文献精选






This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Oncology》by Wound World





This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Medicine》 by Wound World



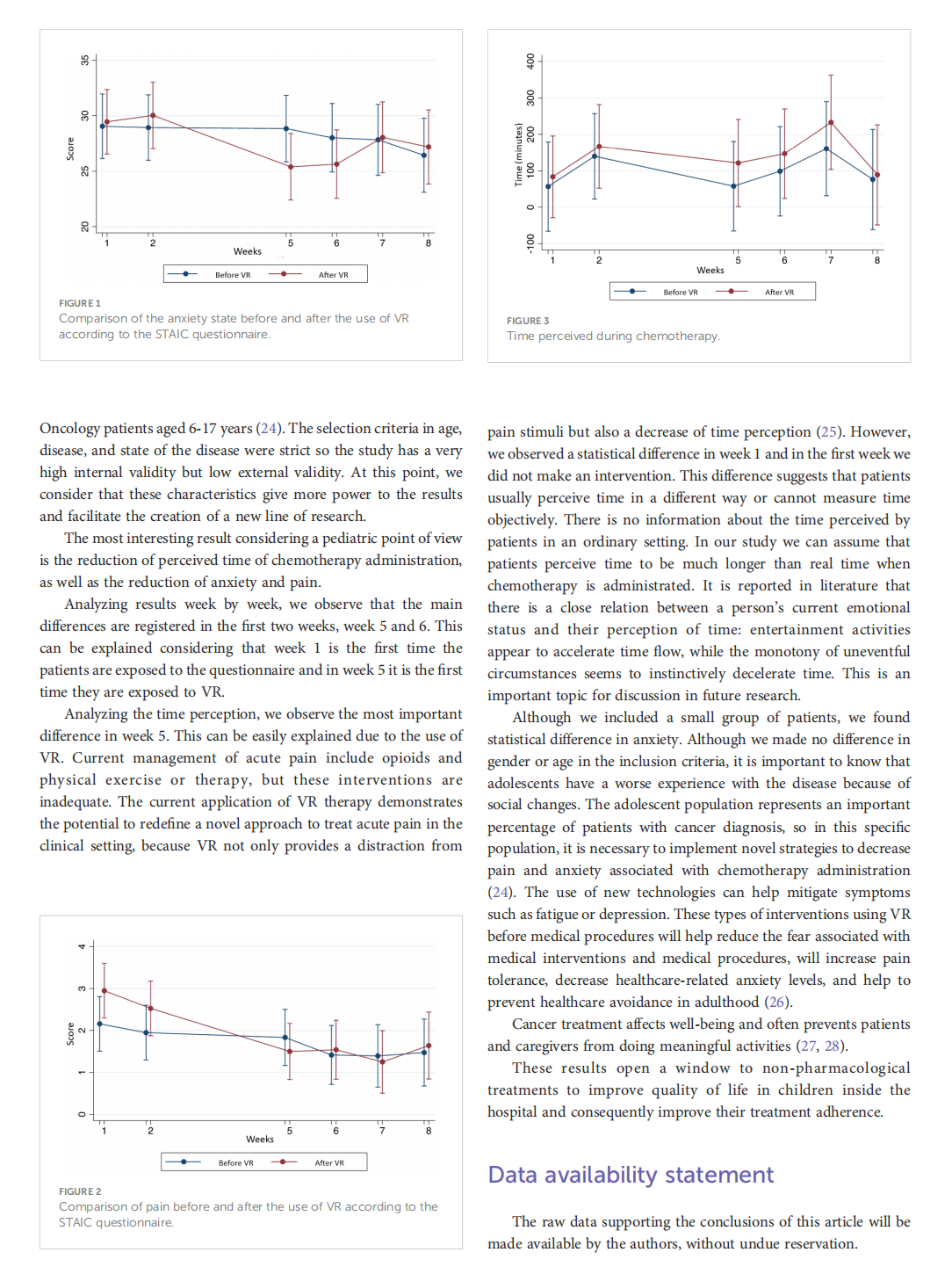


This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Oncology》by Wound World



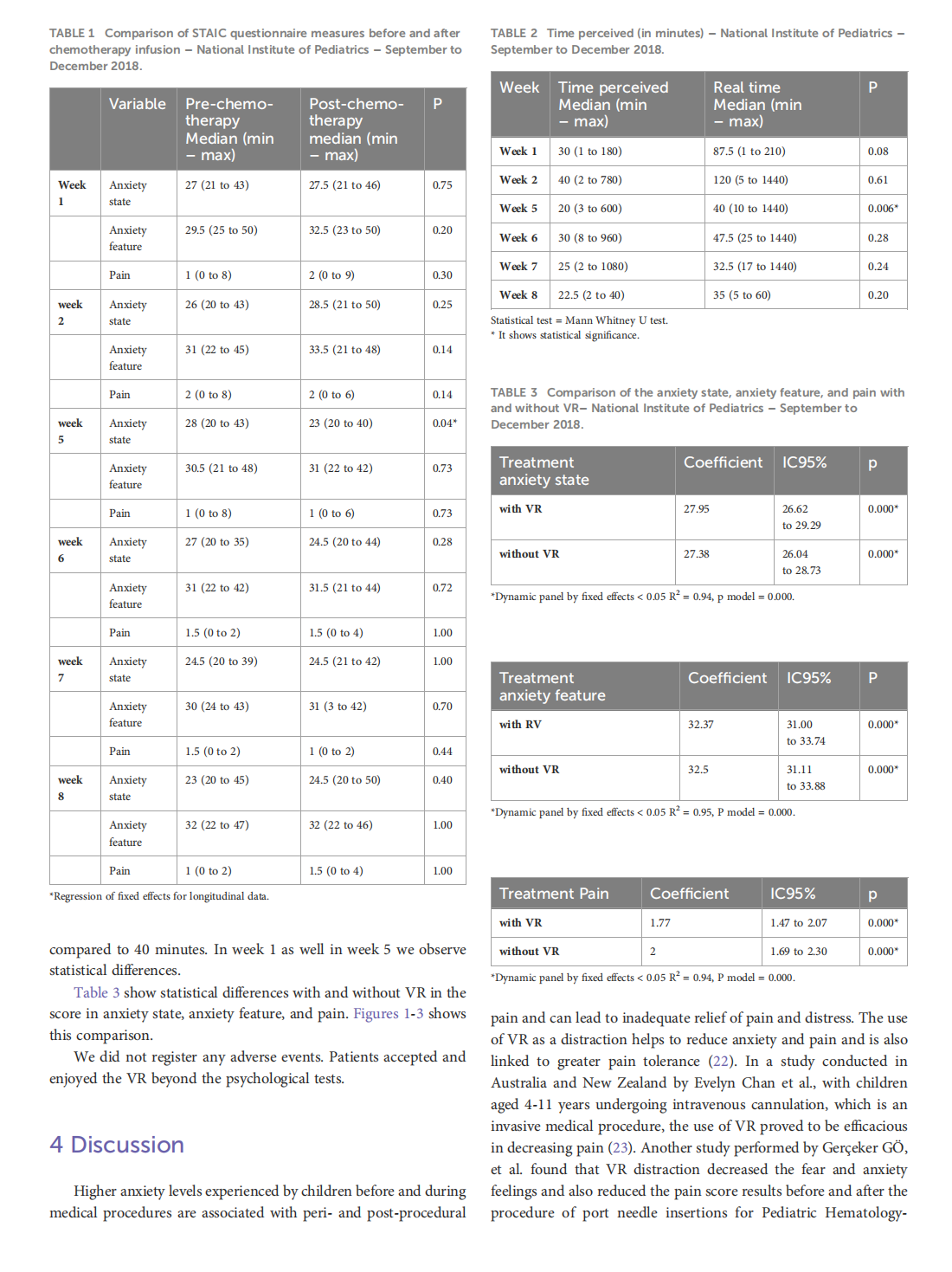
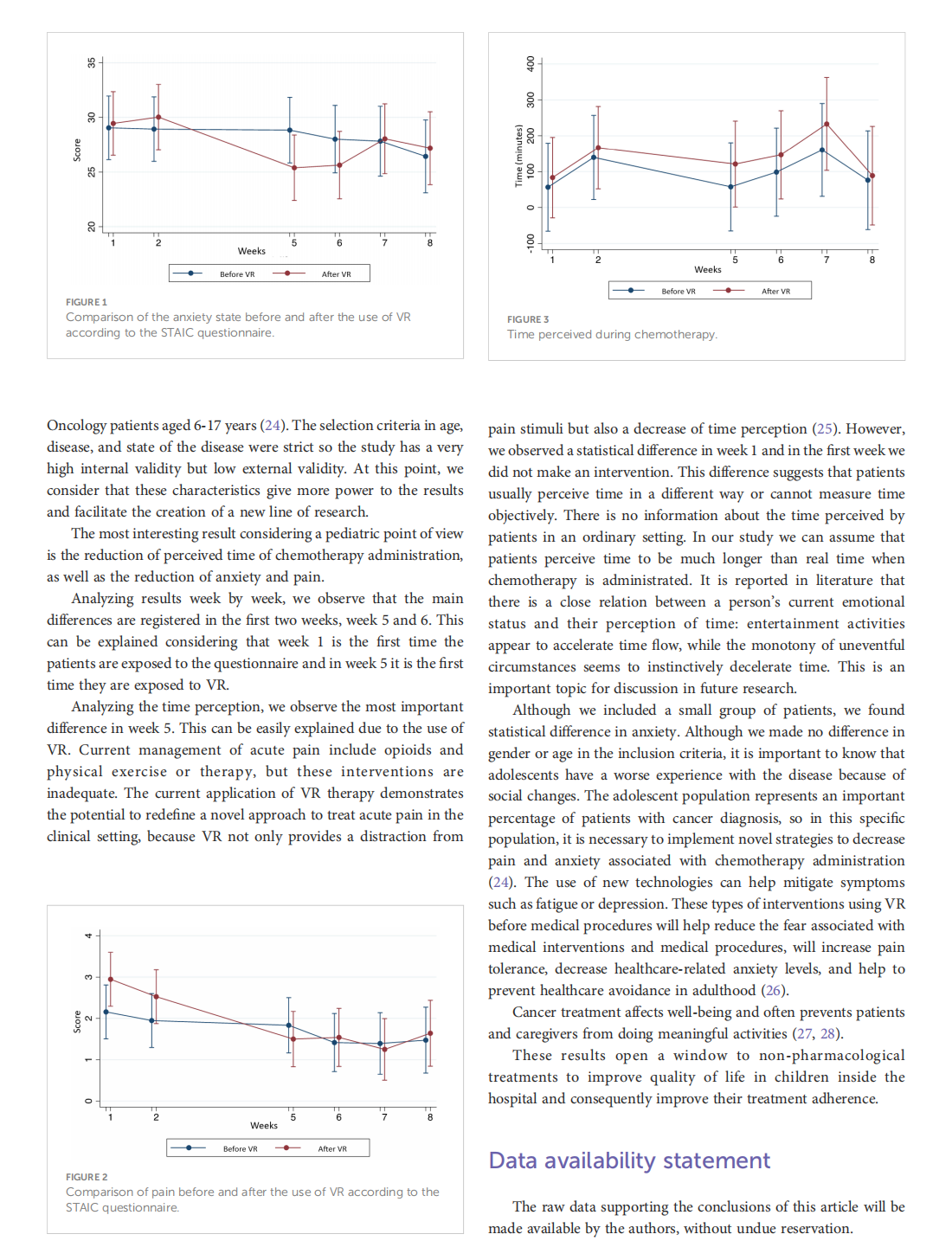


This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Oncology》by Wound World




