose monitoring,CGM)。对于使用磺脲类药物或胰岛素治疗的老年患者,可根据需要使用 CGM 评估低血糖风险[136] 。需及时识别老年患者糖尿病急性并发症 ,如 怀 疑 DKA 和 HHS 应紧急处理后立即转诊[304] 。应注意老年糖尿病患者的足保护,一旦出现足部皮肤破溃,应及时将患者转诊到代谢内分泌专科或糖尿病足病相关科室。
三、老年糖尿病的居家管理
居家老年人中糖尿病患病率高[305] ,糖尿病是居家老年人需重点关注的慢病之一。老年糖尿病患者的居家管理应包括居家老年人自身对健康的管理、家庭成员对居家老年人的照护以及社区医疗机构对居家老年人进行的慢病管理。多学科团队干预模式可改善居家老年糖尿病患者的血糖和心态,并能够在一定程度上提高患者的自我管理能力[306] 。老年糖尿病患者居家管理应注意预防低血糖、高血糖危象以及跌倒等急性事件。
四、围术期管理
老年糖尿病患者围术期血糖控制目标为 7.8~10.0 mmol/L[108,307] 。对于有严重合并症和频繁低血糖 发 作 的 老 年 患 者 ,控 制 目 标 最 高 可 为13.9 mmol/L[307] 。对于拟行心脏手术或其他精细手术的患者,在权衡低血糖风险的基础上,建议可考虑 更 为 严 格 的 血 糖 控 制 目 标 ,即 6.1~7.8 mmol/L[308] 。为尽量减少血糖对患者及手术的影响,糖尿病患者首选在清晨或尽早手术,手术时间较晚的患者需在病房持续监测血糖[309] 。手术需要禁食,于手术当日早上停用所有口服降糖药物,在禁食期间,每 4~6 小时进行一次血糖监测,术中根据情况增加血糖监测频次,如血糖水平超过控制目标给予短效人胰岛素或速效胰岛素类似物。对于接受小手术的患者,若仅应用口服降糖药血糖即可控制良好,则术中无需应用胰岛素,并在术后恢复其口服降糖药。空腹期间注意停用低血糖风险高的药物,手术时应暂停使用 SGLT2i 以避免 DKA风险[309] 。对接受大、中手术的患者,尤其是血糖控制不佳的患者,应及时改为胰岛素治疗,术中应继续应用胰岛素,并密切监测血糖。术后患者恢复正常饮食前可胰岛素静脉输注控制血糖,恢复正常饮食后改为胰岛素皮下注射。拟行急诊手术的患者不建议在术前设定过于严格的血糖控制目标,而应尽快进行术前准备,采用胰岛素静脉输注的方式降低血糖,并在术中加强监测血糖。围术期应关注血糖变化,警惕低血糖发生。
五、感染与疫苗接种
糖尿病患者易并发细菌、真菌、病毒以及非典型致病菌感染,常见的感染部位包括呼吸道、泌尿系统、皮肤和软组织等。与一般人群相比,T2DM患者感染预后更差,其败血症的发病率和死亡率更高[310] 。糖尿病患者比非糖尿病患者有更高的皮肤和软组织感染的风险,但同时合并严重糖尿病神经病变和血管病变的患者不会表现出典型的软组织感染症状[311] 。老年糖尿病患者感染风险较高,且不易控制[312] 。一项回顾性队列研究显示,相较于40~49 岁的糖尿病患者,80~89 岁患者住院风险高3~4倍,其中与感染有关的住院比例很高[313] 。病程长、血糖控制不佳的老年患者并发感染将导致血糖更加难以控制,甚至诱发高血糖危象。
新型冠状病毒感染(corona virus disease 2019,COVID‑19)与已知糖尿病患者和此前未诊断的糖尿病患者的高血糖有关。武汉一项针对住院患者(主要是老年 COVID‑19)的研究显示,21.6% 的患者有糖尿病病史,根据入院时的首次血糖测量,20.8%新诊断为糖尿病,28.4%新诊断为血糖异常。糖尿病患者入院时的血糖水平与全因死亡风险增加有关。新诊断的糖尿病患者更可能进入重症监护病房,并需要有创机械通气,急性呼吸窘迫综合征、急性肾损伤 或 休 克 的 患 病 率 高 ,住 院 时 间 最 长[314] 。COVID‑19患者新发糖尿病的确切机制尚不明确,可能的原因包括:既往未诊断的糖尿病、应激性高血糖、病毒感染或类固醇相关糖尿病[315] 。肥胖、高血糖以及心血管和肾脏疾病是COVID‑19患者预后不良的危险因素,因此,对于急性COVID‑19感染和持续症状(即长新冠)后糖尿病患者的长期管理,推荐使用不增加体重且改善心肾结局的降糖药物(如SGLT2 和 GLP‑1RA),但 是 尚 无 长 期 随 访 的证据[315 ] 。良好的血糖控制、加强自身卫生、进行必要的免疫接种在一定程度上可预防严重的感染性疾病。老年糖尿病患者应根据情况进行流感、肺炎链球菌等疫苗接种,以减少住院和死亡风险,但流感疫苗接种中需要注意避免接种减毒活疫苗[316] 。对于合并感染的老年糖尿病患者,严格控制血糖是首要措施,但对共存疾病多、预期寿命短的患者可适当放宽血糖目标,同时需进行有效的抗感染治疗,必要时行外科手术治疗。
六、舒缓医疗
当老年糖尿病患者进入生命的晚期时应进行不同于其他时期的特殊管理。在这一阶段,维护患者的尊严、减少痛苦和保证生活质量尤为重要。患者有权拒绝检查和治疗,医护人员应考虑减少诊断性检查及不必要的治疗,尽可能使医护人员、患者、家属共同参与医疗决策过程。这一阶段的主要目标并非严格的血糖、血压、血脂管理,采取姑息治疗,减少血糖监测的频率,预防低血糖和高血糖危象,解除患者疼痛等不适症状,有助于提高患者的生活质量。在降糖方案的选择上,可以将口服降糖药物作为一线药物,但不建议使用胃肠道不良反应发生风险高的药物,必要时可给予基础胰岛素。有器官损害的 T2DM 患者应减量使用低血糖风险高的药物,允许血糖处于正常高限或不出现急性代谢异常的可接受范围,根据进食量必要时可停用药物治疗。对于器官衰竭的患者,T1DM 患者胰岛素用量可随着进食量的减少而减少,但不应停用。对于临终状态的 T1DM的治疗方案尚无定论,可以通过小剂量基础胰岛素预防高血糖急性并发症[136] 。
第十五章 老年1型糖尿病及相关问题

老年 T1DM 患者是指年龄≥65岁,包括 65岁以前诊断和 65 岁及以后诊断的 T1DM 患者。随着生活和医疗水平的提高,T1DM 患者的寿命延长,老年T1DM患者的数量会明显增加。老年T1DM患病率较低,但老年期LADA并不少见。与年轻起病的患者相比,老年起病的 LADA 患者残余的胰岛 β细胞功能相对较好,胰岛素抵抗更显著,代谢综合征的特征更明显。老年起病的 LADA 患者中胰岛自身抗体阳性的比例和年轻起病的 LADA 相似,但HLA‑DQ 遗 传 背 景 与 年 轻 起 病 的 LADA 有 显 著差异[317] 。
与老年 T2DM 的管理相似,需结合患者的年龄、预期寿命、功能状态、基础疾病以及并发症情况等确定血糖控制目标以及降糖方案。老年 T1DM患者血糖管理难度大,高血糖危象和低血糖风险均较老年T2DM患者更高。在老年T1DM患者出现微血管或大血管并发症之前,可以考虑较为严格的血糖控制目标,但需权衡低血糖风险。长病程是老年T1DM患者发生低血糖的危险因素,病程超过40年的 老 年 T1DM 患 者 中 严 重 低 血 糖 发 生 率 达18.6%[217] ,应适当放宽患者血糖控制目标。
近年来,糖尿病管理相关技术在胰岛素注射和血糖监测领域取得了较大的进展。在针对老年T1DM患者进行的研究中,使用CGM或胰岛素泵的患者HbA1c水平更低,少[318] 。WISDM 随机临床试验显示 低血糖事件和血糖波动较,与指尖血糖监测相比,老年T1DM患者使用CGM可减少低血糖发生,改善总体血糖控制[319] 。此外,研究也证实了混合闭环胰岛素泵在老年 T1DM患者中的安全性,与实时动态胰岛素泵组比较,混合闭环胰岛素泵组患者的 TIR 更高、TBR 更低[320] 。需要注意的是,前述的临床试验中少有纳入70岁及以上的老年人群。
由于疾病管理的复杂性,老年 TIDM 的自我管理过程依赖于患者良好的认知能力。有严重低血糖的老年 T1DM患者更容易出现认知功能下降,应简化胰岛素治疗方案。TIDM可能导致老年人的身体机能下降,随着身体机能的下降,老年 T1DM 患者的自我管理能力下降,应加强护理支持。对于丧失独立生活能力的老年 TIDM 患者,需护理人员协助患者进食、活动以及注射胰岛素。关于老年 T1DM 患者中血压、血脂、蛋白尿管理的循证医学证据均较缺乏。临床医师应该根据每个患者的个体情况确定治疗目标及策略。
未完待续……

第五章 老年糖尿病患者的健康教育
在疾病诊断初期,医护人员及家庭成员需要帮助患者正视疾病,使其接受糖尿病教育、了解糖尿病相关知识,减轻患者恐惧心理或自暴自弃等负面想法,对于有利于患者糖尿病管理的行为要及时予以肯定和鼓励,引导患者正面评价自我,接受并积极参与到糖尿病的全程管理之中。
老年糖尿病患者通常病程较长,并发症、合并症多,应结合每位患者的特点进行个体化的健康教育。开展健康教育之前需对老年患者进行评估,包括基本信息、受教育程度、经济状况、既往治疗状况、血糖水平、合并症、认知功能及有无看护者等,开展个体化的健康教育与管理。教育内容应包括糖尿病的病因、疾病进展、临床表现、糖尿病的危害、糖尿病急慢性并发症的识别和处理、个体化治疗目标、生活方式干预、各类药物的特点、临床药物选择及使用方法、如何进行血糖监测等。应加强对患者本人、家庭成员及看护者、社区相关人员的健康教育,使其正确了解疾病相关知识,避免过于严格或者过于宽松的血糖管理,从而提高老年糖尿病患者的生活质量。糖尿病教育的形式可以采取集体教育或针对性较强的社区小组教育、同伴教育及个体教育。有条件者也可以采取远程教育的模式,如微信公众号、手机应用程序、网络培训班等。不同的糖尿病教育形式互为补充,可以同时开展,以便更好地传递患者需要的信息资讯。近年来有不少探究老年糖尿病患者教育形 式 的 研 究 ,如夫妻协助管理模型 、PRECEDE‑PROCEED 模型[25‑26],有效的教育形式将助力于老年糖尿病患者的综合管理。随着人工智能技术的快速发展,近年来也有不少探索人工智能在糖尿病教育中作用的研究[27] 。

第六章 老年糖尿病患者的血糖控制目标

通过严格控制血糖减少老年糖尿病患者并发症的获益有限,严格血糖控制在一定程度上会增加低血糖风险。低血糖对老年患者危害极大,应尽可能避免。因此,需权衡患者治疗方案的获益风险比,对老年糖尿病患者进行分层管理、施行个体化血糖控制目标尤为重要。对健康状态差(Group 3)的老年糖尿病患者可适当放宽血糖控制目标,但应遵循以下原则:(1)不因血糖过高而出现明显的糖尿病症状;(2)不因血糖过高而增加感染风险;(3)不因血糖过高而出现高血糖危象。
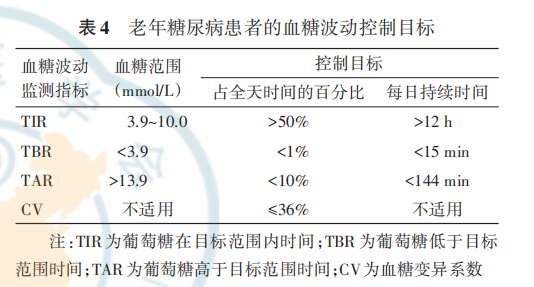
根据老年糖尿病患者健康综合评估的结果和是否应用低血糖风险较高的药物两项指标,推荐患者血糖控制目标见表 3。若老年糖尿病患者使用低血糖风险较高的药物,HbA1c控制目标不应过低。因此,对此类患者设立明确的血糖控制目标下限,降低患者低血糖发生风险。葡萄糖在目标范围内时间(time in range,TIR)、葡萄糖低于目标范围时间(time below range,TBR)、葡萄糖高于目标范围时间(time above range,TAR)及 血 糖 变 异 系 数(coefficient of variation,CV)等指标可以反映血糖波动情况,参照国际共识,可将上述指标作为血糖控制目标的补充[28](表 4)。餐后血糖控制的目标暂无充分的临床证据或指南依据进行推荐,可根据HbA1c对应的餐后平均血糖水平(糖尿病医学诊疗标 准 临 床 指 南[29] )确 定 餐 后 血 糖 控 制 目 标,即HbA1c 6.50%~6.99% 对 应 血 糖 9.1 mmol/L,HbA1c7.00%~7.49% 对应血糖 9.8 mmol/L,HbA7.99% 对应血糖 10.5 mmol/L,HbA1c 8.00 1c 7.50%~%~8.50%对应血糖11.4 mmol/L。
第七章 老年糖尿病患者的生活方式干预

生活方式干预是老年糖尿病的基础治疗。所有的老年糖尿病患者均应接受生活方式干预。对于一部分健康状态良好(Group 1)、血糖水平升高不明显的老年糖尿病患者,单纯的生活方式干预即可达到预期血糖控制。
一、营养治疗
营养治疗是糖尿病治疗的基础,应贯穿于糖尿病治疗的全程。营养治疗对于实现血糖、血压、血脂控制目标,维持目标体重,以及预防或延缓糖尿病并发症均具有重要作用。首先应对老年糖尿病患者的营养状态进行评估,采用营养风险筛查评分2002、微型营养评价简表等营养筛查工具确认患者营养风险。老年患者出现营养不良,可能引发住院日延长、医疗支出增加以及再住院率增加等一系列问题。早期识别并管理营养不良,有助于阻止及延缓并发症的发生发展。
老年人改变长久生活中形成的饮食习惯较为困难,可基于固有的饮食习惯,结合其改变饮食结构的意愿强烈程度、健康食物的获取能力等做适当调整,制定考虑代谢控制目标、总热量、营养质量等因素的个体化营养治疗方案。营养治疗方案应与患者的整体生活方式相协调,包括其运动情况以及用药情况等。老年糖尿病患者肌肉含量较低,足够的能量摄入可避免肌肉蛋白分解,应适度增加蛋白质摄入[30] ,以富含亮氨酸等支链氨基酸的优质蛋白质摄入为主(如乳清蛋白)。健康的老年人需每日摄入蛋白质1.0~1.3 g/kg,合并急慢性疾病的老年患者需每日摄入蛋白质1.2~1.5 g/kg,而合并肌少症或严 重 营 养 不 良 的 老 年 人 每 日 至 少 摄 入 蛋 白 质1.5 g/kg[31] 。除动物蛋白外,也可选择优质的植物蛋白[32] 。碳水化合物是中国老年糖尿病患者主要的能量来源,监测碳水化合物的摄入量是实现血糖目标的重要手段,但老年糖尿病患者的最佳碳水化合物摄入量尚无定论。进食碳水化合物同时摄入富含膳食纤维的食物可以延缓血糖升高,减少血糖波动,改善血脂水平。膳食纤维增加饱腹感、延缓胃排空,胃轻瘫和胃肠功能紊乱的老年患者避免过量摄入。应关注患者进食碳水化合物、蛋白质与蔬菜的顺序,延后进食碳水化合物时间有助于降低患者的餐后血糖增幅[33] 。对于长期食物摄入不均衡的老年糖尿病患者应注意补充维生素和矿物质。老年糖尿病患者与非糖尿病人群相比,营养不良发生风险更高[34] ,更易发生肌少症和衰弱。应避免过度限制能量摄入,强调合理膳食、均衡营养,警惕老年糖尿病合并营养不良,定期营养筛查确认患者营养风险,尽早发现并干预,有利于改善患者临床预后。
二、运动治疗
运动是预防和治疗老年糖尿病的有效方法之一[35‑36] ,以规律运动为主的生活方式干预可以改善糖尿病患者的胰岛素抵抗[37] 。老年患者常伴有多种影响运动的慢性疾病,如合并骨关节病变的患者步行能力下降,合并脑血管病变、周围神经病变或严重肌少症的患者易发生跌倒。老年糖尿病患者开始运动治疗前需要根据病史、家族史、身体活动水平以及相关的医学检查结果等进行运动前健康筛查,通过心肺耐力、身体成分、肌肉力量和肌肉耐力、柔韧性以及平衡能力等多项测试对老年患者的运动能力进行评估,为运动治疗方案的制定提供依据。老年患者常需要服用多种药物,应指导患者合理安排服药时间和运动时间的间隔,并评估运动对药物代谢的影响,避免运动相关低血糖、低血压等事件的发生。低血糖事件可能发生在运动过程中,也可能在运动后出现延迟性低血糖,需加强运动前、后和运动中的血糖监测,运动过程中、运动后或增加运动量时须注意观察患者有无头晕、心悸、乏力、手抖、出冷汗等低血糖症状,一旦发生,立即停止运动并及时处理。若糖尿病患者合并心脏疾病,应按照心脏疾病的运动指导方案进行运动。
老年糖尿病患者首选的运动是中等强度的有氧运动,运动能力较差者,可选用低强度有氧运动。低、中等强度有氧运动对于绝大多数老年糖尿病患者是安全的,具体形式包括快走、健身舞、韵律操、骑自行车、水中运动等。运动强度通常可通过主观用力感觉来评价,在中等强度运动中常感觉心跳加快、微微出汗、轻微疲劳感,也可以是运动中能说出完整句子,但不能唱歌。每周运动5~7 d,最好每天都运动,运动的最佳时段是餐后1 h,每餐餐后运动20 min左右。若在餐前运动,应根据血糖水平适当摄入碳水化合物后再进行运动。
抗阻训练同样适用于老年人群。肌肉发力抵抗阻力产生运动的过程都称作抗阻训练。抗阻运动训练可提高老年 T2DM 患者的力量、骨密度、瘦体重和胰岛素敏感性,并改善HbA1c、血压和血脂水平[38‑39] 。可通过哑铃、弹力带等器械进行抗阻训练,也可以采用自身重量练习(如俯卧撑、立卧撑、蹲起、举腿、肱二头肌弯举、提踵等)。每周运动 2~3次,每次进行1~3组运动,每组/每个动作重复10~15次。
老年糖尿病患者常伴有平衡能力下降等问题,加强柔韧性和平衡能力训练可以增强人体的协调性和平衡能力,从而降低老年糖尿病患者跌倒风险[40] ,增加运动的依从性。交替性单脚站立、走直线都是增强平衡能力的有效方法,太极拳、八段锦、五禽戏和瑜伽也可以提高协调性及平衡能力。一项 Meta 分析发现太极拳对改善老年 T2DM 患者的单腿站立能力具有积极效果,并改善血糖水平[41] 。每周至少进行2~3次平衡训练。
有氧运动、抗阻训练以及平衡练习对老年糖尿病患者均有不同层面的获益。基于现有的证据建议老年人进行多种方式的运动,包括有氧、抗阻、柔韧性和平衡训练,通过结构化的运动处方和随机活动的结合来改善健康状态[42‑43] 。老年糖尿病患者可根据自身情况增加日常生活中的身体活动(如低强度的家务劳动、庭院活动等),减少静坐时间,每坐30 min应起身活动1~5 min。
第八章 老年2型糖尿病患者的降糖药物及治疗路径
结合患者健康状态综合评估结果以及相应的血糖控制目标,经过生活方式干预后血糖仍不达标的老年 T2DM 患者应尽早进行药物治疗。药物治疗的原则包括:(1)优先选择低血糖风险较低的药物;(2)选择简便、依从性高的药物,降低多重用药风险;(3)权衡获益风险比,避免过度治疗;(4)关注肝肾功能、心脏功能、并发症及合并症等因素;(5)不推荐衰弱的老年患者使用低血糖风险高、明显降低体重的药物。
一、二甲双胍
二甲双胍是国内外多个指南和(或)共识推荐的老年 T2DM 患者的一线降糖药物之一,是老年T2DM患者的一级推荐降糖药物。估算的肾小球滤过率(estimated glomerular filtration rate,eGFR)是能否使用以及是否减量的决定性因素。胃肠道反应与体重下降限制了二甲双胍在部分老年患者中的使用,对于老年患者应从小剂量起始(500 mg/d),逐渐增加剂量,最大剂量不应超过 2 550 mg/d。使用缓释剂型或肠溶剂型有可能减轻胃肠道反应,且缓释剂型服药次数减少[44] 。若老年患者已出现肾功能不全,需定期监测肾功能,并根据肾功能调整二甲双胍剂量[45] 。对于 eGFR 为 45~59 ml·min-1
- (1.73 m2)-1 的老年患者应考虑减量,当 eGFR<45 ml·min-1
- (1.73m2)-1 时应考虑停药[45] 。重度感染、外伤以及存在可造成组织缺氧疾病[如失代偿性心力衰竭(heart failure,HF)、呼吸衰竭等]的老年患者禁用二甲双胍。eGFR≥60 ml·min-1
- (1.73 m2)-1 的患者使用含碘对比剂检查当天应停用二甲双胍,在检查完至少48 h且复查肾功能无恶化后可继续用药;若患者 eGFR 为 45~59 ml·min-1
- (1.73 m2 )-1 ,需在接受含碘对比剂及全身麻醉术前48 h停药,之后仍需要停药48~72 h,复查肾功能无恶化后可继续用药[45] 。二甲双胍会增加老年糖尿病患者维生素B12缺乏的风险[46] ,需在用药后定期监测维生素B12水平。
二、磺脲类
常用的磺脲类药物主要有格列本脲、格列齐特、格列吡嗪、格列喹酮和格列美脲。磺脲类药物降糖疗效明确,但易致低血糖及体重增加,长效磺脲类药物上述不良反应更常见,老年患者应慎用[47] ,短效类药物以及药物浓度平稳的缓释、控释剂型可在权衡其获益和风险后选用。磺脲类药物是老年 T2DM 患者的三级推荐降糖药物。该类药物与经 CYP2C9 和 CYP2C19 等肝脏 P450 酶代谢药物(如他汀类、抗菌药物、部分心血管药物及质子泵抑制剂等)合用时,应警惕低血糖事件[48] 及其他不良反应。格列喹酮血浆半衰期 1.5 h,仅 5% 代谢产物经肾脏排泄,轻中度肾功能不全的老年 T2DM患者选择磺脲类药物时应选择格列喹酮。
三、格列奈类
格列奈类药物主要有瑞格列奈、那格列奈。格列奈类药物降糖效果与磺脲类药物相近,体重增加的风险相似,而低血糖风险较低[49] ,是老年 T2DM患者的二级推荐降糖药物。 该类药物需餐前15 min内服用,对患者用药依从性要求较高。格列奈类药物主要经肝脏代谢,轻中度肾损害的老年患者使用那格列奈无需调整剂量,肾功能不全的老年患者使用瑞格列奈无需调整起始剂量。
四、α‑糖苷酶抑制剂
α‑糖苷酶抑制剂主要有阿卡波糖、伏格列波糖、米格列醇。α‑糖苷酶抑制剂通过抑制小肠α‑糖苷酶活性,延缓碳水化合物的分解、吸收,从而降低餐后血糖。适用于高碳水化合物饮食结构和餐后血糖升高的糖尿病患者。该类药物的常见不良反应包括腹胀、腹泻、排气增多等胃肠道反应,一定程度上影响了其在老年人群中的应用[50] 。α‑糖苷酶抑制剂是老年 T2DM 患者的二级推荐降糖药物。应小剂量起始,逐渐增加剂量。该类药物单独使用低血糖风险较低,若出现低血糖应使用葡萄糖升糖,食用淀粉等碳水化合物升糖效果差。
五、噻唑烷二酮类
噻唑烷二酮(thiazolidinedione,TZD)类是胰岛素增敏剂,通过增加骨骼肌、肝脏及脂肪组织对胰岛素的敏感性发挥降糖作用。目前常用的 TZD 有罗格列酮、吡格列酮。单独使用时不易诱发低血糖,但与胰岛素或胰岛素促泌剂联用时可增加患者低血糖风险[49] 。该类药物是老年 T2DM 患者的三级推荐降糖药物。研究显示,吡格列酮可以降低大血管事件高风险的 T2DM患者的全因死亡率、非致死性心肌梗死和卒中的复合终点事件风险[51],Meta分析结果显示,吡格列酮可降低合并胰岛素抵抗、糖尿病前期及糖尿病的缺血性卒中和短暂性脑缺血发作患者卒中复发风险[52] 。回顾性队列研究显示,使用吡格列酮可能降低老年 T2DM患者主要心脑血管事件及痴呆的发生风险[53] 。存在严重胰岛素抵抗的老年 T2DM患者可考虑选用该类药物,但该类药物可能导致患者体重增加、水肿、骨折和HF的风险增加[54] ,使用胰岛素及有充血性HF、骨质疏松、跌倒或骨折风险的老年 T2DM患者应谨慎使用该类药物,低剂量TZD联合其他降糖药物治疗可能会减弱其不良反应[47,55‑56] 。
六、二肽基肽酶Ⅳ抑制剂
二肽基肽酶Ⅳ抑制剂(dipeptidyl peptidase Ⅳ inhibitor,DPP‑4i)是近年来国内外指南和(或)共识推荐的老年 T2DM 患者一线降糖药之一。该类药物通过抑制二肽基肽酶Ⅳ活性提高内源性胰高糖素样肽‑1(glucagon‑like peptide 1,GLP‑1)的水平,葡萄糖浓度依赖性地促进内源性胰岛素分泌,抑制胰高糖素分泌,降低血糖[57] 。目前在国内上市的DPP‑4i 有西格列汀、维格列汀、沙格列汀、阿格列汀、利格列汀、曲格列汀、瑞格列汀和替格列汀,其中多数 DPP‑4i 为日制剂(维格列汀每日两次),曲格列汀为周制剂。该类药物单独应用时一般不出现低血糖,对体重影响中性,胃肠道反应少[58] ,较适用于老年患者[59] 。老年患者在稳定基础胰岛素治疗的基础上加用利格列汀可以改善血糖控制,提升老年患者安全达标比例[60] 。DPP‑4i 是老年 T2DM患者的一级推荐降糖药物。
西格列汀、利格列汀和沙格列汀的心血管结局试验(cardiovascular outcome trial,CVOT)老年亚组结果显示,不增加老年患者的 3P或 4P主要心血管不良事件(major adverse cardiovascular event,MACE)的发生风险[61‑63] 。利格列汀不增加老年患者肾脏复合结局(因肾病死亡、进展为终末期肾病或持续 eGFR 下降≥40%)的风险[62] ,但沙格列汀会增加患者因HF住院的风险[63] 。
利格列汀在肝功能不全、沙格列汀在肝功能受损的患者中应用时无需调整药物剂量,西格列汀对轻中度肝功能不全的患者无需调整剂量,阿格列汀慎用于肝病患者,维格列汀禁用于肝功能异常(血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶或天冬氨酸氨基转移酶超过正常值上限 3 倍或持续升高)的患者。利格列汀、替格列汀可用于任何肾功能状态的老年患者,无需调整药物剂量,其余 DPP‑4i 需根据肾功能调整剂量或停用。若怀疑患者出现胰腺炎,应停止使用本类药物。
七、钠‑葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂
钠‑葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂(sodium‑glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor,SGLT2i)通过抑制近端肾小管钠‑葡萄糖共转运蛋白 2的活性增加尿葡萄糖排泄,从而达到降糖作用[64] 。我国目前批准临床使用的 SGLT2i 包括达格列净、恩格列净、卡格列净、艾托格列净和恒格列净。该类药物对老年患者有效且耐受性可[65] 。由于其降糖机制并不依赖胰岛素[66],因此极少发生低血糖[67‑70]。SGLT2i还有减重的作用,特别是减少内脏脂肪[71] 。EMPA‑ELDERLY 研究显示,恩格列净可在不影响老年患者肌肉量与体能的情况下降低体重[72] 。
SGLT2i 具有明确的心血管及肾脏获益,Meta分析结果显示,SGLT2i能够降低患者3P‑MACE、因HF 住院及肾脏结局风险,且在老年和非老年患者中均一致[73] ,是老年 T2DM患者的一级推荐降糖药物,推荐作为合并 ASCVD 或高危因素、HF 及慢性肾脏病(chronic kidney disease,CKD)的老年患者首选用药。恩格列净和卡格列净的 CVOT 显示其可降低T2DM患者3P‑MACE风险,老年亚组结果与总人群相似[74‑75] 。达格列净、恩格列净的CVOT 显示其能够降低 T2DM 患者的 HF 住院风险,老年亚组结果与总人群相似[74,76] 。卡格列净的肾脏结局试验(renal outcome trial,ROT)显示可降低患者心血管死亡或 HF 住院风险[77] ,老年亚组结果与总体人群具有一致性。达格列净、恩格列净的 CVOT均显示可改善患者肾脏结局[78‑79] ,老年亚组结果显示,达格列净对心肾复合结局和恩格列净对肾脏结局的改善与总体人群一致,卡格列净的 ROT 证实其可改善患者肾脏结局,老年亚组结果与总体人群一致[74‑76] 。EMPA‑KIDNEY 研究结果显示,恩格列净可降低 CKD 患者(合并/不合并T2DM)肾病进展或心血管死亡发生风险[80] 。DAPA‑CKD研究显示,达格列净可降低 CKD 患者(合并/不合并 T2DM)肾功能恶化、终末期肾病、因肾病或心血管死亡风险,老年亚组中观察到与总体人群相似的效应[81‑82]。EMPEROR‑Reduced和EMPEROR‑Preserved研究显示,恩格列净能够降低全射血分数的 HF 患者(合并/不合并 T2DM)心血管死亡及 HF 住院复合终点风险,老年亚组中观察到与总体人群相似的效应[83‑85] 。DAPA‑HF 和 DELIVER 研究显示,达格列净能够降低全射血分数的 HF 患者(合并/不合并T2DM)心血管死亡、HF住院或因HF紧急就诊的复合终点发生风险,在老年亚组中结果与总体人群一致[86‑88]。 艾 托 格 列 净 的 CVOT 显 示 其 不 增 加3P‑MACE 风险与心血管死亡风险,可降低HF住院风险,且老年亚组中结果与总体人群一致[89]。恒格列净在 T2DM 患者中开展的其对心功能及尿白蛋白影响的实效性研究正在进行中。
SGLT2i 常见的不良反应为泌尿生殖系统感染、血容量减少等,上市后临床监测中也发现有酮症酸中毒的报告,老年患者使用时风险有可能更高[90] 。此外,SGLT2i具有降低血压、减轻体重的作用,应用此类药物应关注患者的血压,避免出现低血压,衰弱患者应用此类药物应慎重。eGFR<45 ml·min-1(1.73 m2 )-1 不建议使用卡格列净、艾托格列净;eGFR<30 ml·min-(1.73 m2 )-1 不建议使用恒格列净,禁用卡格列净和艾托格列净;eGFR<25 ml·min-1(1.73 m2 )-1不建议起始使用达格列净;eGFR<20 ml·min-1(1.73m2 )-1 不建议起始使用恩格列净,若已经使用恩格列净、达格列净,除非患者无法耐受或需要肾脏替代治疗,不建议停用[91] 。由于该类药物的降糖机制为增加尿糖排泄,因此当以降糖为目的时,eGFR<45mlmin-1(73m2)-1不建议使用达格列净,eGFR<30mlmin-1(1.73m2)-1 不推荐使用恩格列净。
八、胰高糖素样肽‑1受体激动剂
胰高糖素样肽‑1 受体激动剂(glucagon‑like peptide‑1 receptor agonist,GLP‑1RA) 通 过 与 GLP‑1受体结合发挥作用,以葡萄糖浓度依赖的方式促进胰岛素分泌和抑制胰高糖素分泌降低血糖,并能延缓胃排空,抑制食欲中枢、减少进食量,兼具减轻体重、降低血压和调脂的作用[92‑94] ,且单独应用 GLP‑1RA 时低血糖发生风险低。GLP‑1RA 在老年人群(>65 岁)中的安全性和有效性与成人相似[95‑97]。目前国内上市的GLP‑1RA有艾塞那肽、利拉鲁肽、利司那肽、度拉糖肽、贝那鲁肽、洛塞那肽和司美格鲁肽,均需皮下注射。利拉鲁肽每日注射一次,可在任意时间注射。利司那肽每日注射一次,可在任意一餐前注射。艾塞那肽周制剂、洛塞那肽、度拉糖肽、司美格鲁肽每周注射一次,且无时间限制。GLP‑1RA 灵活的给药方式提高了老年糖尿病患者用药的依从性,周制剂的用药依从性更高。
部分 GLP‑1RA 具有明确的心血管获益,Meta分析显示,该类药物能够显著降低 3P‑MACE、心血管死亡、卒中风险,效应在老年和非老年人群一致[73] 。GLP‑1RA还能降低患者不良肾脏结局风险,其作用主要由减少尿白蛋白排泄量所驱动[98] 。推荐GLP‑1RA作为合并ASCVD或高危因素的老年患者 首 选 用 药 ,老 年 患 者 合 并 CKD 若 无 法 耐 受SGLT2i也可优选 GLP‑1RA。GLP‑1RA 是一般老年T2DM患者的二级推荐降糖药物,但对合并ASCVD或高危因素的患者是一级推荐降糖药物。度拉糖肽显著降低既往有心血管事件或高风险因素的T2DM患者3P‑MACE,在ASCVD高风险的T2DM患者中有一级预防证据,且在基线异质性分析中,≥66 岁与<66 岁患者结果一致[99] 。利拉鲁肽显著降低 合 并 心 血 管 疾 病 高 危 的 T2DM 患 者3P‑MACE[100] 。司美格鲁肽能够显著降低合并心血管疾病、慢性HF、CKD、年龄>60岁或心血管高危因素的T2DM患者的3P‑MACE风险,且在基线异质性分析中,≥65岁与<65岁患者结果一致[101] 。利司那肽和艾塞那肽的 CVOT 显示其不增加 MACE 风险[102‑103] 。艾塞那肽、利拉鲁肽、利司那肽、度拉糖肽和司美格鲁肽的 CVOT 次要研究终点或肾脏结局探索性分析均显示出可降低 T2DM患者肾脏复合结局发生风险,降低尿白蛋白排泄量[99‑103] 。
一些研究也探索了SGLT2i和GLP‑1RA联用的临床获益。Meta 分析显示,相较于单药治疗,两类药物联合治疗血糖、血压、血脂改善更显著[104] 。回顾性队列研究发现,相较于单药治疗,SGLT2i 和GLP‑1RA联合治疗似乎心血管获益更大、全因死亡降低更明显[105] 。暂缺乏老年人群上述两类药物联合治疗的高质量临床获益证据。
推荐选择简便的 、有降糖以外获益的GLP‑1RA[106] 。GLP‑1RA 主要的不良反应为恶心、呕吐、腹泻、食欲减退等胃肠道不良反应,且有延缓胃排空的作用,需警惕诱发或加重老年 T2DM患者的营养不良、肌少症以及衰弱。此外,有研究者观察到使用 GLP‑1RA 后患者肠梗阻、胃轻瘫和胰腺炎等不良反应风险增加[107] ,对于老年患者需要评估其潜在风险,权衡获益风险比。
九、胰岛素
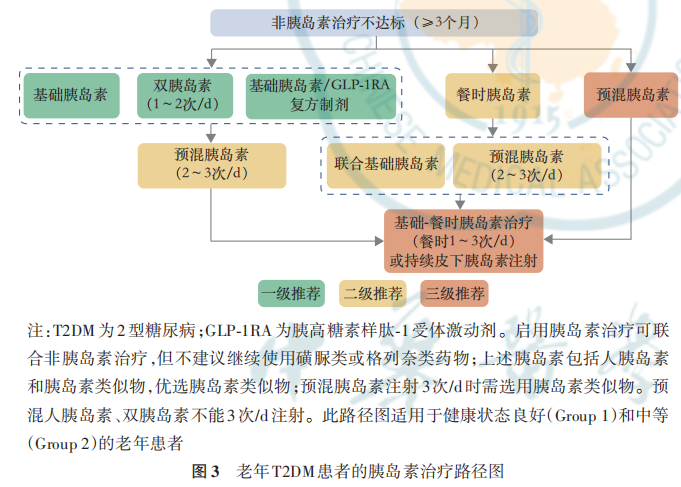
老年 T2DM 患者在生活方式干预和非胰岛素治疗的基础上,如血糖控制仍未达标,可加用胰岛素治疗。在起始胰岛素治疗前,需要充分考虑老年T2DM 患者的整体健康状态、血糖升高的特点和低血糖风险等因素,权衡患者获益风险比,个体化选择治疗方案。
起始胰岛素治疗时,首选基础胰岛素、双胰岛素或基础胰岛素/GLP‑1RA 复方制剂,此方案用药方便、依从性高,适用于多数老年患者[47] 。选择基础胰岛素时,应选择血药浓度较平稳的剂型(如甘精胰岛素U100、德谷胰岛素、甘精胰岛素U300),并在早上注射,以减少低血糖(尤其是夜间低血糖)的发生风险。可根据体重计算起始剂量,通常设定为每日 0.1~0.3 U/kg[108] ,HbA1c>8.0% 者,可考虑每日0.2~0.3 U/kg 起始基础胰岛素[109] ,根据空腹血糖水平,每 3~5 天调整一次剂量,直至空腹血糖达到预定目标。如空腹血糖达标,HbA1c仍不达标时,应重点关注餐后血糖,必要时可添加餐时胰岛素[2] 。基础胰岛素联合餐时胰岛素(3次/d)较符合人体生理胰岛素分泌模式,但复杂的给药方案会降低患者长期治疗的依从性,且不适用于健康状态差(Group 3)、预期寿命短的老年患者。双胰岛素每日注射1~2次,与多次胰岛素注射疗效相当,注射次数少,患者用药依从性较高[110] ,并在老年糖尿病患者中具有与非老年患者相似的药代动力学、疗效和安全性[111‑113] 。预混人胰岛素或预混胰岛素类似物相较于基础胰岛素联合餐时胰岛素的方案注射次数少,但在老年患者中,尤其是长病程、自身胰岛功能较差、进餐不规律的患者中,可能增加低血糖风险[114] 。
老年糖尿病患者HbA1c>10.0%,或伴有高血糖症状(如烦渴、多尿),或有分解代谢证据(如体重降低),或严重高血糖(空腹血糖>16.7 mmol/L)时,根据患者的健康状态及治疗目标,可采用短期胰岛素治疗。除自身胰岛功能衰竭外,老年糖尿病患者经短期胰岛素治疗血糖控制平稳、高糖毒性解除后应及 时 减 少 胰 岛 素 注 射 次 数 并 优 化 与 简 化 降 糖方案[115] 。
在老年糖尿病患者中,胰岛素治疗方案应强调“去强化”。对于已应用胰岛素的老年糖尿病患者,应评估胰岛素治疗是否是必需的,以及是否可以简化胰岛素治疗方案。高龄、预期寿命短或健康状态差(Group 3)的老年糖尿病患者不建议多针胰岛素治疗。相较于多针胰岛素治疗,基础胰岛素与GLP‑1RA 固定复方制剂、双胰岛素、基础胰岛素联合口服降糖药均可减少注射次数,简化方案。非胰岛素治疗可将血糖控制达标的老年糖尿病患者,应逐步将胰岛素进行减停。必须联用胰岛素才能将血糖控制满意的老年糖尿病患者,应尽量简化胰岛素方案,需考虑下列几点:(1)尽量减少注射次数;(2)采用长效或超长效胰岛素类似物控制空腹及餐前血糖满意后,在餐后血糖不达标时考虑加用餐时胰岛素;在无禁忌证的情况,也可考虑换用基础胰岛素与GLP‑1RA固定复方制剂、双胰岛素或基础胰岛素联合 DPP‑4i [60,113,116‑117] ;(3)尝试将预混胰岛素转换为基础胰岛素,以简化方案并减少低血糖风险。
十、固定复方制剂
随着 T2DM的病情进展,降糖治疗常需要联合用药。固定剂量复方制剂(fixed‑dose combination,FDC)和固定比例复方制剂(fixed‑ratio combination,FRC)是将两种或更多活性物质以固定剂量/固定比例组合而制成的复方制剂,可作为联合用药的一种重要选择。FDC 和 FRC 具有覆盖多种病理生理机制、简化治疗方案、减轻用药负担等多方面优势[118] ,有助于提高老年患者治疗依从性与满意度。固定复方制剂的临床优势与局限性取决于各单方成分,临床应用时仍需结合老年患者特征综合考量。我国上市的固定复方制剂包括以二甲双胍为基础的FDC、基础胰岛素和GLP‑1RA的FRC。
一些固定复方制剂也在老年人群中开展了相关研究。GIFT 研究显示,自由联合二甲双胍与DPP‑4i方案转换为二甲双胍与 DPP‑4i的 FDC 可改善血糖控制,且在老年患者中血糖改善更为显著,这与改善了患者依从性有关[119] 。LixiLan系列研究和 DUAL 系列研究分别验证了甘精胰岛素‑利司那肽 FRC与德谷胰岛素‑利拉鲁肽 FRC对 T2DM 患者的有效性与安全性,结果显示上述FRC可改善口服降糖药、基础胰岛素或GLP‑1RA佳患者的血糖[120‑125] ,且 LixiLan‑L/O 治疗血糖控制不研究事后分析及多项DUAL系列研究事后分析显示,相较于各自单组分治疗,甘精胰岛素‑利司那肽 FRC 与德谷胰岛素‑利拉鲁肽可耐受[116‑117,126] 。
十一、降糖药物新进展
近年来,国内有两类全新作用机制的降糖药物获批上市用于 T2DM治疗,包括过氧化物酶体增殖物 激 活 受 体(peroxisome proliferators‑activatedreceptor,PPAR)泛激动剂和葡萄糖激酶激活剂(glucokinase activator,GKA)。PPAR 泛激动剂代表药物为西格列他钠,是新一代的非TZD类胰岛素增敏剂,能够同时激活PPAR‑α、γ和δ亚型受体,提高胰岛素敏感性从而降低血糖[127]。GKA代表药物为多格列艾汀,可以通过葡萄糖依赖的方式调节葡萄糖激酶活性,改善血糖调节稳态,发挥降糖作用[128] 。目前,上述两类药物在老年糖尿病人群中应用的数据有限,在老年 T2DM患者中的疗效及安全性数据有待进一步积累。
十二、治疗路径
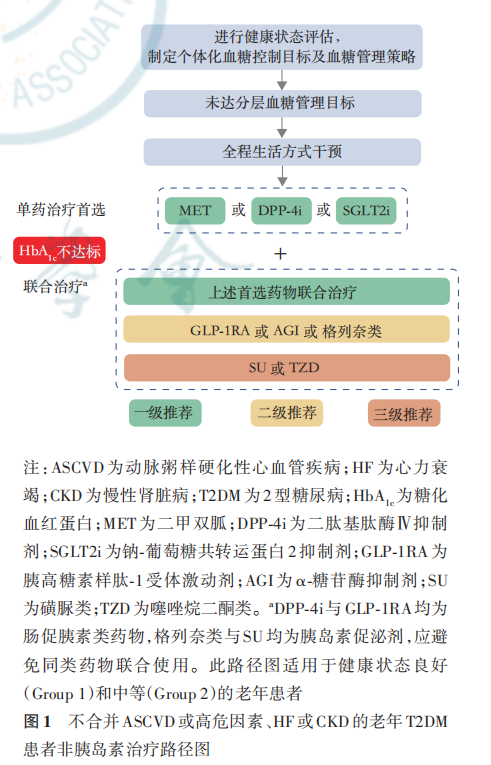
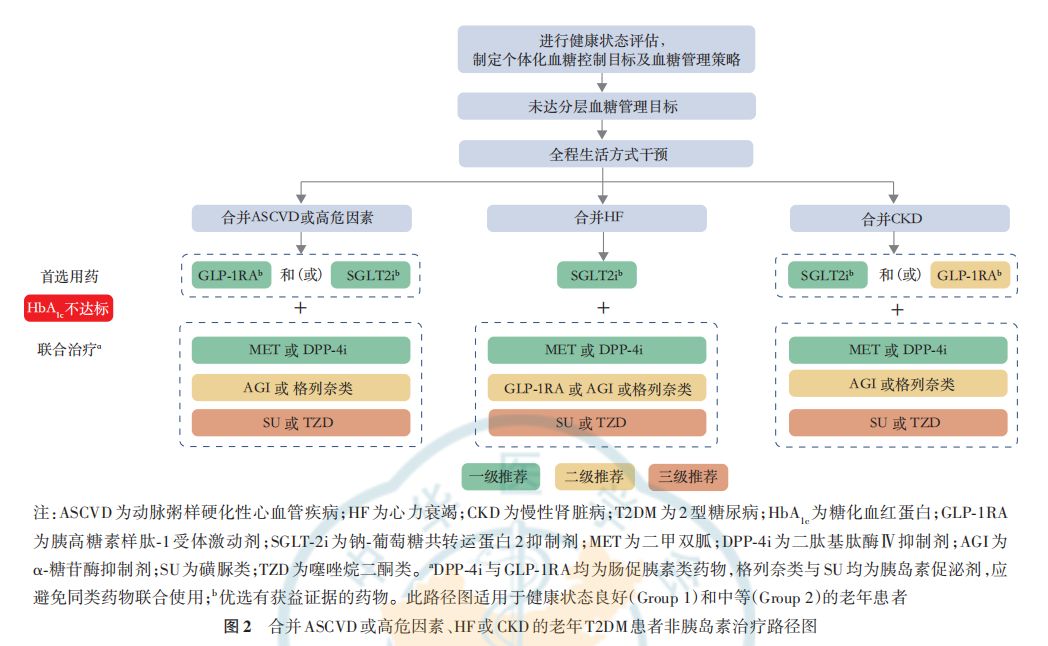
根据老年患者健康状态选择治疗药物,对于健康状态综合评估结果为良好(Group 1)和中等(Group 2)的 老年患者需要根据患者是否合并ASCVD或高危因素、HF及CKD,制定个体化降糖方案,可供参考的方案包括:不合并ASCVD或高危因素、HF或CKD的老年T2DM患者非胰岛素治疗路径图(图1);合并ASCVD或高危因素、HF或CKD的老年 T2DM 患者非胰岛素治疗路径图(图 2)。老年T2DM患者的胰岛素治疗路径图与老年T2DM患者短期胰岛素治疗路径见图3,4。当单药治疗3个月以上仍血糖控制不佳时,应联合不同机制的药物进行治疗,但应注意尽量避免低血糖及其他不良反应风险叠加的药物联用。经过规范的非胰岛素治疗无法达到血糖控制目标的老年患者应及时启动胰岛素治疗,使用胰岛素治疗方案应加强患者低血糖防治及胰岛素注射方法宣教,以减少低血糖的发生和胰岛素注射相关的不良反应。
健康状态综合评估结果为差(Group 3)的患者(包括临终前状态的患者),不建议依据上述路径进行方案选择,而应基于重要脏器功能、药物治疗反应、低血糖风险等,制定相对宽松的血糖控制目标,以不发生低血糖和严重高血糖为基本原则。要尊重患者及家属的意愿,选择合适的降糖方案,应用不易引起低血糖的口服药和(或)长效(超长效)基础胰岛素(如甘精胰岛素 U100、德谷胰岛素、甘精胰岛素 U300 等)较使用一日多次速效胰岛素或预混胰岛素更为安全,剂量也更容易调整,不推荐使用低血糖风险高、减轻体重的药物。
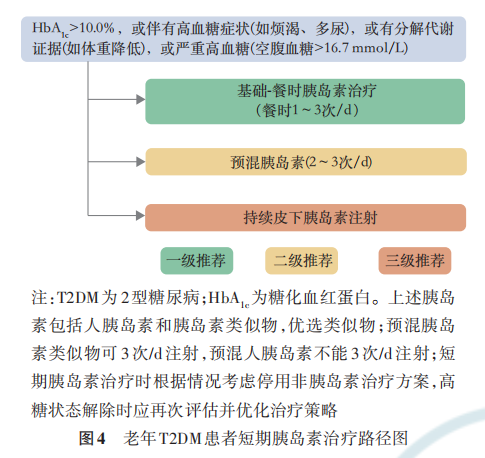
第九章 老年糖尿病合并动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病或危险因素的综合管理

ASCVD 包括动脉粥样硬化所导致的冠心病、脑血管疾病和外周血管疾病,是 T2残和致死原因[129] DM 患者主要的致。T2DM 患者心血管疾病的风险是非糖尿病患者的2倍以上[130] 。临床上应积极地筛查和治疗心血管疾病危险因素,对于合并心血管疾病或高危因素的老年糖尿病患者,应优先选择对心血管具有保护作用的降糖药物,包括具有循证医学证据的GLP‑1RA 或 SGLT2i。年龄本身即是 ASCVD 的危险因素,在非糖尿病的老年人中,ASCVD 也是导致残疾和死亡的重要原因。吸烟、肥胖和超重、高血压、血脂异常等均为老年糖尿病患者发生ASCVD的重要危险因素。绝大多数老年糖尿病患者表现为多种心血管危险因素和(或)心血管疾病及肾脏疾病同时存在。然而,老年人本身的异质性明显,且临床研究倾向排除高龄、身体状态不佳的老年糖尿病患者,导致老年糖尿病患者的相关数据有限,ASCVD 的危险因素管理在老年糖尿病患者中尚未形成广泛共识。
一、筛查及评估
大血管并发症在糖尿病诊断前可能已经进展了多年,这导致ASCVD的管理更加棘手。因此,主动筛查ASCVD及其危险因素极为重要。建议患者每次就诊时进行血压监测,至少每年进行一次ASCVD危险因素的系统评估,包括超重和肥胖、高血压、血脂异常、吸烟、早发冠心病家族史、CKD 以及蛋白尿等,对合并上述 ASCVD 危险因素的老年糖尿病患者,应积极进行颈动脉和下肢动脉超声评估,判断是否存在外周血管病变,以早期识别危险因素并进行干预。
二、心血管危险因素管理
(一)高血压
相对于非老年糖尿病患者,老年糖尿病患者罹患高血压的风险更高。高血压是心血管疾病的独立危险因素,在控制其他危险因素后,收缩压每升高 10 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa),缺血性心脏病和缺血性脑卒中的相对发病风险增加 30%[131] ,降压治疗能够降低糖尿病患者心血管事件的发生风险及死亡风险[132] 。在老年患者中,降压治疗的获益也已被临床研究充分证实[133] 。
- 控制目标:目前尚缺乏针对老年糖尿病患者的血压控制目标的研究。需要强调的是,老年糖尿病患者的血压目标应综合考虑风险获益比后进行个体化治疗。ACCORD BP研究发现,T2DM中强化降压(收缩压目标<120 mmHg)相较于标准降压(收缩压目标<140 mmHg)并不能降低主要复合终点(非致死性心肌梗死、非致死性卒中和心血管死亡),却增加低血压、高钾血症等不良反应风险[134] 。2021 年发表的来自中国的 STEP 研究结果显示,与标准降压组(收缩压目标 130~150 mmHg)相比,强化降压(收缩压目标110~130 mmHg)可使老年患者MACE 风险降低 26%,除低血压风险增加以外,未增加头晕、骨折等不良反应风险。在这个研究中,强化降压组和标准降压组中分别 18.9% 和 19.4%的患者为老年糖尿病(60~80 岁)[135] 。建议健康状态良好同时年龄<80 岁的老年糖尿病患者收缩压控制目标为 130 mmHg 以下,以降低心血管疾病风险[136] ,但需密切监测血压,以防出现体位性低血压、餐后低血压、舒张压过低等情况。不建议将收缩压<120 mmHg 作为老年糖尿病患者的控制目标[137] 。对于年龄≥80岁、预期寿命短或健康状态差(Group 3)的患者可适当放宽收缩压控制目标至<150 mmHg[2] 。
药 物 选 择 :血 管 紧 张 素 转 化 酶 抑 制 剂 -
(angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor,ACEI)显著减少糖尿病患者的 MACE、心血管死亡和全因死亡[138] ,在老年糖尿病患者中,ACEI也可以减少心血管死亡[139] 。血管紧张素Ⅱ受体拮抗剂(angiotensinⅡ receptor blocker,ARB)在糖尿病患者中具有相似效果[140] ,在老年人中,ARB 显著减少脑卒中[141] 。推荐将 ACEI 或ARB 作为老年糖尿病患者控制血压的一线用药[2],但不建议两类药物联合应用[140],以避免高钾血症和急性肾损伤[141] 。在应用过程中密切监测血钾、肌酐水平。如使用 ACEI或 ARB 单药血压控制不佳,可考虑加用钙通道阻滞剂、噻嗪类利尿剂或β受体阻滞剂协同降压[2] 。
(二)血脂异常
老年糖尿病患者常合并血脂异常 ,导致ASCVD的发生风险增加。老年糖尿病患者中降脂治疗的循证医学证据有限,基于专家共识的建议,老年糖尿病患者的低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low‑density lipoprotein‑cholesterol,LDL‑C)控制在2.6 mmol/L 以下[142‑143] ,合并 ASCVD 的老年糖尿病患者 LDL‑C 控制在 1.8 mmol/L 以下[142‑143],对于年龄≥80岁、预期寿命短或健康状态差(Group 3)的患者建议适当放宽 LDL‑C 目标。他汀类药物治疗有助于降低老年患者心血管事件[144‑145] 和全因死亡风险[145‑146] 。HPS‑DIM 研究、CARDS 研究等均提示他汀类药物可降低老年糖尿病患者的心血管事件风险[147‑148] 。但针对80岁以上老年糖尿病患者的证据缺乏。IMPROVE‑IT 研究显示,依折麦布联合辛伐他汀可使急性冠脉综合征患者的缺血性脑卒中风险降低 24%[149] ,合并糖尿病或其他危险因素时,获益更显著[150] 。推荐老年糖尿病患者应用他汀类药物以减少心血管事件和全因死亡。如果单用他汀类药物效果欠佳,可考虑谨慎加用依折麦布或PCSK9 抑制剂作为联合用药[2,142‑143] 。老年糖尿病患者甘油三酯>5.65 mmol/L 时,可应用非诺贝特,以降低胰腺炎风险,但需警惕与他汀类药物联用时增加不良反应的风险。鉴于老年糖尿病患者常合并多种疾病并服用多种药物,应密切关注他汀类药物的安全性及其与其他药物的相互作用,监测肝功能和肌酸激酶变化。
(三)抗血小板治疗
阿司匹林抗血小板治疗获益和风险的权衡取决于出血风险、基础心血管疾病发病风险、阿司匹林治疗依从性以及年龄 4 个方面。尽管阿司匹林一级预防减少了糖尿病患者心血管事件的发生,但却增加了出血事件风险,而年龄越大的患者出血风险越高。ASPREE 研究显示,在年龄≥70 岁具有一定心血管疾病风险的人群中,应用阿司匹林不降低心血管疾病发生率,但却增加出血风险[151] 。新近的Meta分析显示出了相似结果[152] 。目前尚无充足的证据支持在老年糖尿病患者中应用阿司匹林进行一级预防利大于弊,不建议老年糖尿病患者常规应用阿司匹林进行心血管疾病事件的一级预防。推荐合并ASCVD的老年糖尿病患者应用低剂量阿司匹林(75~150 mg/d)作为二级预防[2] 。但在年龄≥80 岁、预期寿命短和健康状态差(Group 3)的患者中需个体化考虑。阿司匹林最常见的不良事件为消化道出血,应用前需充分评估出血风险。出血风险因素包括:阿司匹林剂量大、应用时间长、严重肝功能不全、肾功能不全、消化道溃疡、出血性疾病、血小板减少、应用非甾体类抗炎药、血压控制不佳等。应用后需对患者及其家属进行充分宣教,以便及时识别可能的出血风险。联合应用质子泵抑制剂可能有助于降低消化道出血风险。
(四)戒烟
吸烟增加冠心病、脑卒中等疾病的发病和死亡风险,并呈剂量反应关系[153‑154] 。被动吸烟也可以增加心血管疾病风险[155‑156] 。在老年人中,吸烟仍是心血管疾病重要的独立危险因素之一,戒烟有利于降低心血管疾病风险[157] ,任何年龄的老年人戒烟均可获益。因此,应积极鼓励老年糖尿病患者戒烟。
(五)体重管理
肥胖与多种心血管疾病相关,可以直接或间接增加心血管疾病的发病率和死亡率。减重能够改善血糖及其他心血管危险因素,但对老年糖尿病患者实施减重治疗需考虑老年人身体成分的特点、营养不良、肌少症、骨质疏松的风险。随着年龄增大,老年人出现肌肉减少、脂肪增多的改变,体重指数在反映老年人肥胖方面存在一定的局限性。建议对老年人进行肥胖评估时,除体重指数之外,还需关注腰围、腰臀比、身体肌肉量,综合评价体重、身体成分以及肌肉功能后制定体重管理策略。饮食干预减肥中应避免营养不良,适当增加蛋白质的摄入量。通过饮食减肥而不进行抗阻运动会导致瘦肉组织(肌肉和骨骼)的损失,加剧老年人与年龄相关的肌少症和骨量减少[158] 。应鼓励老年糖尿病患者加强抗阻训练,以增加身体肌肉量。对于合并肥胖的老年糖尿病患者,应首先选择兼具减重和降糖的药物,尤其是减重强度大且具有心血管保护作用证据的 GLP‑1RA(利拉鲁肽、度拉糖肽、司美格鲁肽),如无法耐受,可选用减重强度中等的SGLT2i。
第十章 老年糖尿病慢性并发症的筛查与处理

一、糖尿病肾病
糖尿病肾病是我国CKD的主要原因[159] 。一部分T1DM患者病程超过5~10年后出现糖尿病肾病,T2DM 可能在诊断时即已经出现肾脏病变,糖尿病肾病如不能进行控制,最终进展至终末期肾病,会严重影响患者生活质量,增加医疗负担。此外,糖尿病肾病患者的心血管疾病风险也显著增加。
(一)筛查
老年糖尿病患者确诊时应筛查尿白蛋白/尿肌酐比值(urine albumin/creatinine ratio,UACR)和血肌酐(计算eGFR),同时采用UACR和eGFR进行评估,不同的肾功能状态复查频率不同(表 5)[160‑161] ,有助于发现早期肾脏损害。
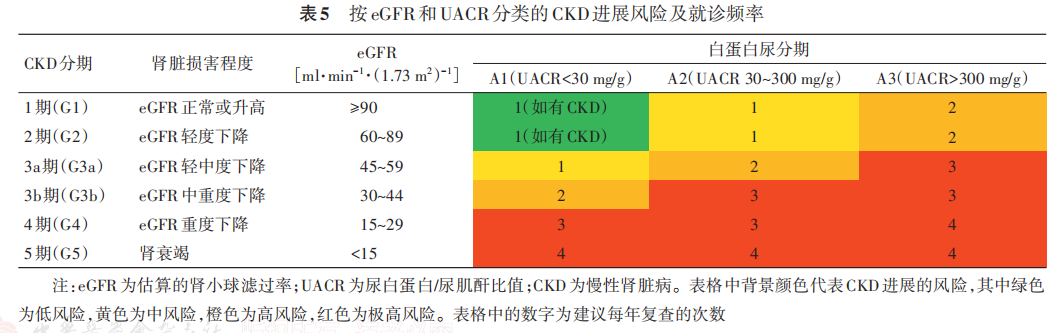
根据 UACR 增高和(或)eGFR 下降,同时排除其他因素导致的 CKD 而做出临床诊断,不建议常规行肾脏穿刺活检。糖尿病肾病的患者多数病程较长,一般同时存在糖尿病视网膜病变,以蛋白尿为主而不伴肉眼血尿,eGFR 逐渐下降。需要注意的是,老年糖尿病患者发生糖尿病肾损伤时,常合并高血压、高血脂、高尿酸、药物性肾损伤等其他因素,存在肾损伤的老年糖尿病患者中,仅1/3患者的肾损伤是单纯因糖尿病所致[162] 。
随机尿检测 UACR 是最为简便的筛查方法,UACR>30 mg/g 即被认为升高,但剧烈运动、感染、发热、充血性HF、血糖或血压明显升高等均可能导致 UACR 升高。有些 UACR 在正常范围内的患者,也可能已经出现肾功能损害。eGFR是评价肾功能的重要手段之一,目前通常推荐采用 CKD 流行病学合作研究公式计算 eGFR[163] ,老年人可能由于体重低、蛋白质摄入少而导致eGFR假性正常化,单独使用 eGFR 对老年人肾功能判断意义有限,且在老年人中eGFR的界定尚存在争议[164] 。
(二)处理
老年糖尿病患者合并 CKD 时,强调以降糖为基础的综合治疗。
- 对于非透析患者,推荐每日优质蛋白质摄入量0.8 g/kg,同时限制钠盐摄入,氯化钠<5g/d或钠<2 g/d有助于降低血压及心血管疾病风险[165]。
- 降糖治疗优先选用具有肾脏保护作用的SGLT2i,如不耐受或有禁忌证,选用有肾脏保护作用证据的GLP‑1RA;其次可选择基本不经过肾脏排泄的药物,如利格列汀、瑞格列奈和格列喹酮。应用各种降糖药物时,均应关注是否需根据 eGFR 进行剂量调整,警惕发生低血糖。
- 降压治疗选择 ACEI 或 ARB 类药物,必要时可联合其他类型降压药物,使用过程中注意关注血压达标情况及肾功能、血钾。控制血压达标对于减轻、减缓肾病的进展至关重要。FIDELIO‑DKD 研究显示,非奈利酮显著降低T2DM伴CKD患者的肾脏复合终点事件风险[166] 。中国亚组数据结果与总体人群相似[167] 。FIDELITY 研究是针对非奈利酮的两项大型国际多中心Ⅲ期研究(FIDELIO‑DKD和 FIGARO‑DKD[168] )进行的预设汇总分析,结果显示,非奈利酮可显著降低T2DM伴CKD患者的远期肾脏及心脏复合事件风险,老年人群获益与总人群保持一致[169] 。对于eGFR≥25 ml·min-1-1 的老年糖尿病合并 CKD 的蛋白尿患者,推荐在使用最大耐受剂量 ACEI 或 ARB 治疗的基础上加用非甾体盐皮质受体阻滞剂非奈利酮,以降低尿蛋白并延缓 CKD进展,使用过程中注意需监测血钾、肾功能。此外,使用该药物尚存在偶发严重贫血的报道。
-
戒烟,控制血脂、尿酸水平。
-
与肾脏专科医师对合并 CKD 的老年糖尿病患者进行多学科的综合管理。
-
慎重用药,避免不必要的中、西药应用,尤其是告诫患者不可自行选用所谓的“保肾药品”。
二、糖尿病相关眼病
糖尿病与多种眼病相关,糖尿病相关眼病可导致患者视力下降甚至失明,致使老年患者无法参与社会活动,检测指血血糖和注射胰岛素的能力下降以及发生意外事故风险增加。老年糖尿病患者在确诊时即应进行眼底检查,必要时去眼科进行全面检查,此后至少每年筛查一次。要常规检查视力、眼压、眼表及眼底,着重筛查糖尿病视网膜病变(diabetic retinopathy,DR)、黄斑水肿,也要检查是否有白内障、青光眼和干眼症等。
(一)糖尿病眼底病变
1.DR:DR是糖尿病常见的微血管并发症之一,其所导致的眼底病变严重影响患者的生活质量。依据病情阶段,可将 DR 分为非增殖期 DR 和增殖期 DR。非增殖期 DR 的表现包括微动脉瘤形成和视网膜内出血,微血管损伤可导致血管的通透性增加(视网膜水肿与渗出)。增殖期 DR 则表现为视盘、视网膜、虹膜以及房角内新生血管,最终导致牵拉性视网膜脱离和新生血管性青光眼。建议老年糖尿病患者诊断时常规进行 DR 筛查,如无 DR 或为轻度非增殖期 DR,应每年复查 1次,如为中度非增殖期 DR 建议每 6 个月复查 1 次,重度非增殖期DR 和增殖期 DR 每 3 个月复查 1 次[170] 。长病程和血糖控制不佳是 DR 发生和进展的危险因素,除此以外,白蛋白尿、高血压、高脂血症等均是 DR 的危险因素。因此,改善血糖、血压、血脂可能有助于减少 DR 的发生。Meta 分析显示,与安慰剂相比,GLP‑1RA 与早期 DR 风险增加明显相关,但与胰岛素相比 ,GLP‑1RA 能保护晚期DR[171] 。 基于GLP‑1RA的CVOT研究数据的Meta分析未发现DR与GLP‑1RA本身有关,但与HbA1c下降有关[172] 。应用 GLP‑1RA 或其他降糖药进行严格血糖管理时,应监测视网膜状态,尤其是针对增殖期和(或)重度DR 的患者。此外,GLP‑1RA 与 DR 的关系可能受GLP‑1RA 种类、患者性别、年龄和病程等影响[171] 。目前 GLP‑1RA 与 DR 的关系尚缺乏针对老年糖尿病人群数据。全视网膜激光光凝术是增殖期DR的主要治疗方法,玻璃体腔内抗血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)也是有效的治疗方法之一。
2. 糖尿病黄斑水肿(diabetic macular edema,DME):DME是一种视网膜黄斑中心凹液体积聚的疾病,是血‑视网膜屏障破坏的后果,导致广泛的毛细血管渗漏引起弥漫性水肿。DME在老年糖尿病患者中常见,可以与 DR 伴发,也可以单独发生,是造成糖尿病患者视力损伤的主要原因之一。光学相干断层扫描是诊断 DME 的金标准,也可用于DME 的筛查、分类、监测以及治疗效果的评估,荧光素血管造影可以了解血管渗漏情况及屏障功能。建议老年糖尿病患者诊断时即进行光学相干断层扫描筛查 DME,此后每年复查,必要时进行荧光素血管造影检查。如已存在有临床意义的黄斑水肿(即位于黄斑中心或威胁黄斑中心的视网膜水肿),应每3个月进行复查。过去,黄斑焦点/网格光凝术为DME的标准治疗方法。近年来,VEGF治疗逐渐得到认可,2017 年欧洲视网膜专家协会指南推荐累及中心凹的黄斑水肿首选VEGF治疗[173] 。
(二)其他相关眼病
T2DM是白内障的危险因素[174] ,年龄与白内障密切相关,在老年人中白内障是最主要的致盲原因[175] 。青光眼是老年人第二大致盲原因[175] ,糖尿病患者的青光眼风险较非糖尿病更高[176] 。在老年糖尿病患者中检查视力、眼压,筛查白内障、青光眼尤为重要。除上述可能引起视力下降的眼病应得到关注之外,老年糖尿病中干眼症也应受到重视。干眼症是最常见的眼表疾病[177] 。糖尿病与干眼症的风险显著相关[178] 。上海一项基于社区的调查显示,平均年龄为 69 岁的 T2DM 患者中干眼症患病率为17.5%[179] 。干眼症可造成各种眼部不适(眼干、眼红、沙粒感、烧灼感、异物感、多泪、畏光等)和视力损害[180] ,还可能导致睡眠质量下降及发生焦虑和抑郁[181] 。因此,在老年糖尿病患者中应注意询问是否存在干眼症状,必要时进一步检查和相应的治疗。
三、糖尿病神经病变

糖尿病神经病变是糖尿病常见的慢性并发症之一,是一组具有多种临床表现的异质性疾病,病变可累及中枢神经和周围神经。远端对称性多发性神经病变(distal symmetrical multiple neuropathy,DSPN)是最具代表性的糖尿病周围神经病变。除DSPN 外,糖尿病自主神经病变也是糖尿病周围神经病变中较为常见的类型。糖尿病自主神经病变包括心脏自主神经病变(cardiac autonomicneuropathy,CAN)、胃肠道及泌尿生殖系统自主神经病变和泌汗功能异常,临床表现多样,包括对低血糖无感知、静息心动过速、体位性低血压、胃轻瘫、便秘、腹泻、勃起障碍、神经源性膀胱、泌汗功能异常等,其中 CAN 最受关注。CAN 独立于其他心血管危险因素,与死亡风险相关[182] 。此外,胃肠道自主神经病变表现为吞咽困难、呃逆、胃轻瘫、便秘及腹泻等,一旦出现,严重影响老年糖尿病患者的生活质量。
(一)DSPN
是最常见的类型,约占糖尿病神经病变的75%,是糖尿病足溃疡的重要危险因素,也是跌倒及骨折的重要原因[183] 。年龄是 DSPN 的独立危险因素[184],但目前尚缺乏全国性老年糖尿病合并DSPN 的流行病学调查数据。北京地区的数据显示,老年 T2DM 中 DSPN 患病率 42.6%、疑似 DSPN患病率26.2%[185] 。DSPN患者临床上表现为双侧肢体麻木、疼痛、感觉异常。对于新诊断的老年糖尿病患者应进行 DSPN 评估,具体包括详细的病史、小纤维功能(温度觉、针刺痛觉)和大纤维功能(压力觉、踝反射和振动觉)的评估,此后每年进行筛查。此外,每年均应进行 10 g 尼龙丝测试,以早期识别足溃疡和截肢风险。目前尚无有效治疗手段逆转 DSPN,一旦考虑 DSPN 诊断时,应尽早开始治疗以延缓 DSPN进展。血糖控制是预防 DSPN发生和延缓其进展的主要手段。针对血压、血脂等多种危险因素的综合管理同样也有助于延缓 DSPN 进展,对 DSPN 患者应制定上述危险因素的综合管理目标。此外,有数据显示,甲钴胺营养神经、硫辛酸抗氧化应激、前列腺素E1改善微循环、醛糖还原酶抑制剂依帕司他等对老年 DSPN 患者的治疗也有一定的效果。
(二)CAN
尚缺乏全国性老年糖尿病合并 CAN 的流行病学调查数据。北京地区的数据显示,CAN 患病率高,发生 CAN 的 T2DM 中 55.7% 为老年患者[186],T2DM 中 CAN 的患病率高达 62.6%,其中≥60 岁的T2DM 患者中 CAN 的患病率为 67.5%,略高于总体人群,多因素logistic回归分析显示年龄是 CAN的独立危险因素[187]。对于老年糖尿病患者,关注CAN非常重要。对已有微血管和神经并发症、低血糖感知缺乏的老年糖尿病患者应评估是否存在CAN症状或体征。此外,血糖变异性大的糖尿病患者更有可能出现 CAN[188] 。在 CAN 的早期阶段,患者可能无症状,仅在查体时发现心率变异性下降,随着疾病进展,患者出现静息心动过速和体位性低血压,常见症状为头晕、乏力,甚至出现晕厥、无痛性心肌梗死等。心血管反射试验、心率变异性、体位变化时测定血压、24 h动态血压监测等手段有助于明确诊断。如怀疑存在CAN,应进一步排查其他并存的可能影响心脏自主神经功能的疾病或药物。对于存在 CAN的患者,应加强患者及家属教育,谨防跌倒,同时避免低血糖,尤其是夜间低血糖发生。研究显示,有氧运动结合抗阻训练可改善中老年T2DM女性患者的心率变异性,对CAN具有积极影响[189]。拟交感神经药物(如米多君)是治疗体位性低血压的药物之一[190] ,老年糖尿病患者如存在体位性低血压可考虑应用。
(三)糖尿病痛性神经病变
糖尿病神经病变可通过多种致病机制导致神经病理性疼痛。神经痛的典型表现为烧灼痛、针刺痛或枪击样(电休克)痛,伴有感觉异常,多种症状可同时出现,夜间加重为其特点。神经痛干扰日常生活,严重影响生活质量,甚至会造成残疾和精神疾病。应注重睡眠和情绪障碍的评估和治疗。美国神经病学学会的最新研究表明,加巴喷丁类药物、5‑羟色胺‑去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂(serotonin‑norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor,SNRI)、钠 通 道 阻 滞 剂 和 三 环 类 抗 抑 郁 药(tricyclic antidepressant, TCA)都可用于治疗糖尿病周围神经病变所致疼痛[191] 。头对头试验表明,加巴喷丁类药物、SNRI和TCA在治疗DPN疼痛方面具有等效性,且联合治疗优于单药治疗[192]。由于TCA药物的不良反应较多,在老年糖尿病患者中使用应关注。
四、下肢动脉病变和糖尿病足

下肢动脉病变是 一种外周动脉疾病(peripheral arterial disease,PAD),表现为下肢动脉的狭窄或闭塞。糖尿病患者下肢动脉病变通常是指下肢动脉粥样硬化性病变(lower extremity atherosclerotic disease,LEAD)。China DIALEAD 研究显示,我国50岁以上 T2DM中 LEAD的总患病率为 21.2升高[193 %,且患病率随着年龄、糖尿病病程增加而]。在患 LEAD 的 T2DM患者中,年龄与病变严重程度独立相关[194] 。LEAD患者的心肌梗死、脑卒中、冠心病导致的死亡风险均增加[195] ,LEAD 也是糖尿病足的主要危险因素之一。西洛他唑、沙格雷酯、己酮可可碱、前列腺素等血管扩张药物可改善下肢缺血症状,而对于内科治疗无效、严重间歇性跛行影响生活质量、皮肤出现溃疡或坏疽的LEAD 持功能状态和独立生活能力 患者可根据情况考虑施行血运重建术,以维。
糖尿病足是指糖尿病患者因下肢远端神经病变和血管病变导致的足部感染、溃疡,甚至深层组织破坏,是糖尿病最严重的慢性并发症之一,严重者可以导致截肢和死亡。糖尿病足与多种因素有关,其中最主要的是外周动脉病变和周围神经病变,此外还包括外伤、感染、足畸形导致的足部压力过高和关节活动受限等。中国糖尿病患者的足溃疡主要为神经缺血性溃疡,单纯神经性溃疡或夏科足畸形所致溃疡少见[196] 。老年糖尿病患者由于视力欠佳、行动不便、弯腰困难而难以自查或自我护理双脚,足部问题难以及早发现。因此,老年糖尿病患者糖尿病足的发生风险更高,老年糖尿病患者是我国糖尿病足的主要人群[197]。
糖尿病足强调“预防重于治疗”,在糖尿病足的预防中,应注意检查并消除患者糖尿病足的危险因素,教育患者及其家属,并积极寻求多学科合作。问诊和检查的内容:足溃疡病史,鞋具穿着是否合适,保护性感觉丧失与否,是否存在血管功能障碍(足背和胫后动脉搏动),有无足部畸形、胼胝或溃疡前病变等,及早识别并去除上述危险因素是预防糖尿病足溃疡的主要措施。糖尿病足相关知识的教育可降低糖尿病足溃疡的发生率[198] ,降低复发率。教育内容包括:建议患者定期检查双足,尤其是足趾间;定期洗脚并擦干足趾间;避免穿着过紧的袜子或鞋子;穿鞋前检查鞋内是否有异物等。
老年糖尿病患者更要关注足部护理[199] :(1)每天检查双脚,包括趾间,必要时由家属或护理人员帮助;(2)避免烫灼伤;(3)对于干燥的皮肤,可使用润滑油或乳霜,但不要在脚趾之间使用;(4)直接横剪指甲,棱角可用指甲锉修平;(5)不要使用化学药剂或膏药去除鸡眼和老茧;(6)穿鞋子之前检查鞋内有否异物;(7)避免赤脚行走;(8)医护人员定期检查患者的双脚;(9)如果发现足部皮肤起泡、割伤、刮伤或疮痛,患者需立即就诊。对于出现糖尿病足的患者 应积极对老年糖尿病患者足部情况进行评估,,应区分溃疡的病因(缺血型、神经型、神经‑缺血型)、坏疽的性质(湿性坏疽、干性坏疽),并进行糖尿病足分级(Wagner 分级、Texas 分级等)。我国糖尿病足以神经‑缺血型多见,应治疗神经病变、运动锻炼和重建下肢血流,进行患肢减压、局部清创,促进溃疡愈合,如糖尿病足合并感染,应积极抗感染。一旦出现以下情况,如皮肤颜色的急剧变化、局部疼痛加剧并有红肿等炎症表现、新发生的溃疡、原有的浅表溃疡恶化并累及软组织和(或)骨组织、播散性的蜂窝组织炎、全身感染征象、骨髓炎等,在积极内科治疗的同时,应寻求血管外科、骨科、创面外科等相关专科协助,必要时手术治疗。及时转诊或多学科协作诊治,有助于提高足溃疡的愈合率,降低截肢率[200] 。
未完待续……
国家老年医学中心 中华医学会老年医学分会
中国老年保健协会糖尿病专业委员会
通信作者:郭立新,北京医院内分泌科 国家老年医学中心 中国医学科学院老年医学研究院,北京 100730,Email:该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。;肖新华,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院
北京协和医院内分泌科,北京 100730,Email:该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
本指南由《中华糖尿病杂志》《中华老年医学杂志》和《Aging Medicine》于 2024年 2月同步发表
【摘要】 随着我国老龄化的加剧,老年糖尿病的患病率明显增高,其规范化管理对改善老年糖尿病患者的临床结局至关重要。2021年国家老年医学中心、中华医学会老年医学分会以及中国老年保健协会糖尿病专业委员会组织专家撰写了我国首部老年糖尿病指南,即《中国老年糖尿病诊疗指南(2021年版)》,强调老年糖尿病患者存在高度异质性,需要综合评估,采取分层和个体化的管理策略,首次提出针对老年糖尿病患者的“简约治疗理念”和“去强化治疗策略”。这版指南为临床医师提供了实用的、可操作的临床指导,对我国老年糖尿病患者全方位、全周期的规范化综合管理起到了极大的推动作用,同时也推动了我国老年糖尿病及相关领域的临床和基础研究的广泛开展。指南发布近三年来,国内外老年糖尿病及相关领域的循证医学证据进一步积累,新的治疗理念、新型药物及治疗技术不断涌现,指南编委会及时对第一版指南进行了更新,对老年糖尿病的血糖管理路径进行了进一步细化和优化,编写了《中国老年糖尿病诊疗指南(2024年版)》,以期继续助力中国老年糖尿病患者的规范化管理及临床结局的改善。
【关键词】 糖尿病; 老年人; 指南; 治疗路径
Guideline for the management of diabetes mellitus in the elderly in China (2024 edition)
National Center of Gerontology, Chinese Society of Geriatrics, Diabetes Professional Committee of Chinese Aging Well Association
Corresponding authors: Guo Lixin, Department of Endocrinology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China, Email: glx1218@163. com; Xiao Xinhua, Department of Endocrinology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China, Email: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
目录
前言 ……………………………………………………… 148
编写说明 ………………………………………………… 148
第一章 老年糖尿病及其并发症的流行病学 ………… 149
第二章 老年糖尿病的诊断、分型及特点 …………… 149
第三章 老年糖尿病的三级预防 ……………………… 150
第四章 老年糖尿病患者的健康状态综合评估 ……… 150
第五章 老年糖尿病患者的健康教育 ………………… 151
第六章 老年糖尿病患者的血糖控制目标 …………… 152
第七章 老年糖尿病患者的生活方式干预 …………… 152
第八章 老年2型糖尿病患者的降糖药物及治疗路径……………………………………………… 154
第九章 老年糖尿病合并动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病或危险因素的综合管理 ……………………… 159
第十章 老年糖尿病慢性并发症的筛查与处理 ……… 162
第十一章 老年糖尿病的急性并发症 ………………… 166
第十二章 老年糖尿病的共患疾病 …………………… 167
第十三章 老年糖尿病的多重用药 …………………… 171
第十四章 老年糖尿病的特殊情况 …………………… 172
第十五章 老年1型糖尿病及相关问题 ……………… 174
第十六章 糖尿病管理相关技术 ……………………… 174
第十七章 老年糖尿病与中医药学 …………………… 176
附录 ……………………………………………………… 177
庄惠人1 王文静2 俞海萍2 尤永梅1 顾英杰1 姚佳丽1
1 同济大学附属东方医院伤口门诊,上海 201123;
2 同济大学附属东方医院护理部,上海 201123
通信作者:王文静,Email:该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
【摘要】 目的 检索糖尿病高危足患者自我管理临床实践的相关指南和专家共识,并对高质量指南和专家共识推荐意见的内容进行分析,为构建糖尿病高危足患者自我管理的指导方案提供借鉴。方法 计算机检索数据库、指南网和相关专业网站中的糖尿病高危足患者自我管理临床实践指南和专家共识,检索时限为2012至1月1日至2022年6月5日。由2名研究者对纳入文献进行质量评价,证据提取与整合,邀请专家对总结的证据进行评价。
结果 根据文献质量评价情况,共纳入12篇指南(A级10篇、B级2篇)和3篇专家共识(专家讨论决定),确定8个主题,分别为定期随访、自我评估、足部及减压管理、运动管理、营养管理、指标管理、心理管理、健康教育,共计28条推荐意见,其中A级推荐23条,B级推荐5条。
结论 本研究纳入指南和专家共识的质量较高,总结所得证据推荐等级亦较高,可为临床医护人员构建及指导糖尿病高危足患者自我管理临床实践提供参考及依据。
【关键词】 糖尿病足; 自我管理; 临床实践; 质量评价; 循证护理
基金项目:上海市护理学会2021年度学会级立项课题(2021MS-B08);上海市浦东新区卫生健康委员会卫生科技项目(PW2021A-17);同济大学医学院“护理学院(筹)学科建设三年行动计划”项目(JS2210328)
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn211501-20220822-02663
Quality evaluation and content analysis of clinical practice guidelines and expert consensus on self-management of patients with high-risk foot diabetes
Zhuang Huiren1 , Wang Wenjing2 , Yu Haiping2 , You Yongmei1 , Gu Yingjie1 , Yao Jiali1
1 Department of Wound Clinic, Oriental Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University, Shanghai 201123, China;
2 Department of Nursing, Oriental Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University, Shanghai 201123, China
Corresponding author: Wang Wenjing, Email: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
[Abstract]
Objective
To retrieve the relevant guidelines and expert consensus on selfmanagement of patients with high-risk foot diabetes, and analyze the content of high-quality guidelines and expert consensus recommendations, so as to provide a reference for the construction of a guidance program for self- management of patients with high- risk foot diabetes.
Methods
Computer- retrieved clinical practice guidelines and expert consensus for self-management of patients with high-risk foot for diabetes from databases, guideline networks, and related professional websites. The search period was from January 1, 2012 to June 5, 2022. The quality of the included literature was evaluated and the evidence was extracted and integrated by 2 researchers. Experts were invited to evaluate the summarized evidence.
Results
According to the quality of literature, a total of 12 guidelines (10 at level A and 2 at level B) and 3 expert consensus (expert discussion and decision) were included, and 8 themes were defined as regular follow- up, self- assessment, foot and decompression management, exercise management, nutrition management, indicator management, psychological management, and health education, a total of 28 recommendations. Among them, there were 23 A-level recommendations and 5 B-level recommendations.
Conclusions
The quality of the guidelines and expert consensus included in this study is high, the recommended level of the summarized evidence is high. This study provides the reference and basis for the clinical staff to construct and guide the clinical practice of self- management of high-risk diabetic foot
[Key words]
Diabetic foot; Self management; Clinical practice; Quality evaluation; Evidence-based nursing
Fund program: 2021 Academic Level Project of Shanghai Nursing Society (2021MS-B08); Shanghai Pudong New Area Health Commission Health Science and Technology Project (PW2021A- 17); Tongji University "Third Year Action Plan for Discipline Construction of School of Nursing" (JS2210328)
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn211501-20220822-02663



