文献精选



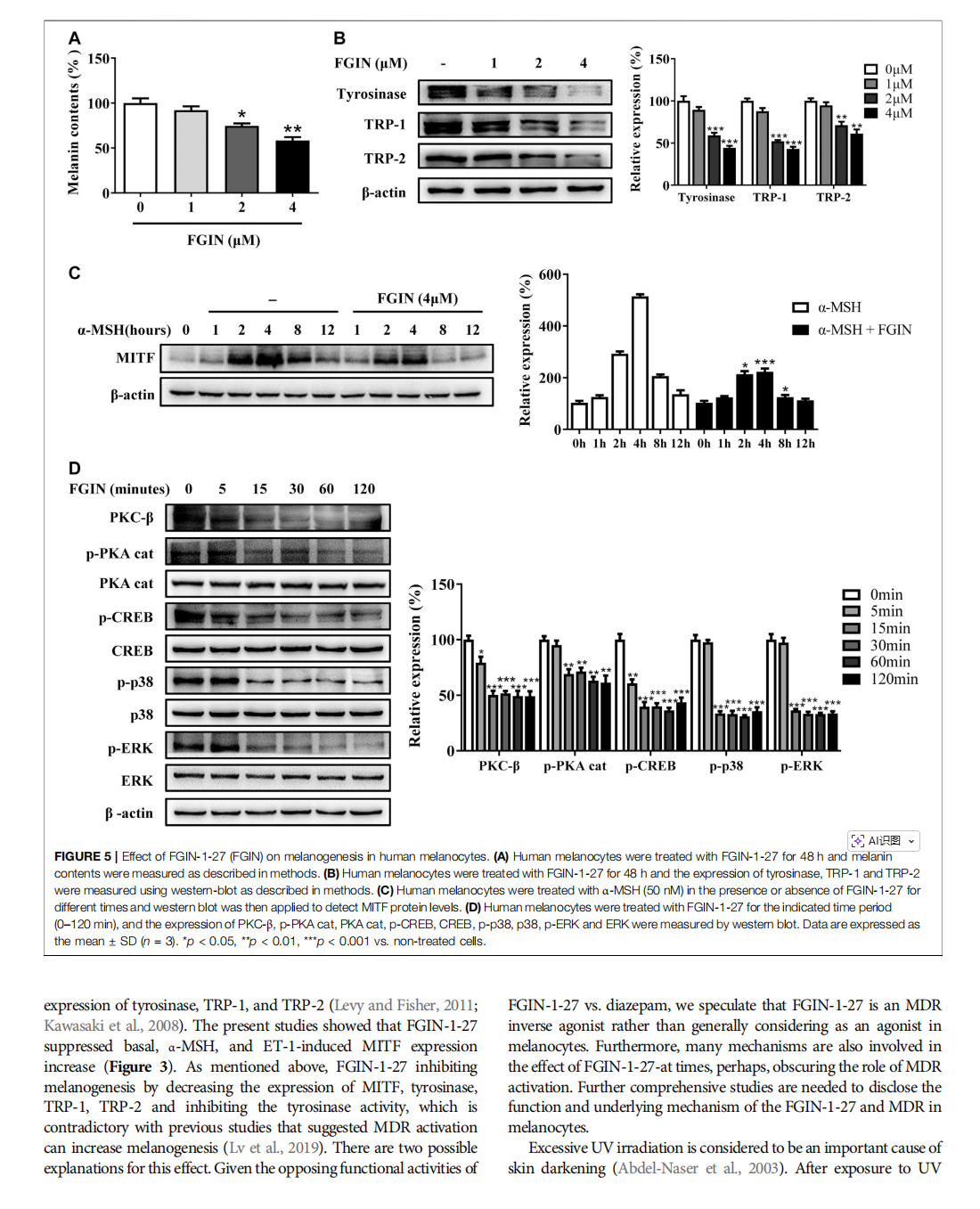
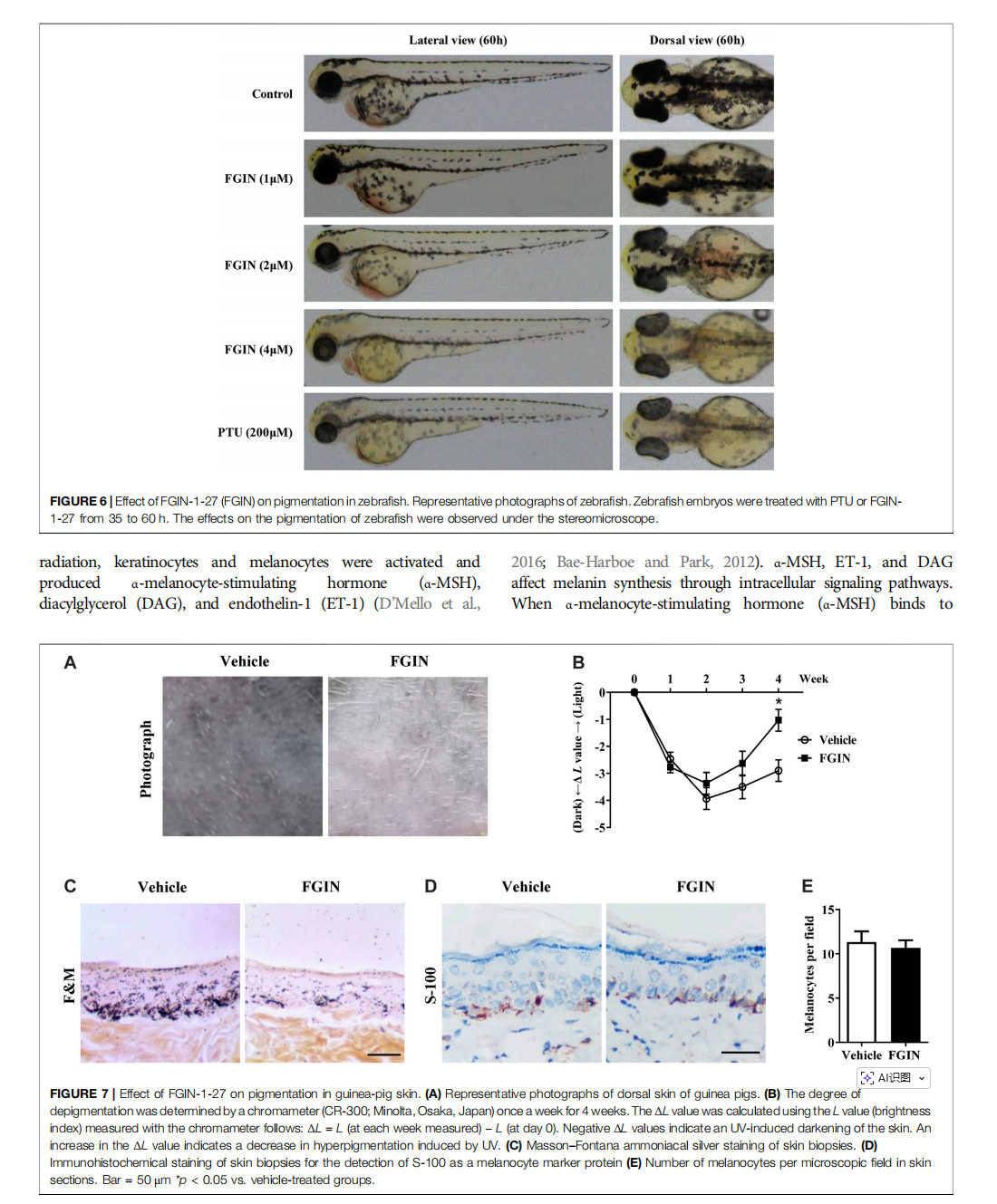


This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Pharmacology》 by Wound World



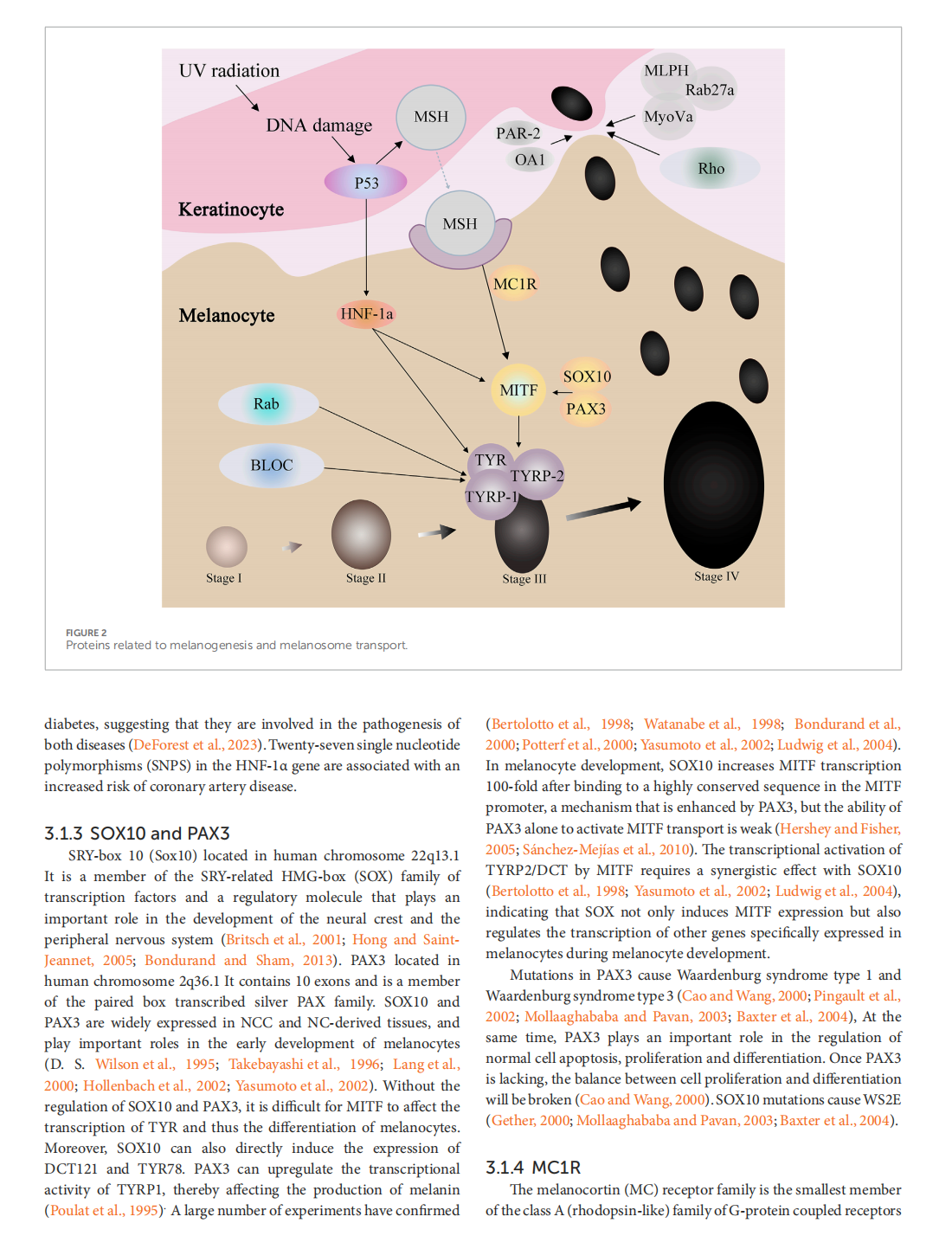



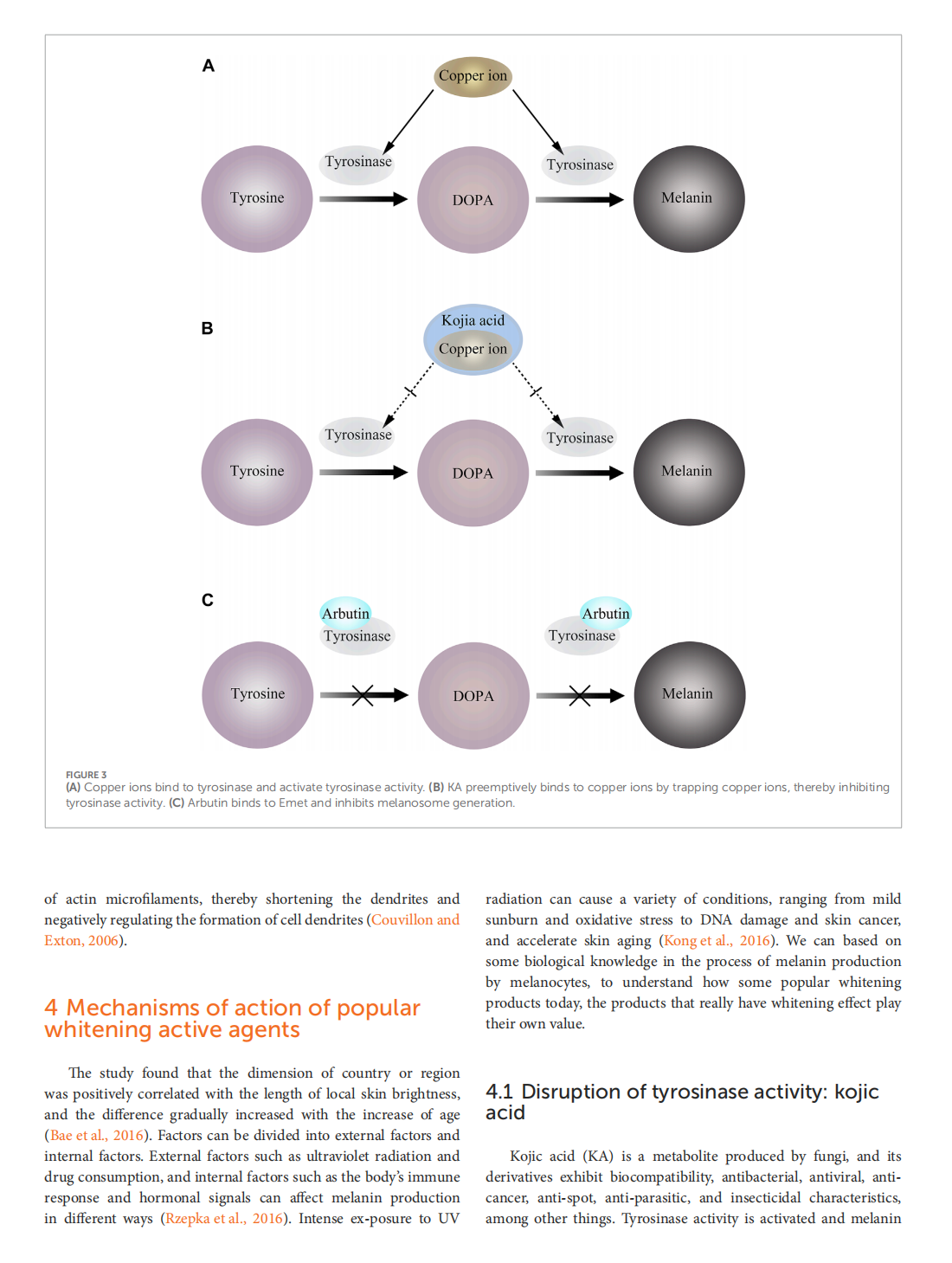
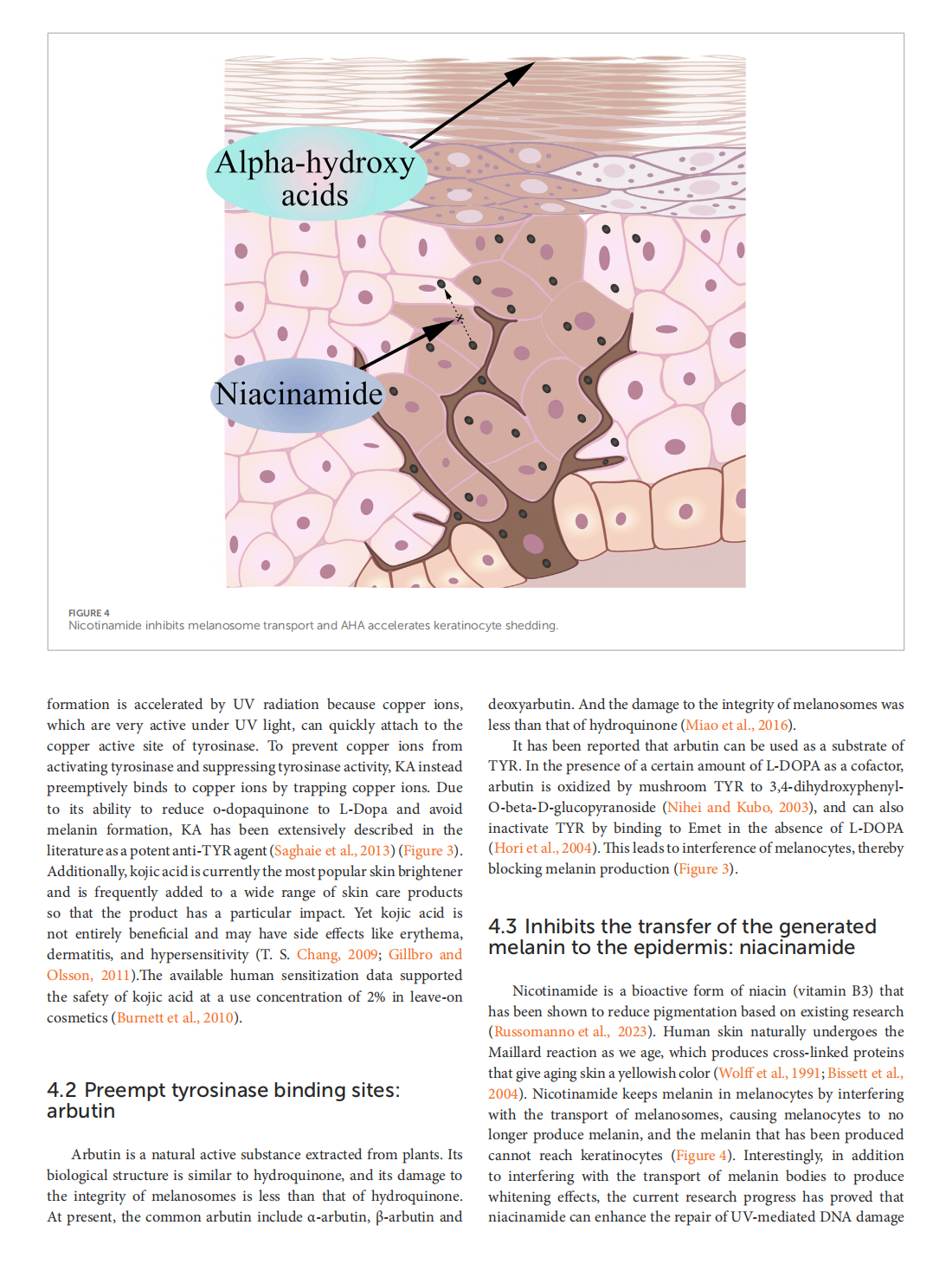






This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences》 by Wound World




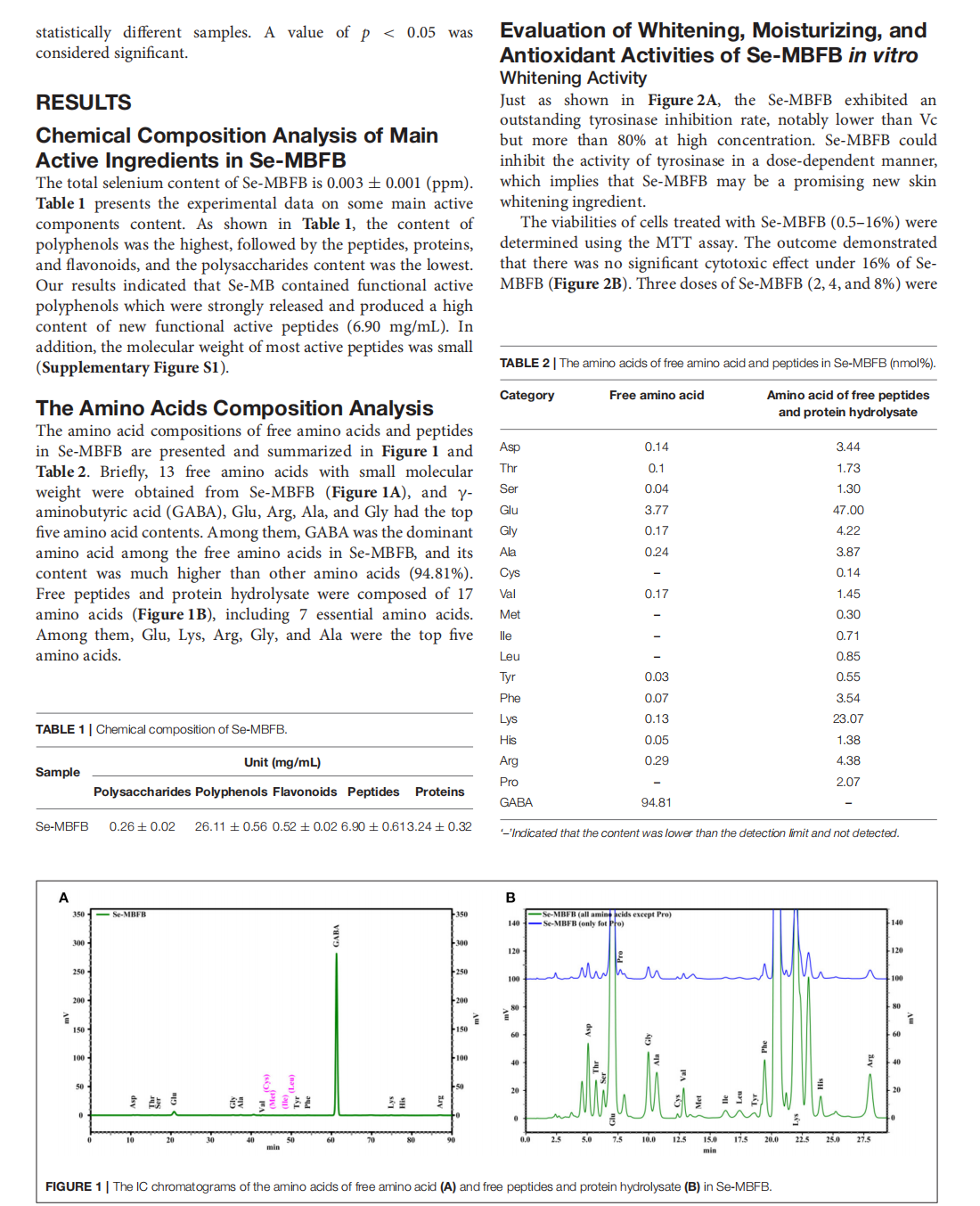
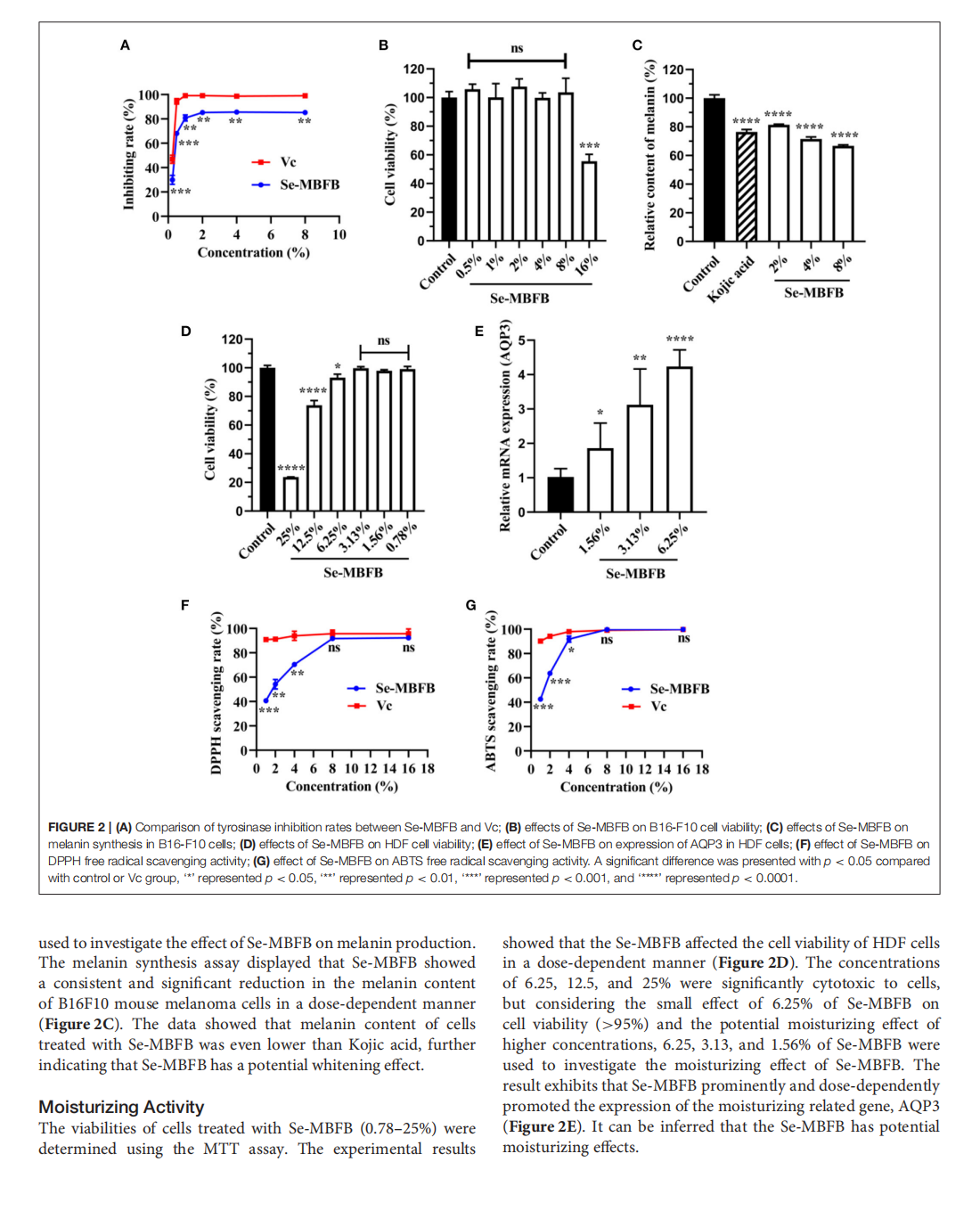

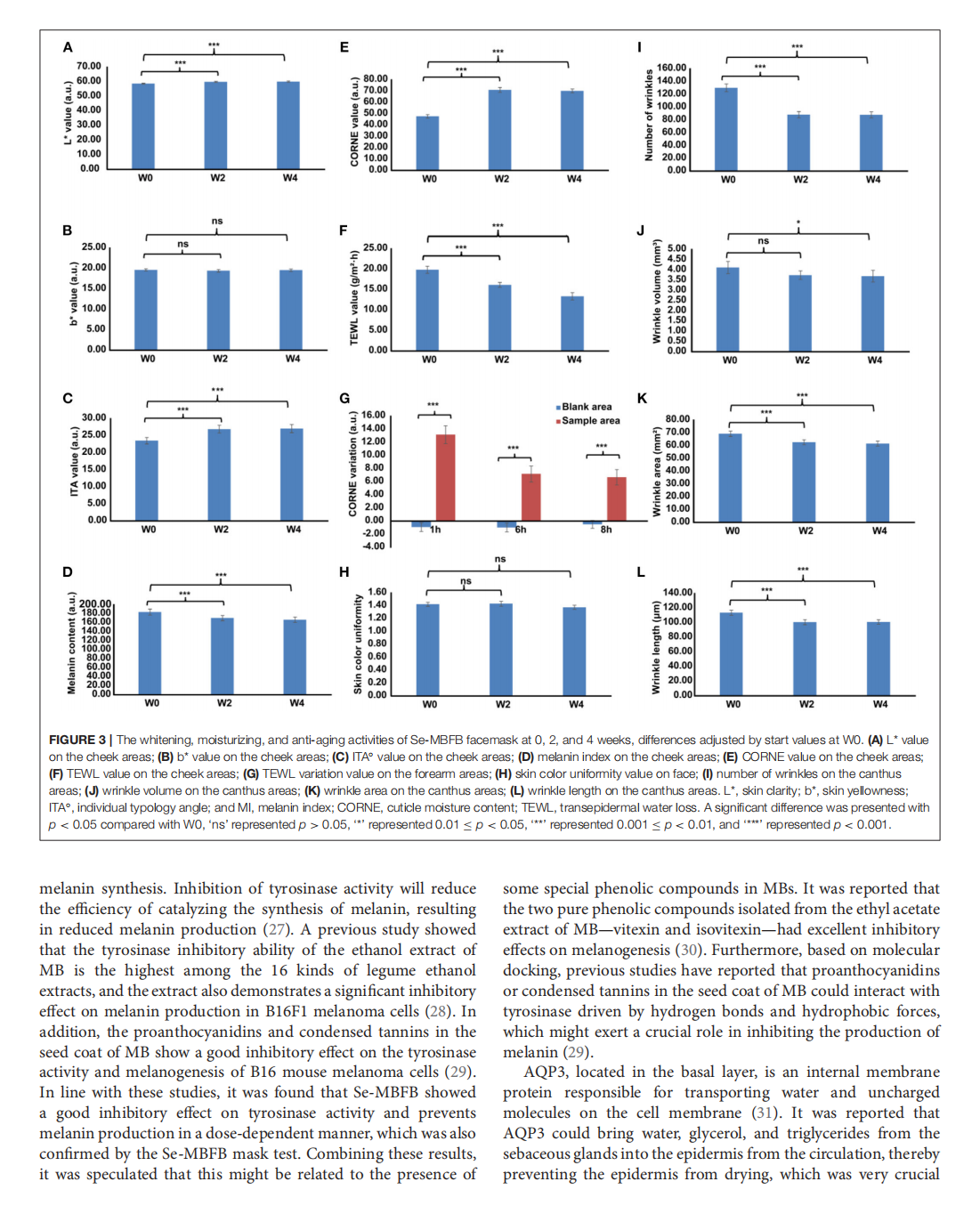
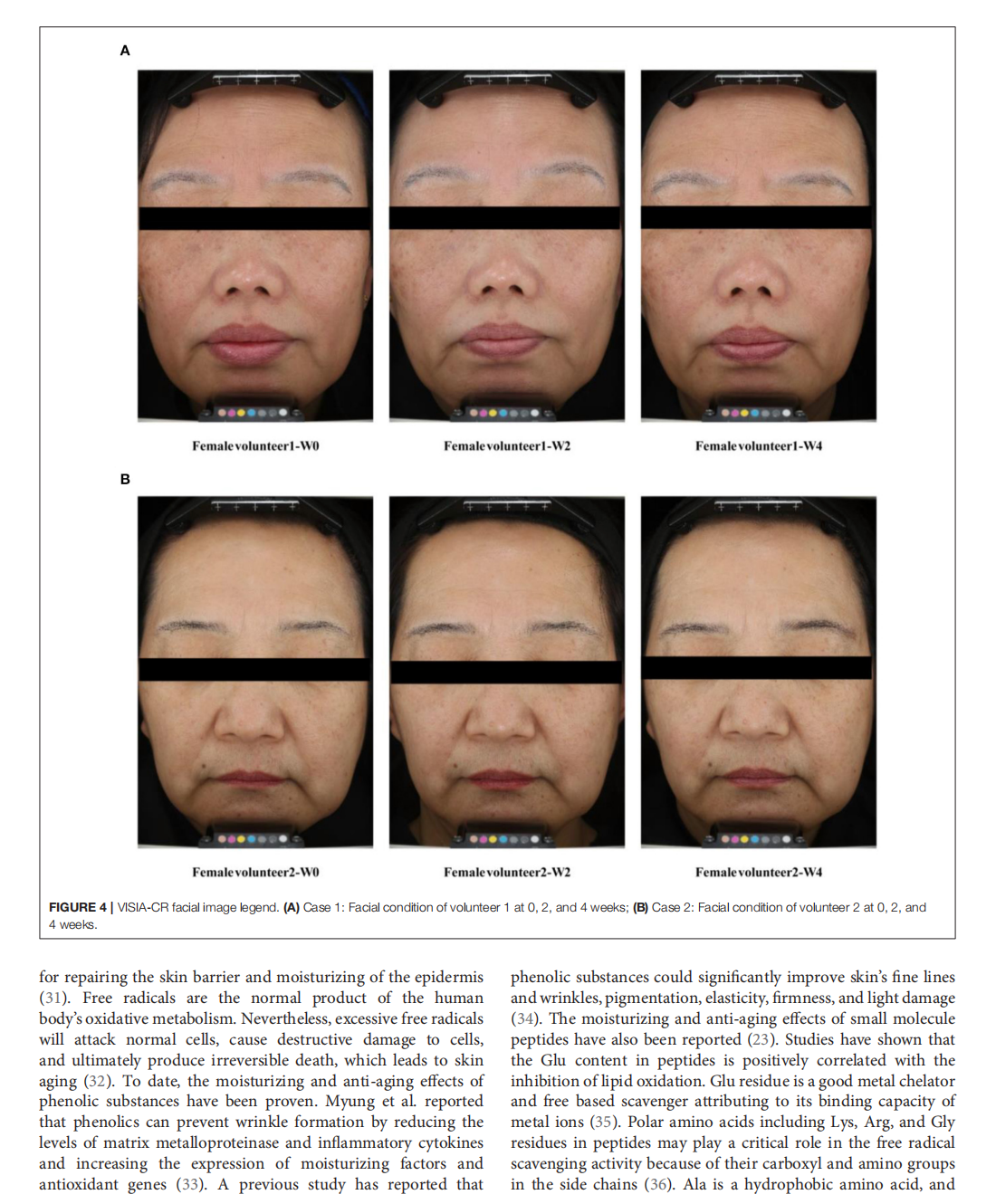
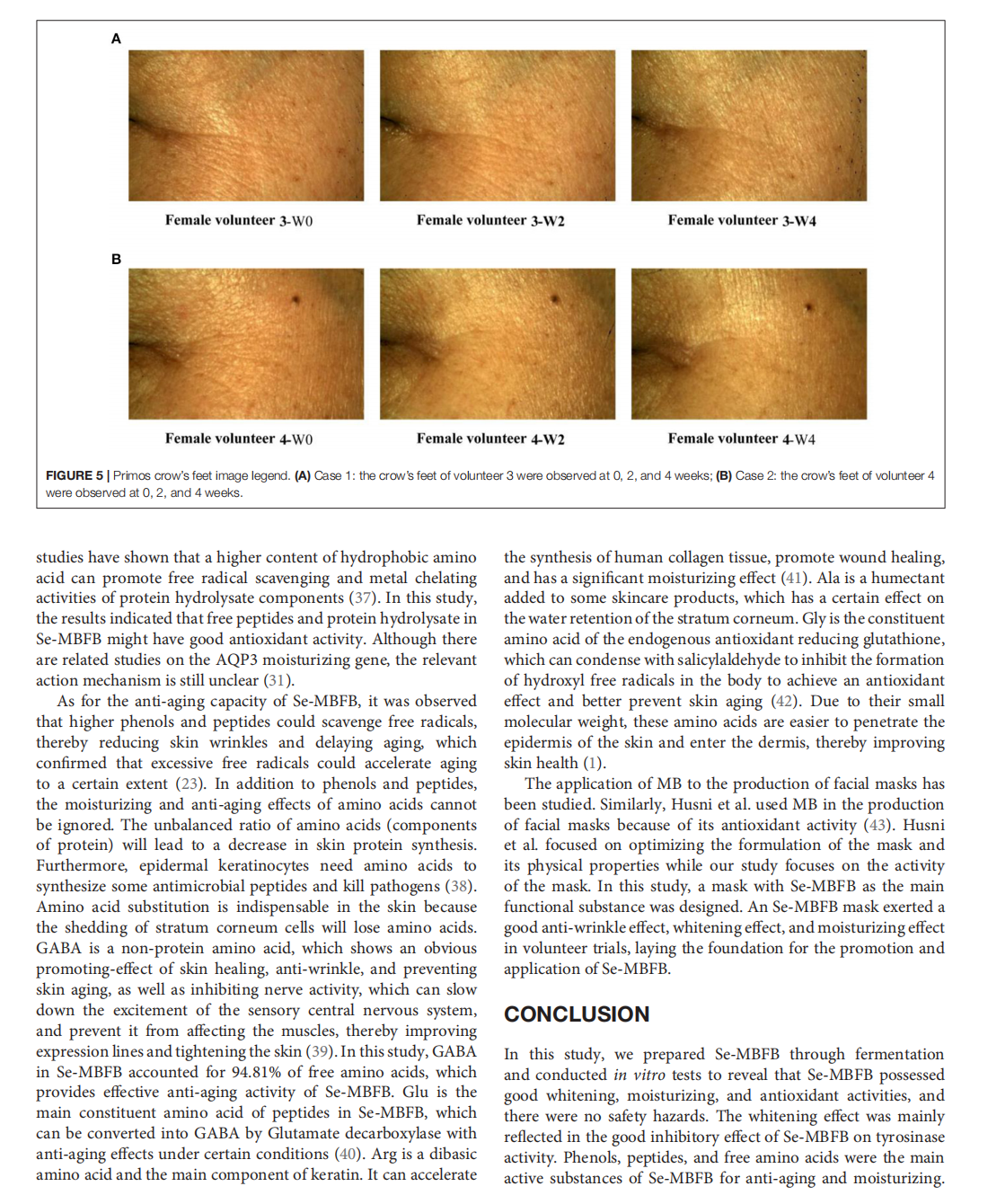

This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Nutrition》 by Wound World





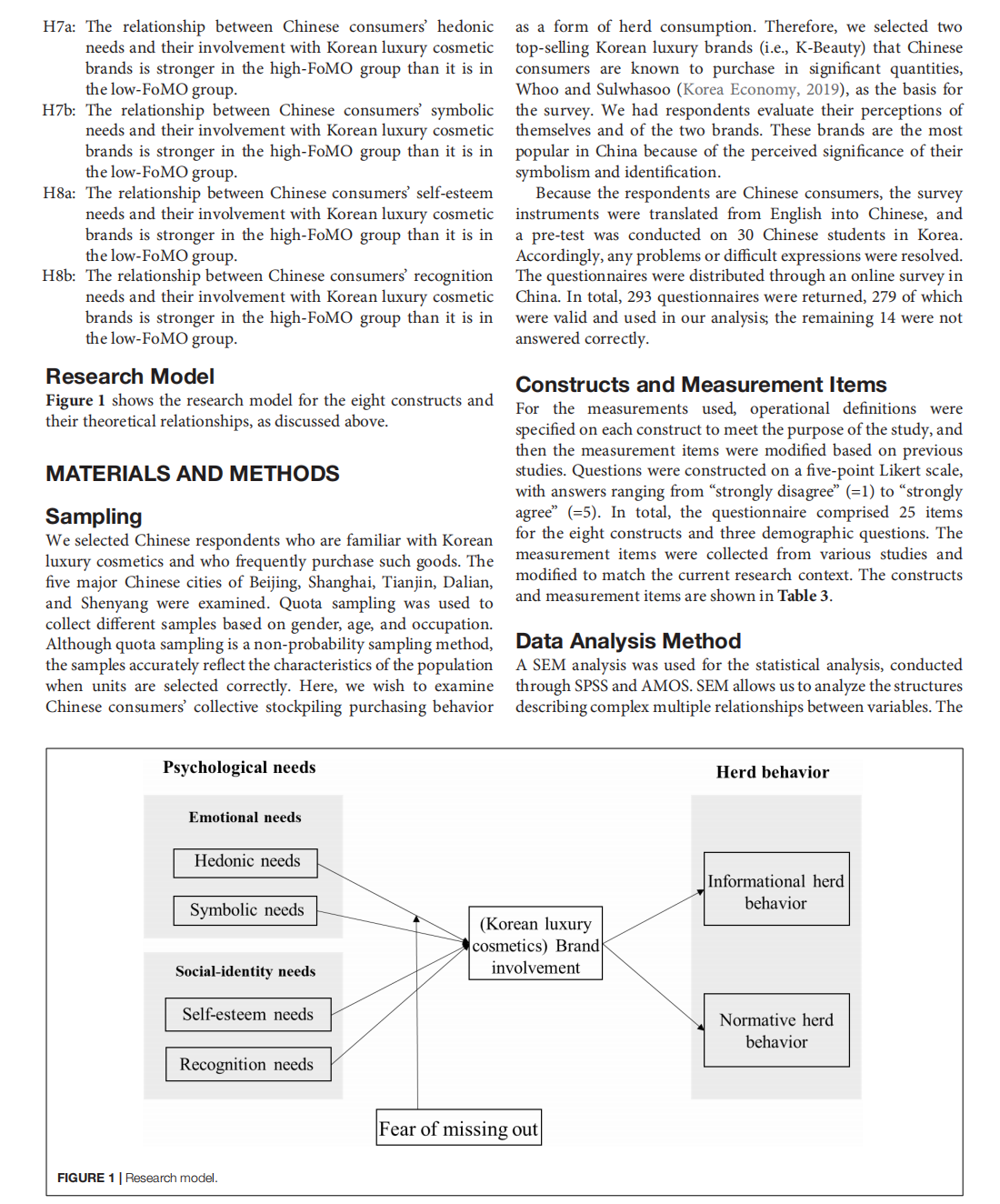

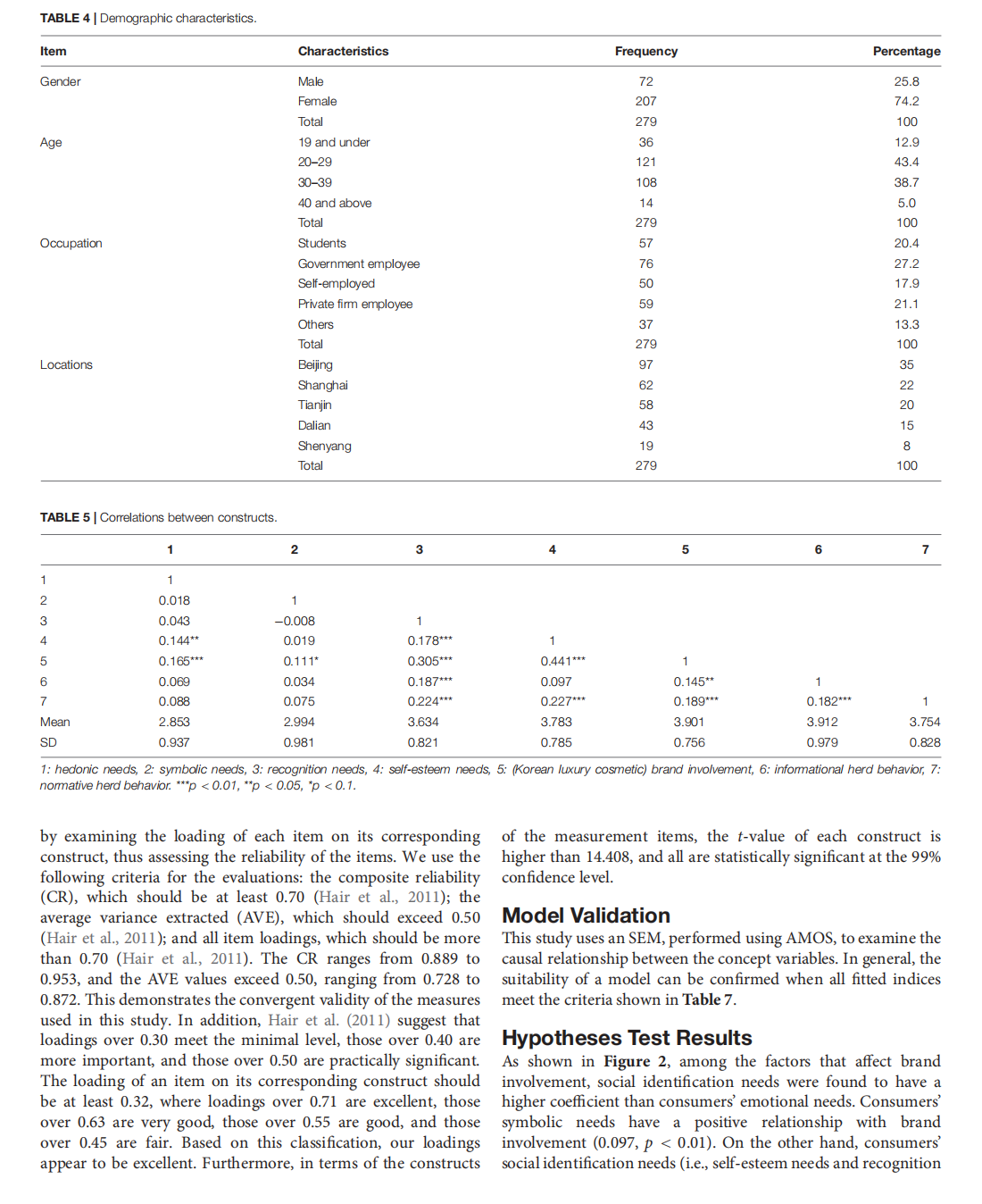
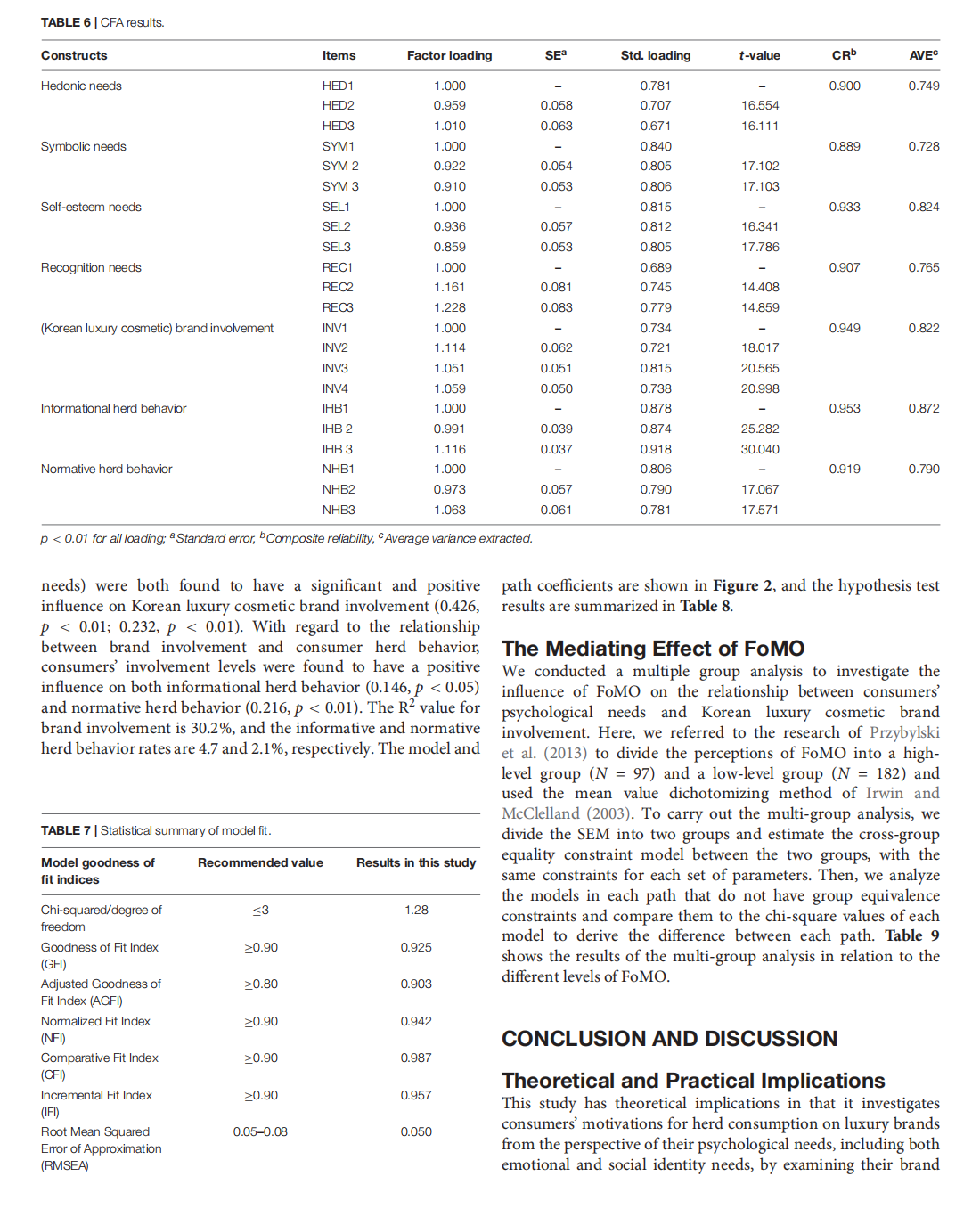
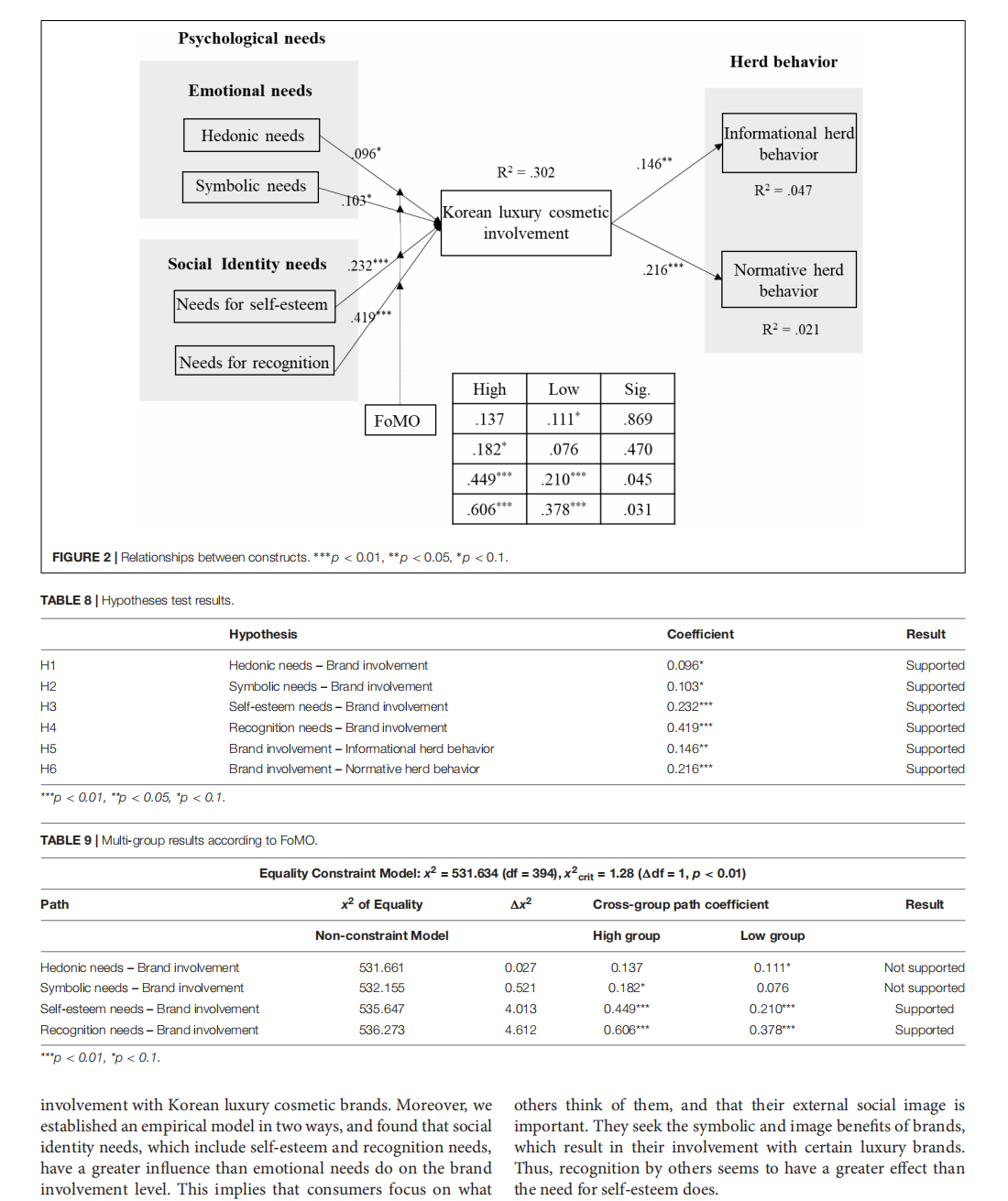



This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Psychology》 by Wound World




