文献精选
Ellie Kelepouris . Wendy St. Peter . Joshua J. Neumiller .Eugene E. Wright
Received: March 27, 2023 / Accepted: April 19, 2023 / Published online: May 20, 2023 @ The Author(s) 2023
ABSTRACT
Diabetes is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD), a condition associated with significant morbidity and mortality. As these patients have a high risk of developing cardiovascular disease and end-stage kidney disease, there is a need for early detection and early initiation of appropriate therapeutic interventions that slow disease progression and prevent adverse outcomes. Due to the complex nature of diabetes and CKD management, a holistic, patient-centered, collaborative care approach delivered by a coordinated multidisciplinary team (ideally including a clinical pharmacist as part of a comprehensive medication management program) is needed. In this review, we discuss the barriers to effective care, the current multidisciplinary approach used for CKD prevention and treatment, and the potential ways that the multidisciplinary management of CKD associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus can be refined to improve patient outcomes.
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARY
People living with type 2 diabetes mellitus are at risk of developing chronic kidney disease. Having chronic kidney disease means that over time the kidneys may not work as well as they should. Some people with chronic kidney disease will eventually need a new kidney (transplant) or will need to use a machine that does the job of their kidneys (dialysis). To slow the rate at which the kidneys get worse, chronic kidney disease needs to be detected and treated early. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals is needed to help people with type 2 diabetes reduce their chances of getting chronic kidney disease, or to prevent their chronic kidney disease from getting worse. Some healthcare teams include a clinical pharmacist who makes sure medicines are given in the correct amount and at the correct time. It is important that the healthcare team members communicate well and include the person with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease and their family members or caregivers (if needed) in the decision-making process to achieve better health results. Barriers stopping people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease from getting good healthcare include a shortage of nephrologists, not having enough healthcare insurance, limited access to healthcare, and poor understanding about what chronic kidney disease is and how it can be treated. This review article discusses the barriers to better healthcare in chronic kidney disease and how the current healthcare team approach could be changed to improve health results.
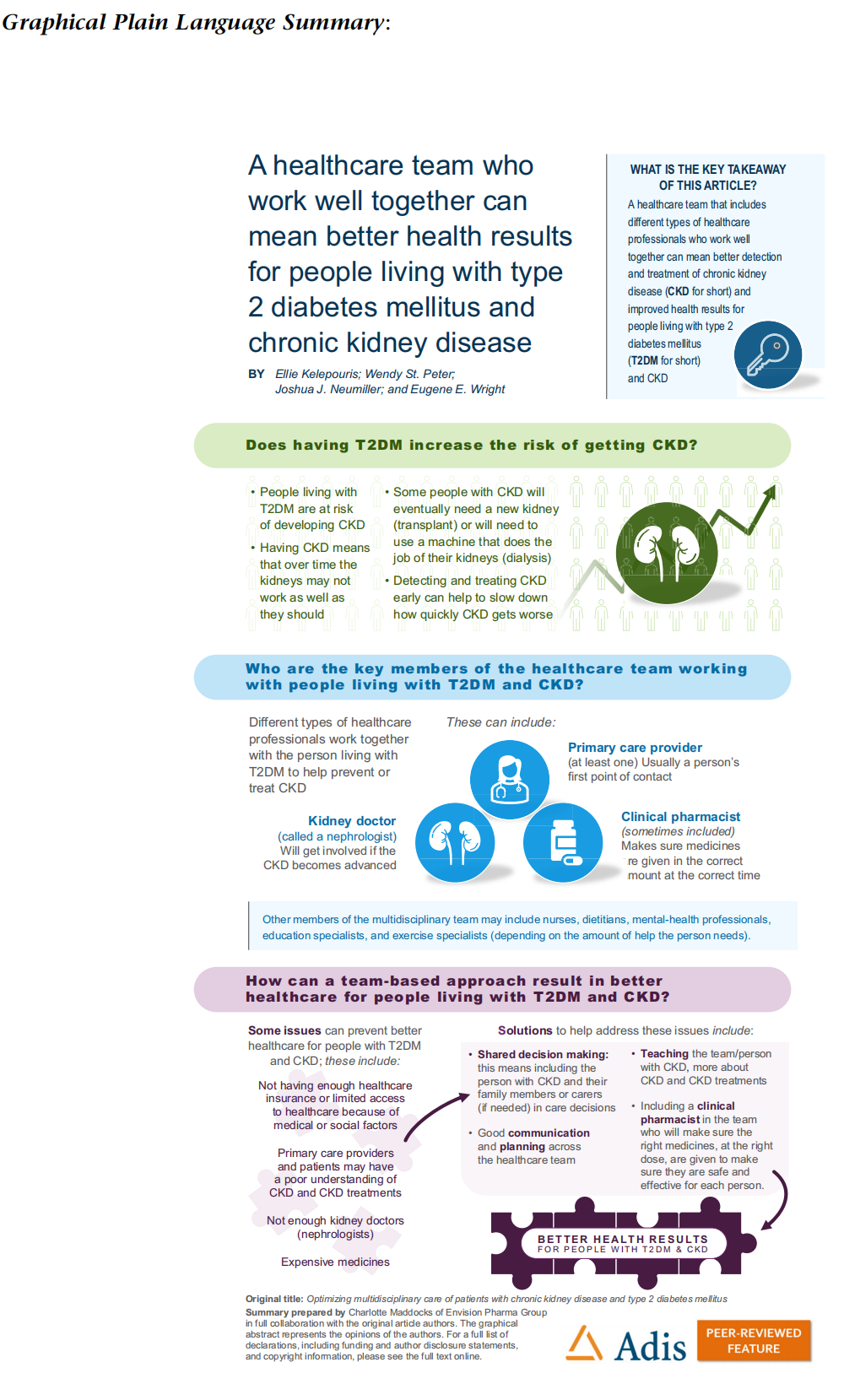
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Multidisciplinary care; Multidisciplinary team; Care optimization; Prevention
Key Summary Points
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are chronic conditions associated with long-term health, financial, and quality-of-life consequences for patients.
Barriers to optimized CKD care in people with T2DM include a shortage of specialist clinicians (nephrologists), delays in initiation or appropriate adjustment of evidence-based therapies, inconsistent screening practices, poor health literacy, inadequate healthcare insurance coverage, and limited access to healthcare.
An effective and well-coordinated multidisciplinary team (MDT), especially one that includes a clinical pharmacist as part of a comprehensive medication management (CMM) program, should proactively address many of these barriers to effective care.
Implementation of a collaborative care MDT approach (incorporating CMM) for CKD associated with T2DM across the USA is recommended.
DIGITAL FEATURES
This article is published with digital features, including a graphical plain language summary, to facilitate understanding of the article. To view digital features for this article go to https:// doi.org/https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.22644406.
Polly Q. X. Lim1,2 iD · Merridy J. Lithgow1,2 iD · Michelle R. Kaminski1,3,4 iD · Karl B. Landorf1,2 iD · Hylton B. Menz1,2 iD· Shannon E. Munteanu1,2 iD
Polly Q. X. Lim
该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
1 Discipline of Podiatry, School of Allied Health, Human Services and Sport, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria 3086, Australia
2 La Trobe Sport and Exercise Medicine Research Centre, School of Allied Health, Human Services and Sport, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria 3086, Australia
3 Department of Podiatry, Monash Health, Melbourne, Victoria 3168, Australia
4 School of Primary and Allied Health Care, Monash University, Melbourne, Victoria 3199, Australia
Received: 1 March 2023 / Accepted: 31 March 2023 / Published online: 24 April 2023 © The Author(s) 2023
Abstract
This systematic review aims to investigate the efficacy of non-surgical interventions for midfoot osteoarthritis (OA). Key databases and trial registries were searched from inception to 23 February 2023. All trials investigating non-surgical interventions for midfoot OA were included. Quality assessment was performed using the National Institutes of Health Quality Assessment Tool. Outcomes were pain, function, health-related quality of life, and adverse events. Effects (mean differences, standardised mean differences, risk ratios) were calculated where possible for the short (0 to 12 weeks), medium (>12 to 52 weeks), and long (>52 weeks) term. Six trials (231 participants) were included (one feasibility trial and five case series)— all were judged to be of poor methodological quality. Two trials reported arch contouring foot orthoses to exert no-to-large effects on pain in the short and medium term, and small-to-very-large effects on function in the short and medium term. Two trials reported shoe stiffening inserts to exert medium-to-huge effects on pain in the short term, and small effects on function in the short term. Two trials of image-guided intra-articular corticosteroid injections reported favourable effects on pain in the short term, small effects on pain and function in the medium term, and minimal long term effects. Two trials reported minor adverse events, and none reported health-related quality of life outcomes. The current evidence suggests that arch contouring foot orthoses, shoe stiffening inserts and corticosteroid injections may be effective for midfoot OA. Rigorous randomised trials are required to evaluate the efficacy of non-surgical interventions for midfoot OA.
Keywords Foot · Foot joints · Midfoot · Osteoarthritis · Midfoot osteoarthritis
Shelby Sydnor . Swarnendu Chatterjee . Philip Cooney . Simarjeet Kaur . Tom Macmillan iD . Daisy Stewart . Isobel Munro iD . Ca ´tia Bandeiras iD . Abby Paine iD . Federico Felizzi
Received: March 24, 2023 / Accepted: April 12, 2023 / Published online: May 17, 2023
© The Author(s) 2023
S. Sydnor
Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd., London, England, UK
S. Chatterjee S. Kaur
CONEXTS, Novartis Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad, India
P. Cooney C. Bandeiras
CONEXTS, Novartis Ireland Ltd., Dublin, Ireland
T. Macmillan D. Stewart A. Paine
Source Health Economics, Oxford, England, UK
I. Munro
Source Health Economics, London, England, UK
F. Felizzi (&)
Novartis Pharma AG, Fabrikstrasse 2, 4056 Basel, Switzerland
e-mail: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Key clinical guidelines recommend anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy as first-line treatment for visual impairment due to diabetic macular oedema (DMO). A systematic literature review (SLR) and network meta-analysis (NMA) were conducted comparing the relative efficacy of the anti-VEGF brolucizumab with a focused network of the most relevant comparator dosing regimens approved in countries other than the USA (aflibercept, ranibizumab). The safety and tolerability of brolucizumab were also assessed.
Methods: A broad SLR was conducted to identify randomised controlled trials to ensure all relevant potential comparators were captured. Identified studies were refined to those appropriate for inclusion in the NMA. A Bayesiani NMA was conducted comparing brolucizumab 6 mg (every 12 [Q12W]/every 8 weeks [Q8W]) with relevant aflibercept 2 mg and ranibizumab 0.5 mg regimens.
Results: Fourteen studies were included in the NMA. At 1-year follow-up, the various aflibercept 2 mg and ranibizumab 0.5 mg regimens were mostly comparable with brolucizumab 6 mg Q12W/Q8W across key visual and anatomical outcomes, except brolucizumab 6 mg was favoured over ranibizumab 0.5 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) for the change from baseline (CFB) in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and BCVA loss/gain of pre-specified numbers of letters, and over ranibizumab 0.5 mg pro re nata for CFB in diabetic retinopathy severity scale, and retinal thickness. At year 2, where data were available, brolucizumab 6 mg showed similar results across efficacy outcomes versus all other anti-VEGFs. In most cases, discontinuation rates (all cause, and due to adverse events [AE]) and serious and overall rates of AEs excluding ocular inflammatory events were similar (in unpooled and pooled-treatment analyses) versus comparators.
Conclusion: Brolucizumab 6 mg Q12W/Q8W was comparable or superior to aflibercept 2 mg and ranibizumab 0.5 mg regimens for various visual and anatomical efficacy outcomes and discontinuation rates.
Keywords: Aflibercept; Anti-VEGF; Bestcorrected visual acuity; Brolucizumab; Diabetic macular oedema; Diabetic retinopathy; Network meta-analysis; Ranibizumab; Retinal thickness; Visual impairment
Key Summary Points
Diabetic macular oedema (DMO) leads to progressive retinal dysfunction and if left untreated, irreversible vision loss. The disease affects 5.47% of patients with diabetes, globally.
Across key clinical guidelines, antivascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies, administered via intravitreal (IVT) injection, are recommended as first line treatment for patients with visual impairment due to DMO. The efficacy and safety of the anti-VEGF brolucizumab for this indication has been investigated by two phase 3 randomised head-to-head studies versus aflibercept (KESTREL and KITE).
The main aim of this study was to compare the relative efficacy of brolucizumab 6 mg via network metaanalysis (NMA) based on a focused network of the most relevant available anti-VEGFs (aflibercept 2 mg, ranibizumab 0.5 mg) approved in a number of countries other than the USA, including the UK; the safety and tolerability of brolucizumab were also assessed.
Brolucizumab 6 mg showed similar efficacy for key visual and anatomic outcomes including best-corrected visual acuity, diabetic retinopathy severity, and retinal thickness outcomes versus the relevant anti-VEGFs. Brolucizumab 6 mg showed an overall favourable benefit/risk \ profile with comparable rates of discontinuation and serious and overall adverse events to the other anti-VEGFs, except for ocular inflammatory and occlusive events.
This is the first analysis assessing the efficacy and safety of brolucizumab 6 mg for the treatment of patients with visual impairment due to DMO using this focused network of comparators.
Jonathan V. Mui1 · Lifang Li2 · Oscar Hou In Chou1,3 ·iD. Nida Azfar1 · Athena Lee1,4 · Jeremy Hui1,3 · Sharen Lee1 · Gary Tse1,5,6,8,9 · Jiandong Zhou7
Received: 29 October 2022 / Accepted: 24 February 2023 / Published online: 31 March 2023 © The Author(s) 2023
Abstract
Introduction The risk of new onset depression associated with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2I) use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remains unclear. This study investigated the risk of new onset depression between SGLT2I and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor (DPP4I) users.
Methods This was a population-based cohort study of T2DM patients in Hong Kong between January 1st, 2015, and December 31st, 2019. T2DM patients over 18 with either SGLT2I or DPP4I use were included. 1:1 propensity-score matching using the nearest-neighbour method was conducted based on demographics, past comorbidities and non-DPP4I/SGLT2I medication use. Cox regression analysis models were used to identify significant predictors for new onset depression.
Results The study cohort included a total of 18,309 SGLT2I users and 37,269 DPP4I users (55.57% male, mean age: 63.5±12.9 years) with a median follow-up duration of 5.56 (IQR: 5.23–5.8) years. After propensity score matching, SGLT2I use was associated with a lower risk of new onset depression compared to DPP4I use (HR: 0.52, 95% CI: [0.35, 0.77], P=0.0011). These findings were confirmed by Cox multivariable analysis and sensitive analyses.
Conclusion SGLT2I use is associated with significantly lower risk of depression compared to DPP4 use in T2DM patients using propensity score matching and Cox regression analyses.
Keywords Type 2 diabetes · Depression · Anti-diabetic medication · SGLT2 inhibitor · DPP4 inhibitor
Jonathan V. Mui and Lifang Li are joint first authors.
“This article belongs to the topical collection “Health Education and Psycho-Social Aspects, managed by Massimo Porta and Marina Trento”.
Gary Tse
该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
* Jiandong Zhou
该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
1 Diabetes Research Unit, Cardiovascular Analytics Group, Hong Kong, China
2 Department of Biostatistics and Health Informatics, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King’s College London, London, UK
3 Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
4 Department of Medicine & Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
5 Department of Cardiology, Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
6 Kent and Medway Medical School, Canterbury, UK
7 Nufeld Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
8 School of Nursing and Health Studies, Hong Kong Metropolitan University, Hong Kong, China
9 Tianjin Institute of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300211, China




