
伤口世界

- 星期五, 14 7月 2023
人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞不同途径移植治疗 1 型糖尿病鼠
郭 璇 1 ,解 军 1 ,索金荣 2 ,李英蕊 1 ,黄 磊 1 ,马牧南 1 ,李静静 3 ,傅松涛 1,2,3
1 山西医科大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,山西省太原市 030001;2 山西宾大干细胞科技有限公司,山西省太原市 030001;3 山西省生物医药健康研究生教育创新中心,山西省太原市 030001 第一作者:郭璇,男,1994 年生,陕西省延安市人,汉族,2020 年山西医科大学毕业,硕士,主要从事干细胞与组织再生研究。
通讯作者:傅松涛,硕士,教授,山西医科大学基础医学院,山西省太原市 030001;山西宾大干细胞科技有限公司,山西省太原市 030001;山西省生物医药健康研究生教育创新中心,山西省太原市 030001 https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7907-0316( 郭璇 )
基金资助:山西省‘1331 工程’重点学科建设计划经费,项目负责人:解军;山西省国际科技合作基金 (201703d421022),项目负责人:解军;山西省重点研发计划 ( 国际科技合作 )(201903D421023),项目负责人:解军
引用本文:郭璇,解军,索金荣,李英蕊,黄磊,马牧南,李静静,傅松涛 . 人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞不同途径移植治疗 1 型糖尿病鼠 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):78-83.
https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.
2095-4344.2144
投稿日期:2020-01-04
送审日期:2020-01-10
采用日期:2020-02-19
在线日期:2020-08-10
中图分类号:R459. 9;R394.2;R587.1
文章编号:
2095-4344(2021)01-00078-06
文献标识码:B
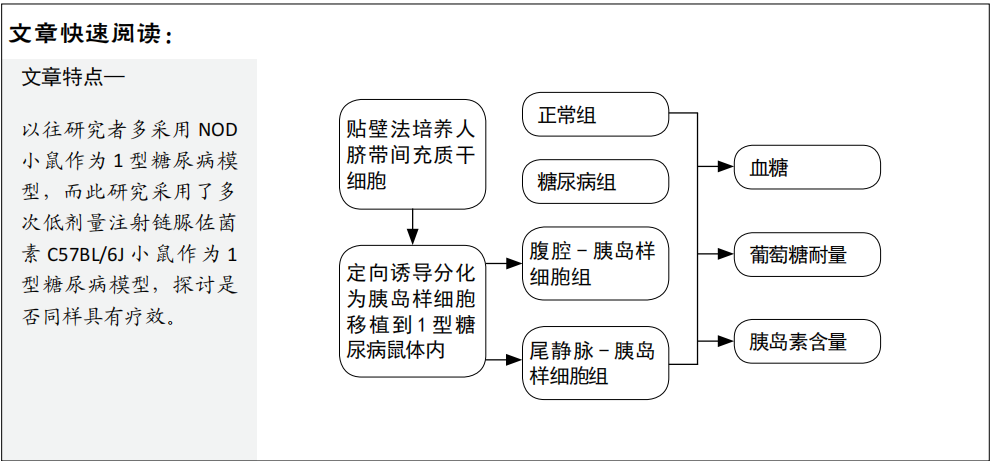
文题释义:
人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样细胞:人脐带间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能,可分化为骨细胞、脂肪细胞、胰岛细胞等,在相关因子作用下,可使其分化为分泌胰岛素的细胞,称为胰岛样细胞。
葡萄糖耐量:检测胰岛样细胞移植后糖尿病鼠是否可以更好地响应外周血糖浓度变化,释放胰岛素,降低血糖。
摘要
背景:人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞移植于1型糖尿病鼠体内,会使血糖降低,糖尿病症状有所改善,但腹腔移植的方式少有报道。
目的:观察不同途径移植人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞对于1型糖尿病小鼠的治疗效果。
方法:选采用组织块贴壁法分离培养人脐带间充质干细胞,然后将其定向分化为胰岛样细胞。从15只雄性C57BL/6J小鼠中随机取3只小鼠做正常组,其余12只小鼠腹腔注射链脲佐菌素制备1型糖尿病模型。造模成功9只小鼠随机分为糖尿病组、尾静脉-胰岛样细胞组、腹腔-胰岛样细胞组,每组3只。造模10 d后,正常组和糖尿病组不予处理,尾静脉-胰岛样细胞组经尾静脉注射0.4 mL胰岛样细胞悬液(含5×105个细胞),腹腔-胰岛样细胞组经腹腔注射0.4 mL胰岛样细胞悬液(含5×105 个细胞)。移植后每周检测2次血糖,移植后28 d进行葡萄糖耐量实验,移植后42 d检测胰岛素水平。
结果与结论:①与糖尿组相比,尾静脉-胰岛样细胞组在移植后第10天开始血糖明显下降,一直维持到31 d,胰岛素水平升高,葡萄糖耐量改善,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);腹腔-胰岛样细胞组血糖、胰岛素水平、葡萄糖耐量未见明显改善;②结果提示,应用人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞治疗1型糖尿病鼠,尾静脉注射是一种比较理想的移植方式,腹腔注射的效果不佳。
关键词:人脐带间充质干细胞;1型糖尿病;胰岛样细胞;腹腔;静脉;移植;鼠;实验
Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice Guo Xuan1 , Xie Jun1 , Suo Jinrong2 , Li Yingrui1 , Huang Lei1 , Ma Munan1 , Li Jingjing3 , Fu Songtao1, 2, 3
1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China;
2 Shanxi Binda Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Provincial Biomedical Health Graduate Education Innovation Center, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China Guo Xuan, Master, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province,China
Corresponding author: Fu Songtao, Master, Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Binda Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Provincial Biomedical Health Graduate Education Innovation Center, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Transplanting islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) into type 1 diabetic mice can reduce blood glucose level and improve the symptoms of diabetes mellitus. However, there are few reports on intraperitoneal transplantation.
OBJECTIVE: To study the therapeutic effect of transplantation of islet-like cells induced by hUC-MSCs in different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice.
METHODS: The hUC-MSCs were isolated and cultured by tissue explants adherent method and differentiated into islet-like cells. The 3 of 15 male C57BL/6J mice were used as normal group, and the remaining mice were taken to prepare a mouse model of type 1 diabetes using intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin. After successful modeling, nine model mice were randomly divided into diabetes group, tail vein-islet-like cells group, and abdomen-islet-like cells group, with three mice in each group. After 10 days of modeling, the normal group and diabetic group were not treated. The tail vein-islet-like cells group was injected with 5×105 cells/0.4 mL islet-like cells via the tail vein and the abdomen-islet-like cells group was intraperitoneally injected with 5×105 cells/0.4 mL islet-like cells. During the treatment, the blood glucose and insulin levels were measured twice a week; glucose tolerance test was performed at 28 days after cell transplantation; and fasting insulin level was detected at 42 days after cell transplantation.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSION: (1) Compared with the diabetic group, in the tail vein-islet-like cells group, the blood glucose level began to decrease on the 10th day after transplantation and maintained until the 31st day, and the insulin level and glucose tolerance significantly improved (P < 0.05). However, there was no significant improvement in blood glucose level, insulin level and glucose tolerance in the abdomen-islet-like cells group. (2) To conclude, transplantation of hUCMSCs induced islet-like cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice via tail vein is an ideal transplantation method, and the effect of intraperitoneal injection is unsatisfactory.
Key words: human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; type 1 diabetes mellitus; islet-like cells; abdomen; vein; transplantation; mouse; experiment
Funding: the Fund for Shanxi “1331 Project” Key Subject Construction (to XJ); The International Scientific and Technological Cooperative Foundation of Shanxi
Province, No. 201703d421022 (to XJ); Key R&D Program of Shanxi Province (International Cooperation), No. 201903D421023 (to XJ)
How to cite this article: GUO X, XIE J, SUO JR, LI YR, HUANG L, MA MN, LI JJ, FU ST. Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2021;25(1):78-83.

- 星期四, 13 7月 2023
达格列净与吡格列酮联合二甲双胍治疗2型糖尿病的疗效及对胰岛素敏感性和胰岛a和β细胞功能的影响
黎俏洁
(海南医学院第二附属医院内分泌科,海南海口570100)
[摘要]目的:探讨达格列净与吡格列酮联合二甲双胍治疗2型糖尿病(T2DM)的疗效及对胰岛素敏感性和胰岛a和β细胞功能的影响。方法:选取100例T2DM患者为研究对象,依据治疗方法不同分为达格列净组和吡格列酮组,每组各50例。达格列净组予以达格列净+二甲双胍治疗;吡格列酮组予以吡格列酮+二甲双胍治疗。比较两组患者血糖指标[空腹血糖(FPG) .餐后2 h血糖(2hPG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbAle)]、血脂指标[总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇( LDL-C)]、胰岛素抵抗指数( HOMA-IR)、胰岛素敏感性[葡萄糖输注率(GIR)]、胰岛a和β细胞功能指标[a:胰高血糖素曲线下面积( AUCglc);β:早相胰岛素分泌指数( I30/G30)、胰岛素分泌曲线下面积(AUCins)]及不良反应发生情况。结果:治疗后,两组患者FPG、2hPG、HbAle .TC、TG、LDL-C、HOMA-IR、AUCgle均降低(P<0.05),且达格列净组低于吡格列酮组(P <0.05) ;GIR、I30/G30、AUCins均升高(P<0.05),且达格列净组高于吡格列酮组(P<0.05)。两组患者不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:达格列净与吡格列酮联合二甲双胍治疗T2DM均可有效改善患者糖脂代谢,减轻IR并可提高胰岛素敏感性,保护胰岛a和β细胞功能,但达格列净联合二甲双胍的作用相对更好。
[关键词]达格列净;吡格列酮;二甲双胍;2型糖尿病;胰岛素敏感性;胰岛细胞功能[中图分类号] R587.1
[文献标志码] A
Effect of daglitazone and pioglitazone combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its influence on insulin sensitivity and islet a and β cell function
LI Qiao-jie
( Department of Endocrinology , the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College , Haikou 570100 , Hainan ,China)
[ Abstract] Objective: To investigate the effect of dapagliflozin and pioglitazone combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus ( T2DM) and its effect on insulin sensitivity and islet a and β cell function.
Methods : 100 patients with T2DM were selected and divided into daglitazone group and pioglitazone group according to different treatment methods, with 50 cases in each group. The daglitazone group was treated with daglitazone + metformin , and the pioglitazone group was treated with pioglitazone + met-formin. The blood glucose [ fasting plasma glucose ( FPG), 2 h postprandial blood glucose ( 2hPG ),glycosy lated hemoglobin ( HbAlc) ] , blood lipids [ total cholesterol ( TC),triglyceride ( TG ) , low density lipoprotein cholesterol ( LDL-C)] , insulin resistance[ insulin resistance index ( HOMA-IR )], insulin sensitivity [ glucose infusion rate ( GIR) ] and islet a and β cell function [ a :area under the curve of glucagon ( AUCglc),β: early phase insulin secretion index ( I30/ G30) ,area under insulin secretion curve (AUCins) ] and adverse effects were compared between the two groups.
Results : After treatment , FPG ,2hPG, HbAlc , TC, TG, LDL-C, HOMA-IR and AUCglc in the two groups were signific antly dec reased , and daglitazone group was lower than the pioglitazone group
(P<0.05). GIR , I30/G30 and AUCins were significantly increased (P<0. 05) , and daglitazone group was higher than the pioglitazone group ( P < 0. 05). There was no significant difference in the total inlcidence of adverse reactions between the two groups (P >0.05).
Conclusion : Dagliptin and pioglitazone combined with metformin in the treatment of T2DM can effectively improve glucose and lipid metabolism ,reduce IR , improve insulin sensitivity, and protect the function of islet a and β cells , and the efficacy of dagliptin is relatively better.
[Key words] Type 2 diabetes ;Dapagliflozin ;Pioglitazone ; Metformin; Insulin sensitivity; Islet cells function

- 星期二, 11 7月 2023
Sleep Apnea, Obesity, and Diabetes — an Intertwined Trio
Soumya Kurnool1 · Karen C. McCowen1 · Nicole A. Bernstein1 · Atul Malhotra1 iD
Accepted: 18 April 2023 / Published online: 6 May 2023 © The Author(s) 2023
Abstract
Purpose of Review To synthesize the existing literature regarding the complex interplay between sleep disturbance, obesity, and diabetes. The review emphasizes the three pillars of health being diet, exercise, and sleep, with the notion that if one is ignored, then the other two could suffer.
Recent Findings Sleep deprivation is associated with incident obesity, perhaps mediated by dysregulation in leptin and ghrelin — hormones important in regulation of appetite. Sleep apnea is very common particularly among obese people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Treatment of sleep apnea has clear symptomatic benefits although its impact on long-term cardiometabolic health is less clear.
Summary Sleep disturbance may be an important modifiable risk for patients at risk of cardiometabolic disease. An assessment of sleep health may be an important component of the comprehensive care of patients with obesity and diabetes mellitus.
Keywords Sleep · Apnea · Obesity · Metabolic · Diabetes · Vascular
Atul Malhotra 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
Soumya Kurnool 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
Karen C. McCowen 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
Nicole A. Bernstein 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
1 UC San Diego Department of Medicine, 9500 Gilman Drive, UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA

- 星期一, 10 7月 2023
Optimizing Multidisciplinary Care of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ellie Kelepouris . Wendy St. Peter . Joshua J. Neumiller .Eugene E. Wright
Received: March 27, 2023 / Accepted: April 19, 2023 / Published online: May 20, 2023 @ The Author(s) 2023
ABSTRACT
Diabetes is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD), a condition associated with significant morbidity and mortality. As these patients have a high risk of developing cardiovascular disease and end-stage kidney disease, there is a need for early detection and early initiation of appropriate therapeutic interventions that slow disease progression and prevent adverse outcomes. Due to the complex nature of diabetes and CKD management, a holistic, patient-centered, collaborative care approach delivered by a coordinated multidisciplinary team (ideally including a clinical pharmacist as part of a comprehensive medication management program) is needed. In this review, we discuss the barriers to effective care, the current multidisciplinary approach used for CKD prevention and treatment, and the potential ways that the multidisciplinary management of CKD associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus can be refined to improve patient outcomes.
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARY
People living with type 2 diabetes mellitus are at risk of developing chronic kidney disease. Having chronic kidney disease means that over time the kidneys may not work as well as they should. Some people with chronic kidney disease will eventually need a new kidney (transplant) or will need to use a machine that does the job of their kidneys (dialysis). To slow the rate at which the kidneys get worse, chronic kidney disease needs to be detected and treated early. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals is needed to help people with type 2 diabetes reduce their chances of getting chronic kidney disease, or to prevent their chronic kidney disease from getting worse. Some healthcare teams include a clinical pharmacist who makes sure medicines are given in the correct amount and at the correct time. It is important that the healthcare team members communicate well and include the person with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease and their family members or caregivers (if needed) in the decision-making process to achieve better health results. Barriers stopping people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease from getting good healthcare include a shortage of nephrologists, not having enough healthcare insurance, limited access to healthcare, and poor understanding about what chronic kidney disease is and how it can be treated. This review article discusses the barriers to better healthcare in chronic kidney disease and how the current healthcare team approach could be changed to improve health results.
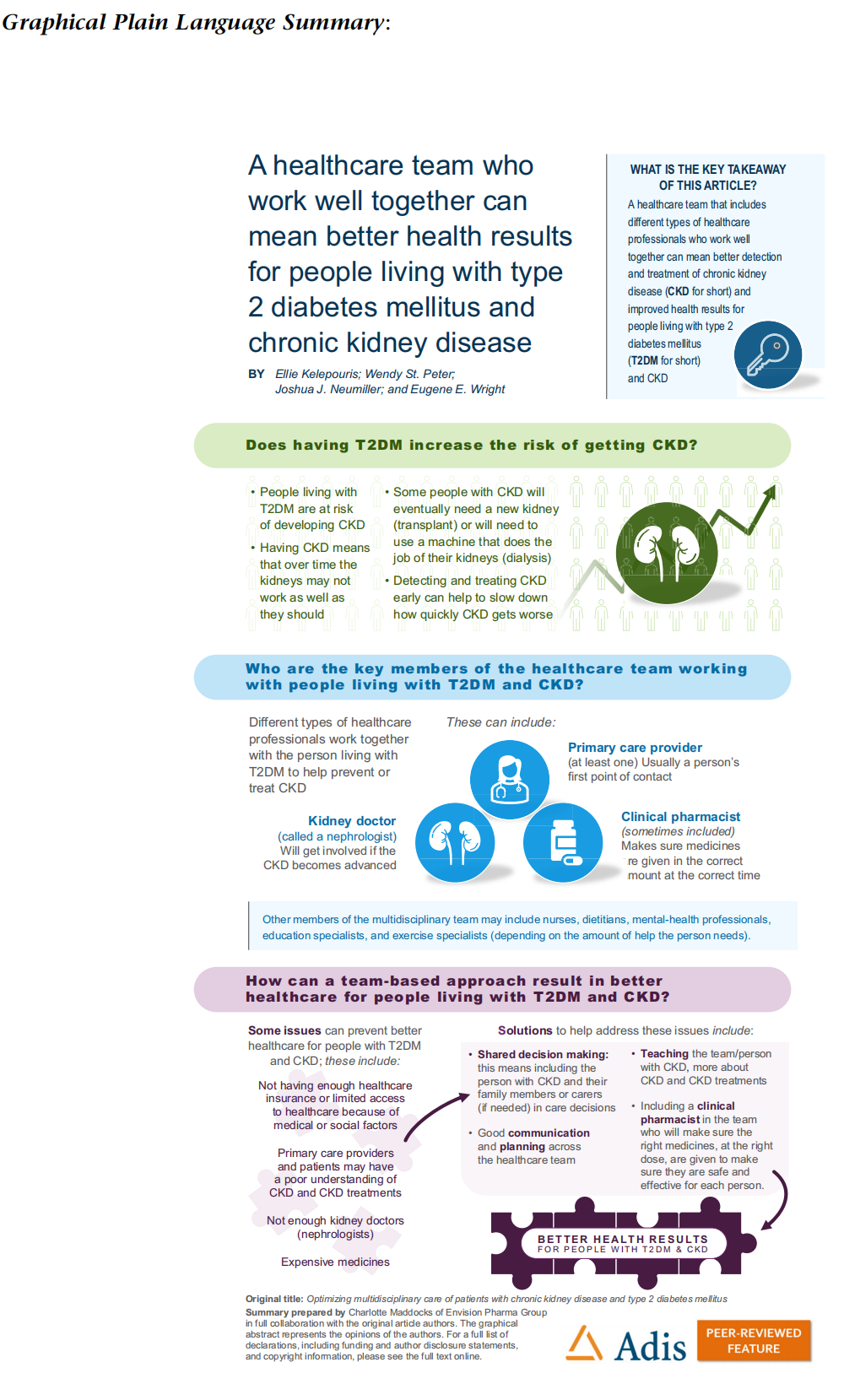
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Multidisciplinary care; Multidisciplinary team; Care optimization; Prevention
Key Summary Points
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are chronic conditions associated with long-term health, financial, and quality-of-life consequences for patients.
Barriers to optimized CKD care in people with T2DM include a shortage of specialist clinicians (nephrologists), delays in initiation or appropriate adjustment of evidence-based therapies, inconsistent screening practices, poor health literacy, inadequate healthcare insurance coverage, and limited access to healthcare.
An effective and well-coordinated multidisciplinary team (MDT), especially one that includes a clinical pharmacist as part of a comprehensive medication management (CMM) program, should proactively address many of these barriers to effective care.
Implementation of a collaborative care MDT approach (incorporating CMM) for CKD associated with T2DM across the USA is recommended.
DIGITAL FEATURES
This article is published with digital features, including a graphical plain language summary, to facilitate understanding of the article. To view digital features for this article go to https:// doi.org/https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.22644406.

- 星期一, 03 7月 2023
Efficacy of non‑surgical interventions for midfoot osteoarthritis: a systematic review
Polly Q. X. Lim1,2 iD · Merridy J. Lithgow1,2 iD · Michelle R. Kaminski1,3,4 iD · Karl B. Landorf1,2 iD · Hylton B. Menz1,2 iD· Shannon E. Munteanu1,2 iD
Polly Q. X. Lim
该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
1 Discipline of Podiatry, School of Allied Health, Human Services and Sport, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria 3086, Australia
2 La Trobe Sport and Exercise Medicine Research Centre, School of Allied Health, Human Services and Sport, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria 3086, Australia
3 Department of Podiatry, Monash Health, Melbourne, Victoria 3168, Australia
4 School of Primary and Allied Health Care, Monash University, Melbourne, Victoria 3199, Australia
Received: 1 March 2023 / Accepted: 31 March 2023 / Published online: 24 April 2023 © The Author(s) 2023
Abstract
This systematic review aims to investigate the efficacy of non-surgical interventions for midfoot osteoarthritis (OA). Key databases and trial registries were searched from inception to 23 February 2023. All trials investigating non-surgical interventions for midfoot OA were included. Quality assessment was performed using the National Institutes of Health Quality Assessment Tool. Outcomes were pain, function, health-related quality of life, and adverse events. Effects (mean differences, standardised mean differences, risk ratios) were calculated where possible for the short (0 to 12 weeks), medium (>12 to 52 weeks), and long (>52 weeks) term. Six trials (231 participants) were included (one feasibility trial and five case series)— all were judged to be of poor methodological quality. Two trials reported arch contouring foot orthoses to exert no-to-large effects on pain in the short and medium term, and small-to-very-large effects on function in the short and medium term. Two trials reported shoe stiffening inserts to exert medium-to-huge effects on pain in the short term, and small effects on function in the short term. Two trials of image-guided intra-articular corticosteroid injections reported favourable effects on pain in the short term, small effects on pain and function in the medium term, and minimal long term effects. Two trials reported minor adverse events, and none reported health-related quality of life outcomes. The current evidence suggests that arch contouring foot orthoses, shoe stiffening inserts and corticosteroid injections may be effective for midfoot OA. Rigorous randomised trials are required to evaluate the efficacy of non-surgical interventions for midfoot OA.
Keywords Foot · Foot joints · Midfoot · Osteoarthritis · Midfoot osteoarthritis

- 星期二, 20 6月 2023
Efficacy and Safety of Brolucizumab, Aflibercept, and Ranibizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Visual Impairment Due to Diabetic Macular Oedema: A Systematic Review and Network MetaAnalysis
Shelby Sydnor . Swarnendu Chatterjee . Philip Cooney . Simarjeet Kaur . Tom Macmillan iD . Daisy Stewart . Isobel Munro iD . Ca ´tia Bandeiras iD . Abby Paine iD . Federico Felizzi
Received: March 24, 2023 / Accepted: April 12, 2023 / Published online: May 17, 2023
© The Author(s) 2023
S. Sydnor
Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd., London, England, UK
S. Chatterjee S. Kaur
CONEXTS, Novartis Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad, India
P. Cooney C. Bandeiras
CONEXTS, Novartis Ireland Ltd., Dublin, Ireland
T. Macmillan D. Stewart A. Paine
Source Health Economics, Oxford, England, UK
I. Munro
Source Health Economics, London, England, UK
F. Felizzi (&)
Novartis Pharma AG, Fabrikstrasse 2, 4056 Basel, Switzerland
e-mail: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Key clinical guidelines recommend anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy as first-line treatment for visual impairment due to diabetic macular oedema (DMO). A systematic literature review (SLR) and network meta-analysis (NMA) were conducted comparing the relative efficacy of the anti-VEGF brolucizumab with a focused network of the most relevant comparator dosing regimens approved in countries other than the USA (aflibercept, ranibizumab). The safety and tolerability of brolucizumab were also assessed.
Methods: A broad SLR was conducted to identify randomised controlled trials to ensure all relevant potential comparators were captured. Identified studies were refined to those appropriate for inclusion in the NMA. A Bayesiani NMA was conducted comparing brolucizumab 6 mg (every 12 [Q12W]/every 8 weeks [Q8W]) with relevant aflibercept 2 mg and ranibizumab 0.5 mg regimens.
Results: Fourteen studies were included in the NMA. At 1-year follow-up, the various aflibercept 2 mg and ranibizumab 0.5 mg regimens were mostly comparable with brolucizumab 6 mg Q12W/Q8W across key visual and anatomical outcomes, except brolucizumab 6 mg was favoured over ranibizumab 0.5 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) for the change from baseline (CFB) in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and BCVA loss/gain of pre-specified numbers of letters, and over ranibizumab 0.5 mg pro re nata for CFB in diabetic retinopathy severity scale, and retinal thickness. At year 2, where data were available, brolucizumab 6 mg showed similar results across efficacy outcomes versus all other anti-VEGFs. In most cases, discontinuation rates (all cause, and due to adverse events [AE]) and serious and overall rates of AEs excluding ocular inflammatory events were similar (in unpooled and pooled-treatment analyses) versus comparators.
Conclusion: Brolucizumab 6 mg Q12W/Q8W was comparable or superior to aflibercept 2 mg and ranibizumab 0.5 mg regimens for various visual and anatomical efficacy outcomes and discontinuation rates.
Keywords: Aflibercept; Anti-VEGF; Bestcorrected visual acuity; Brolucizumab; Diabetic macular oedema; Diabetic retinopathy; Network meta-analysis; Ranibizumab; Retinal thickness; Visual impairment
Key Summary Points
Diabetic macular oedema (DMO) leads to progressive retinal dysfunction and if left untreated, irreversible vision loss. The disease affects 5.47% of patients with diabetes, globally.
Across key clinical guidelines, antivascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies, administered via intravitreal (IVT) injection, are recommended as first line treatment for patients with visual impairment due to DMO. The efficacy and safety of the anti-VEGF brolucizumab for this indication has been investigated by two phase 3 randomised head-to-head studies versus aflibercept (KESTREL and KITE).
The main aim of this study was to compare the relative efficacy of brolucizumab 6 mg via network metaanalysis (NMA) based on a focused network of the most relevant available anti-VEGFs (aflibercept 2 mg, ranibizumab 0.5 mg) approved in a number of countries other than the USA, including the UK; the safety and tolerability of brolucizumab were also assessed.
Brolucizumab 6 mg showed similar efficacy for key visual and anatomic outcomes including best-corrected visual acuity, diabetic retinopathy severity, and retinal thickness outcomes versus the relevant anti-VEGFs. Brolucizumab 6 mg showed an overall favourable benefit/risk \ profile with comparable rates of discontinuation and serious and overall adverse events to the other anti-VEGFs, except for ocular inflammatory and occlusive events.
This is the first analysis assessing the efficacy and safety of brolucizumab 6 mg for the treatment of patients with visual impairment due to DMO using this focused network of comparators.
