文献精选
张静彦,郭 璇,段 渠
成都中医药大学附属医院,医学美容科,四川 成都
收稿日期:2023年9月8日;录用日期:2023年10月11日;发布日期:2023年10月23日
摘 要
黄芪作为中医常用的补气要药,在诸多损美性疾病中应用广泛,其对于治疗黄褐斑有着显著的疗效。现代药理学研究表明黄芪通过防护紫外线损伤、抗氧化、改善皮肤微循环等作用有效减少色素沉着。传统医学表明黄芪内服健脾补气、外用美白祛斑以达到治疗黄褐斑的作用。为进一步开发使用黄芪,文章对黄芪在黄褐斑中的应用及相关作用机制进行了综述。
关键词
黄芪,黄褐斑,色素增加性疾病,中医美容,中药应用
Overview of Mechanism and Application of Astragalus in Treating Melasma
Jingyan Zhang, Xuan Guo, Qu Duan
Department of Medical Cosmetology, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,
Chengdu Sichuan
Received: Sep. 8 th, 2023; accepted: Oct. 11th, 2023; published: Oct. 23 rd, 2023
Abstract
Astragalus is commonly used as an essential medicine for supplementing qi in Chinese medicine. It is widely used in many aesthetic diseases and has a remarkable effect on the treatment of melasma. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that astragalus effectively reduces pigmentation by protecting against ultraviolet damage, antioxidant, improving skin microcirculation and other effects. Traditional medicine shows that astragalus can achieve the effect of treating melasma by invigorating spleen, invigorating qi, whitening and removing freckles. In order to further develop the use of astragalus. This article reviewed the application of astragalus in melasma and the related mechanism of action.
文章引用: 张静彦, 郭璇, 段渠. 黄芪治疗黄褐斑的作用机制及应用概述[J]. 中医学, 2023, 12(10): 3055-3059.
DOI: 10.12677/tcm.2023.1210459
Keywords
Astragalus, Chloasma, Hyperpigmented Disorders, Traditional Chinese Medical Cosmetology, Application of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Copyright © 2023 by author(s) and Hans Publishers Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY 4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Standards for the development and methodology of the 2023 International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot
Guidelines :Part of the 2023 IWGDF Guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetes-related foot desease
Sicco A. Bus1,2 ,Matilde Monteiro-Soares3.4.5, Fran Game', Jaap J. van Netten1.2, Jan Apelqvist7 ,Robert Fitidge8 ,
Eric Sennville,Nicolaas C. Schaper0 ,on behalf of the IWGDF Editorial Board
1. Amsterdam UMC, University of Amsterdam, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,Amsterdam, the Netherlands;
2.Amsterdam Movement Sciences,program Rehabilitation & Development , Amsterdam, the Netherlands;
3. Higher School of Health of the Portuguese Red Cross, Lisbon, Portugal;
4. Department of Community Medicine, Information and Health Decision Sciences ( MEDCIDS),Faculty of Medicine, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal;
5. RISE@ CINTESIS, Faculty of Medicine, Oporto University, Porto, Portugal;
6. Department of Diabetes and Endocrinology ,University Hospitals of Derby and Burton NHS Foundation Trust, Derby, UK;
7. Department of Endocrinology, University Hospital of Malmo, Sweden;
8. Discipline of Surgery, The University of Adelaide and Vascular and Endovascular Service, Royal Adelaide Hospital, Australia;
9. Department of Infectious Diseases ,Gustave Dron Hospital, Tourcoing, France;
10. Division of Endocrinology, MUMC+,CARIM and CAPHRI Institute ,Maastricht, the Netherlands.
朱 虹1 何 洁1 (译) 刘 芳2 (审校)
( 1 . 温州医科大学附属第一医院内分泌科, 浙江 温州 325000;2 . 上海交通大学医学院附属第一医院内分泌代谢科, 上海 200080)
【摘要】 糖尿病相关的足病是造成糖尿病患者经济负担和增加社会成本的主要原因之一。 本指南以主要目标为导向,以循证医学为依据,且在全球得到合理实施。 践行国际糖尿病相关的足病指南对于减轻患者经济负担和社会成本有着重要影响。
国际糖尿病足工作组(IWGDF)从 1999 年起开始发布并随后更新国际指南。 2023 年更新版指南相关推荐均基于推荐、评估、发展和评价分级(GRADE)系统,包括制定相关临床问题和重要结局,完成系统的文献系统综述和荟萃分析,完成评判表汇总,并且给予具体、明确、操作性强的推荐以及理论依据。
本文阐述了《国际糖尿病足工作组:糖尿病相关的足病预防和管理指南(2023 版)》(以下简称为指南)的制定过程。指南由 7 个部分组成,包括预防、糖尿病相关的足溃疡分类、减压、周围动脉病变、感染、创面愈合干预以及活动性夏科神经骨关节病,分别由 7 个独立的国际专家工作组编写。 IWGDF 编辑委员会对 7 个章节进行了整合和简化,形成 IWGDF实践指南。 指南中的每条推荐均经过 IWGDF 编辑委员会成员和相关领域的独立的国际专家审阅通过。 本文是 IWGDF指南的制定和方法学。
我们相信,医务人员、公共卫生机构和政策制定者采用和实施 2023 年 IWGDF 指南,将会改善糖尿病相关的足病的预防和管理水平,从而减少全球该疾病患者和减轻该疾病引起的全球社会负担。
【关键词】 指南; 糖尿病; 糖尿病相关的足病; 方法学; 国际糖尿病足工作组
www.iwgdfguidelines.org
中图分类号:R587.2;R-01
文献标识码:C
Luca Busetto, Dror Dicker, Gema Frühbeck, Jason C. G. Halford, Paolo Sbraccia, Volkan Yumuk & Gijs H. Goossens
The European Association for the Study of Obesity presents a new framework for the diagnosis, staging and management of obesity in adults to better align with the concept of obesity as an adiposity-based chronic disease.
Obesity is a multifactorial, chronic, relapsing, non-communicable disease marked by an abnormal and/or excessive accumulation of body fat that presents a risk to health. It is well established that obesity acts as a gateway to a range of other non-communicable and communicable diseases1–3 .
Despite this wide recognition of obesity as a chronic disease, the clinical recommendations that guide the diagnosis of obesity and its management have not been aligned sufficiently with the clinical processes normally adopted for other chronic diseases. In many settings, the diagnosis of obesity is still based solely on body mass index (BMI) cut-off values, and does not reflect the role of adipose tissue distribution and function in the severity of the disease1 . Moreover, the indications for using the different therapeutic approaches now available for obesity management remain mostly based on anthropometric measurements, rather than on a more complete clinical evaluation of the individual4 . This is in sharp contrast with other chronic diseases, for which clear therapeutic indications are described, targets are set, and the choice of the type and intensity of treatment is based on the probability of reaching the treatment target, with adequate and prompt treatment intensification when the target is not reached.
To stimulate the development and implementation of clinical guidelines for obesity that are more aligned with those already in place for other chronic diseases, the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) initiated and conducted a consensus process to propose a new framework for the diagnosis, staging and management of obesity in adults.
Consensus process
We performed a modified Delphi study5,6 to identify a set of statements that can aid in the diagnosis, staging and management of obesity according to a framework that is more adherent to the concept of obesity as an adiposity-based chronic disease (ABCD)1 . A steering committee identified by the EASO, consisting of the authors of this paper, discussed and prepared an initial set of statements used for a voting process by a group of experts. Voting was performed on a five-point scale, as follows: (1) strongly disagree; (2) disagree; (3) neither agree nor disagree; (4) agree; and (5) strongly agree. In each round of voting, experts were also asked to provide comments to explain their voting score, and responses were anonymized. The steering committee evaluated the voting and comments received at each round and generated a modified set of statements for the subsequent round of voting. Consensus was defined as ≥75% of expert agreement on a statement (score ≥4).
The steering committee retained responsibility for the selection of experts involved in the process. Selection was based on international reputation and known expertise in obesity science and management.
In total, 29 experts were contacted, and all agreed to participate in the present study. Most of the experts belong to the endocrinology, nutrition or internal medicine fields (72%), but the group also included five bariatric surgeons, two primary care physicians and one expert on patient advocacy. A standard conflict of interest form was completed by each participant before the start of the Delphi process. This study was performed by the EASO without any external funding, and approval by the ethics committee was not required.
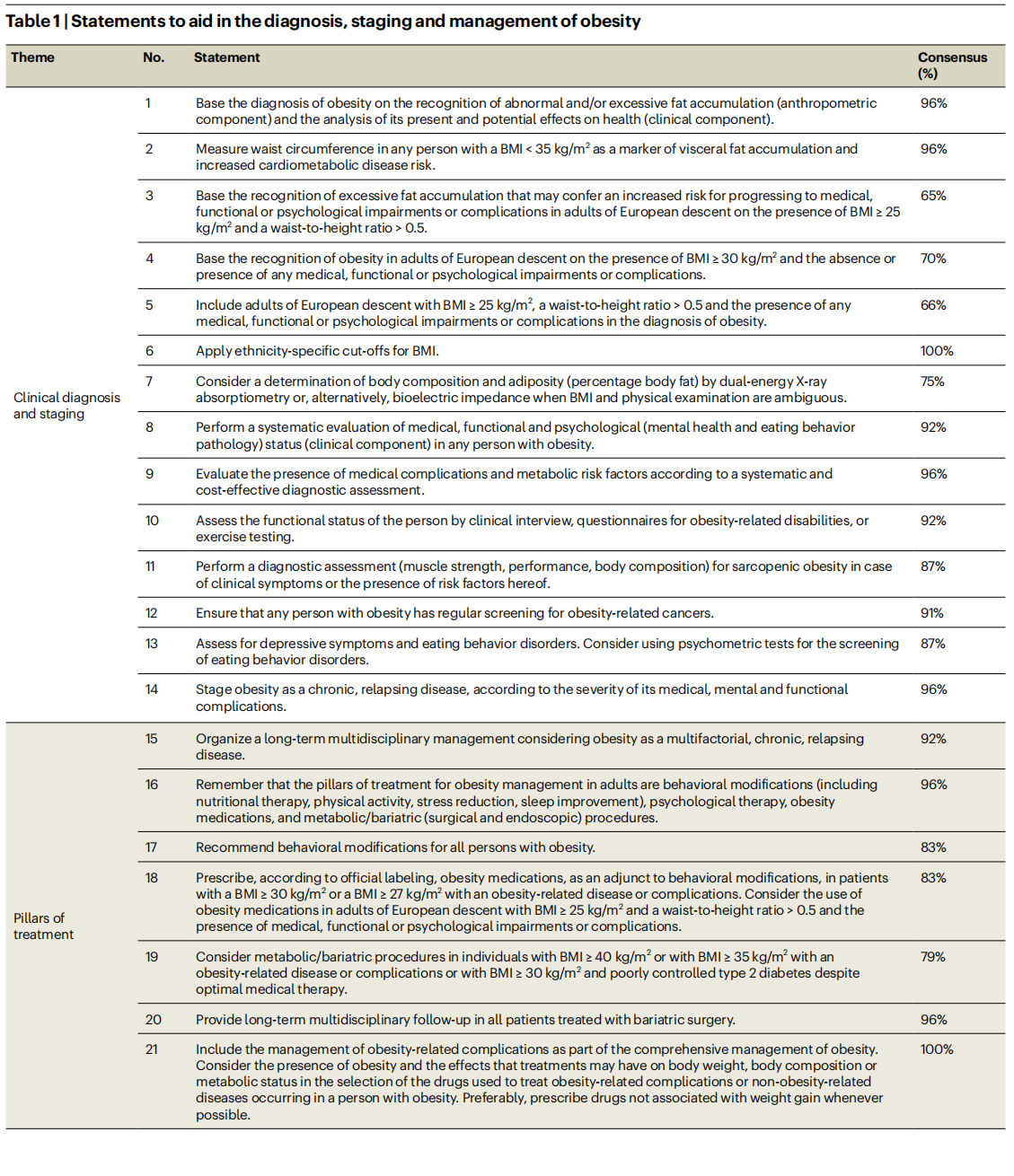
The study comprised three Delphi rounds. In the first round, 25 experts (86%) voted and commented on 30 original statements that were prepared by the steering committee. A total of 21 statements (70%) received consensus. The steering committee evaluated voting and comments and generated a second set of 28 statements submitted for a second Delphi round. In the second round, 24 experts (83%) voted and commented on the statements. A total of 24 statements (86%) received consensus. The steering committee discussed the comments received for the four non-consented statements, reconsidered the formulations of these statements, and submitted the four revised statements for the final Delphi round. In the third round, 24 experts (83%) voted and provided final comments related to the four revised statements. One of these four statements (statement 12) reached full consensus, whereas most experts approved the other three revised statements (statements 3–5), with only a few experts providing a score <3 (that is, strongly disagree or disagree). The steering committee performed a final revision and decided to approve a list of 28 statements, covering clinical diagnosis and staging of obesity, pillars of treatment, therapeutic targets, and initial level of intervention. The final list of statements and final percentages of approval by the experts is shown in Table 1. A flowchart of the diagnostic and therapeutic pathways resulting from the statements is presented in Fig. 1.
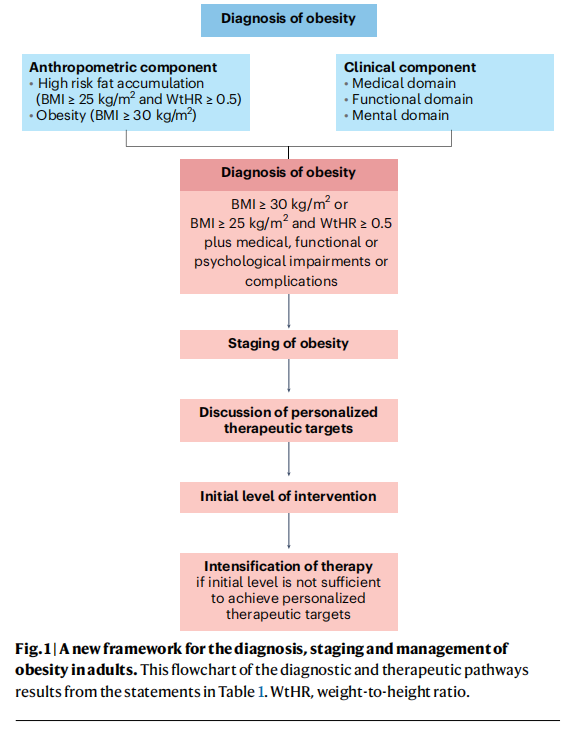

A chronic progressive disease
The recognition of obesity as a complex chronic non-communicable disease should inform the development of evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and management of obesity. We anticipate that, in conjunction with other ongoing initiatives7 , this Delphi process will contribute to improving obesity management in adults living with obesity.
Based on current clinical evidence, the diagnosis of obesity should not be based solely on the presence of an abnormal and/or excessive fat accumulation (anthropometric component). The diagnosis of obesity should instead include a careful analysis of the present and potential effects that dysfunctional and/or excessive fat accumulation may have on health (clinical component) (statement 1). This statement aligns with what has been suggested by other recent guidelines on obesity management8,9 . Moreover, this statement fully adheres to the concept that obesity should be considered a chronic progressive disease process that may transit from a relatively asymptomatic state to a phase in which abnormal and/or excessive fat accumulation is accompanied by health impairments, and finally to a life-threatening or disabling condition10.
Abdominal fat accumulation
An important novelty of our framework regards the anthropometric component of the diagnosis. The basis for this change is the recognition that BMI alone is insufficient as a diagnostic criterion, and that body fat distribution has a substantial effect on health. More specifically, the accumulation of abdominal fat is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiometabolic complications and is a stronger determinant of disease development than BMI, even in individuals with a BMI level below the standard cut-off values for obesity diagnosis11. This is reflected by two important statements. First, we make explicit that abdominal (visceral) fat accumulation is an important risk factor for health deterioration, also in people with low BMI and still free of overt clinical manifestations (statement 3). Second, the new framework includes people with lower BMI (≥25–30kg/m2 ) but increased abdominal fat accumulation and the presence of any medical, functional or psychological impairments of complications in the definition of obesity, hence reducing the risk of undertreatment in this particular group of patients in comparison to the current BMI-based definition of obesity (statement 4). The choice of introducing waist-to-height ratio, instead of waist circumference, in the diagnostic process is due to its superiority as a cardiometabolic disease risk marker12.
Diagnostics and staging
The clinical component of the diagnosis should include a systematic evaluation of medical, functional and psychological (such as mental health and eating behavior pathology) impairments in any person with obesity, as also suggested in other guidelines8,9 . A detailed description of the clinical aspects and methodologies that need to be included in this systemic clinical evaluation was beyond the scope of this exercise. For the medical evaluation (statement 9), several documents are available to provide guidance4,8 . For the functional and psychological evaluation, examination may be performed using an array of methods, ranging from easy-to-perform tests that are applicable in the primary care setting to more sophisticated tests, which may be reserved for specialized centers (statements 10 and 13). Considering the emerging problem of obesity in older individuals, statement 11 was included to emphasize the importance of performing a diagnostic assessment (muscle strength, performance and body composition) for sarcopenic obesity13. Finally, considering the strong association between obesity and several types of cancer, a statement calling for regular screening for obesity-related cancers in any person with obesity was included (statement 12).
Clinical staging processes are frequently used to evaluate and describe an individual’s health status and the progression of chronic diseases. Clinical staging usually expresses the severity of a disease in a simplified, condensed and standardized way. This has prognostic implications, and it may guide or mandate therapeutic interventions. In our Delphi process, the experts agreed on the importance of staging obesity as a chronic, relapsing disease, according to the severity of its clinical manifestations and complications (statement 14), as proposed by previous guidelines9 .
Obesity management
Considering the pillars of treatment of people with obesity (statements 15–21), our recommendations substantially adhere to current available guidelines4,8,9 . Behavioral modifications, including nutritional therapy, physical activity, stress reduction and sleep improvement, were agreed as main cornerstones of obesity management, with the possible addition of psychological therapy, obesity medications and metabolic or bariatric (surgical and endoscopic) procedures. For the latter two options, the steering committee discussed the fact that current guidelines are based on clinical evidence derived from clinical trials, in which inclusion criteria were mostly based on anthropometric cut-off values rather than on a complete clinical evaluation4,8,9,14. In current practice, the strict application of these evidence-based criteria precludes the use of obesity medications or metabolic/bariatric procedures in patients with a substantial burden of obesity disease, but low BMI values. Therefore, members of the steering committee proposed, and experts subsequently agreed (79%), that, in particular, the use of obesity medications should be considered in patients with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 and a waist-to-height ratio > 0.5 and the presence of medical, functional or psychological impairments or complications, independently from current BMI cut-off values (statement 18). This statement may also be seen as a call to pharmacological companies and regulatory authorities to use inclusion criteria that are more adherent to the clinical staging of obesity and less to traditional BMI cut-offs when designing future clinical trials with obesity medications15.
Full agreement among the experts was reached for the statement that the management of obesity should move beyond weight loss alone, and should include the prevention, resolution or improvement of obesity-related complications, a better quality of life and mental wellbeing, and improvement of physical and social functioning and fitness (statement 22). This statement will move obesity management closer to the management of other non-communicable chronic diseases, in which the goal is not represented by short-term intermediate outcomes, but by long-term health benefits. Defining long-term personalized therapeutic goals should inform the discussion with the patients from the beginning of the treatment, considering the stage and severity of the disease, the available therapeutic options and possible concomitant side effects and risks, patient preferences, individual drivers of obesity and possible barriers to treatment (statements 23 and 24). Emphasis on the need for a long-term or life-long comprehensive treatment plan rather than short-term body weight reduction is warranted.
The concept of obesity as a chronic disease and the discussion of therapeutic targets should also inform the choice of the initial level of intervention and eventual intensification of therapy (statements 26–28), avoiding the same repetitive and futile cycles of intervention that are not effective enough to achieve patient benefit, and preventing therapeutic inertia16.
This Delphi process represents the current vision of the EASO on the diagnosis, staging and management of obesity as a complex, relapsing, non-communicable chronic disease in adults. We anticipate that the recommendations outlined in this paper, in conjunction with other ongoing international initiatives7 , will contribute to improved obesity management strategies that are more consistent with treatment algorithms already applied for other non-communicable chronic diseases. Moreover, this framework may aid scientific advancements and the development of new clinical practice guidelines.
Luca Busetto1 , Dror Dicker2 , Gema Frühbeck 3 , Jason C. G. Halford4 , Paolo Sbraccia5 , Volkan Yumuk6 & Gijs H. Goossens 7
1 Department of Medicine, University of Padova, Padova, Italy.
2 Internal Medicine Department and Obesity Clinic, Hasharon Hospital-Rabin Medical Center, Petach-Tikva, Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel.
3 Department of Endocrinology and Nutrition, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, CIBEROBN, IdiSNA, Pamplona, Spain.
4 School of Psychology, University of Leeds, Leeds,UK.
5 Department of Systems Medicine, University of Rome Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy.
6 Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes, Department of Internal Medicine, Cerrahpasa Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa, Istanbul, Turkey.
7 Department of Human Biology, Institute of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism (NUTRIM), Maastricht University Medical Center⁺, Maastricht, The Netherlands.
e-mail: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
Published online: 05 July 2024
References
1. Fruhbeck, G. et al Obes. Facts12, 131-136 (2019).
2. Dicker, D. et al. Obes. Facts 13, 430- -438 (2020).
3. Burki, T. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.9, 418 (2021).
4. Yumuk, V. et aL Obes. Facts 8, 402- -424 (2015).
5. Clayton, M. J. Educ. Psychol. 17, 373- -386 (1997).
6. Hasson, F., Keeney, S. & McKenna, H. J. Adv. Nurs.32, 1008- 1015 (2000).
7. Rubino, F. et aL Lancet Diabetes EndocrinoLl. 11, 226- 228 (2023).
8. Garvey, W. T. et al Endocr. Pract. 22, 1-203 (2016).
9. Wharton, S. et aL CMAJ192, E875-E891 (2020).
10. Bray, G. A.,. Kim, K. K., Wilding, J P. H. & on behalf of World Obesity Federation. Obes. Rev. 18, 715-723 (2017).
11. Goossens, G. H. Obes. Facts 10, 207 -215 (2017).
12. Ashwell, M.. Gunn, P. & Gibson, S. Obes. Rev. 13, 275- -286 (2012).
13. Donini, L. M. et al. Obes. Facts.15, 321-335 (2022).
14. Di Lorenzo, N. et al Surg. Endosc.34, 2332- -2358 (2020).
15. Agarwal, A. A., Narayan, A. & Stanford, F. C. JAMA Intern. Med. 184, 341-342 (2024).
16. Busetto, L, Sbraccia, P. & Vettor, R. Eat Weight Disord. 27, 761-768 (2022).
List of experts
The Steering Commitee identifed by EASO for this project, consisting of the authors of this paper, takes full responsibility for the contents of this Comment. The below specialists participated in the voting process of the Delphi methodology, but not in interpretation of the results or writing of the Comment, and agreed to be mentioned here: M. Agarwal, R. Barazzoni, T. Comuzzie, M. De Luca, N. Di Lorenzo, D. Durrer-Schutz, T. Garvey, C. Hughes, L. Kaplan, C. LeRoux, J. Mechanick, N. Montano, Jean-M. Oppert, R. Peterli, K. Pietilainen, G. Prager, X. Ramos-Salas, D. Ryan, M. Ryden, A. Sharma, and E. van Rossum.
Competing interests
L.B. received personal funding from Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingetheim, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Bruno Farmaceutici as a member of advisory boards, and from Rythms Pharmaceuticals and Pronokal as a speaker. D.D. received personal funding from Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly as a member of advisory boards, and from Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly as a speaker. G.F. received payment of honoraria from Lilly and Novo Nordisk as a member of advisory boards, and payment of honoraria for lectures as member of the OPEN Spain Initiative. The University of Leeds received funding from Novo Nordisk for J.C.G.H.s participation in the ACTION-Teens study. PS. received payment of honoraria and consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lly, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim and Bruno
Farmaceutici as a member of advisory boards. V.Y. received personal funding from Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly as a member of advisory boards and from Novo Nordisk as a speaker. G.H.G. received research funding from the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes, the Dutch Diabetes Research Foundation and the Dutch Research Council (NWO).
This article is excerpted from the naturemedicine by Wound world.
中华医学会整形外科学分会女性雄激素性脱发诊断与治疗专家共识编写组 中国女医师协会整形美容专业委员会
通信作者:张菊芳,浙江大学医学院附属杭州市第一人民医院医学美容科,杭州
310006,Email: zhjuf@ vip.sina. com;吴文育,复旦大学附属华山医院皮肤科,上海200040,Email: wuwenyu@ huashan.org.cn
【摘要】 女性雄激素性脱发与男性雄激素性脱发在病因、诊断、治疗等方面均有所不同,但目前国内外缺乏针对女性雄激素性脱发的诊断与治疗共识。 为了统一女性雄激素性脱发诊断及治疗标准,我国多个学术组织的专家共同启动了女性雄激素性脱发诊断与治疗专家共识的制定。 该共识包括女性雄激素性脱发的命名、流行病学、发病机制、临床表现、诊断依据及鉴别诊断要点、脱发分级、诊断流程、治疗方法。 基于相关循证医学证据,将共识编写组专家意见汇总,形成推荐意见,为临床医生提供参考。
【关键词】 脱发; 女性雄激素性脱发; 诊断; 治疗; 专家共识
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金 ( 82173442, 82103759); 上海毛发医学工程技术研究中心(19DZ2250500);上海申康医院发展中心临床三年行动计划( SHDC2020CR2033B);上海市科学技术委员会西医引导类项目(19411962400);杭州市医学重点学科(OO20200044)
DOI:10




