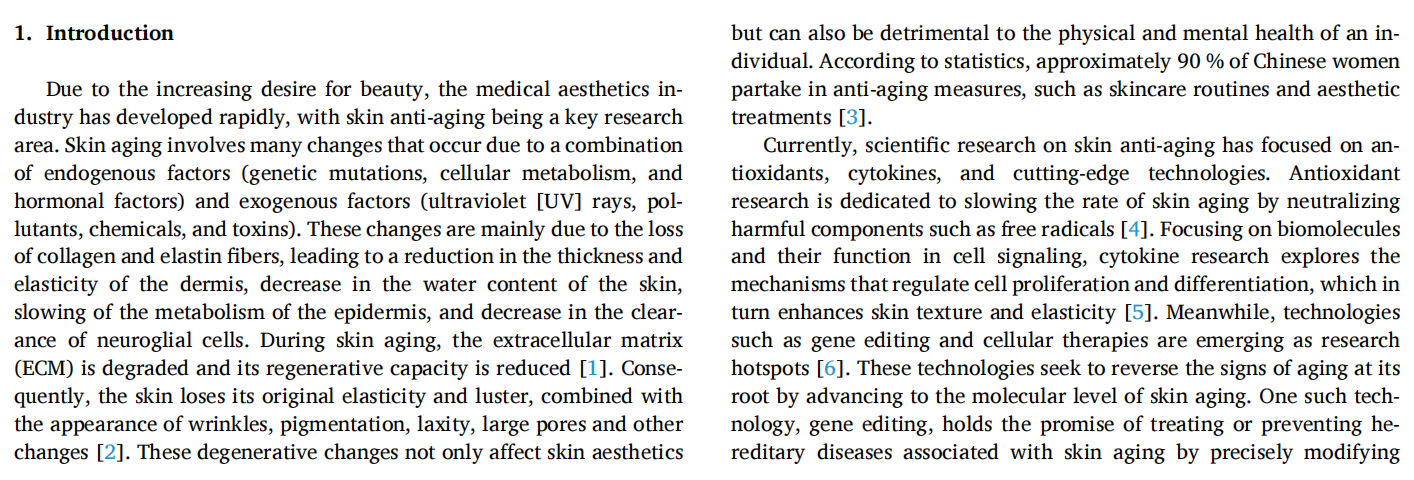

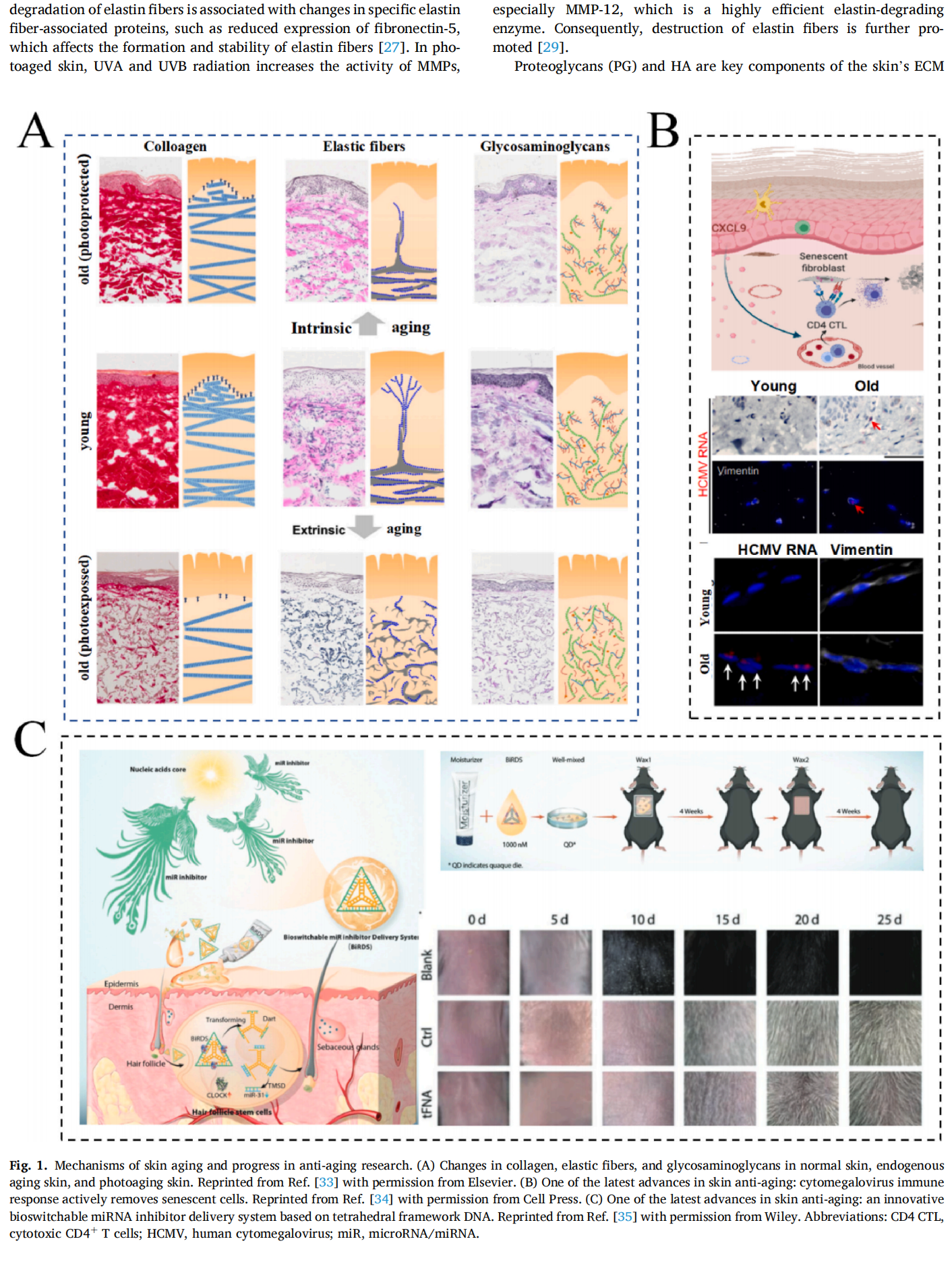

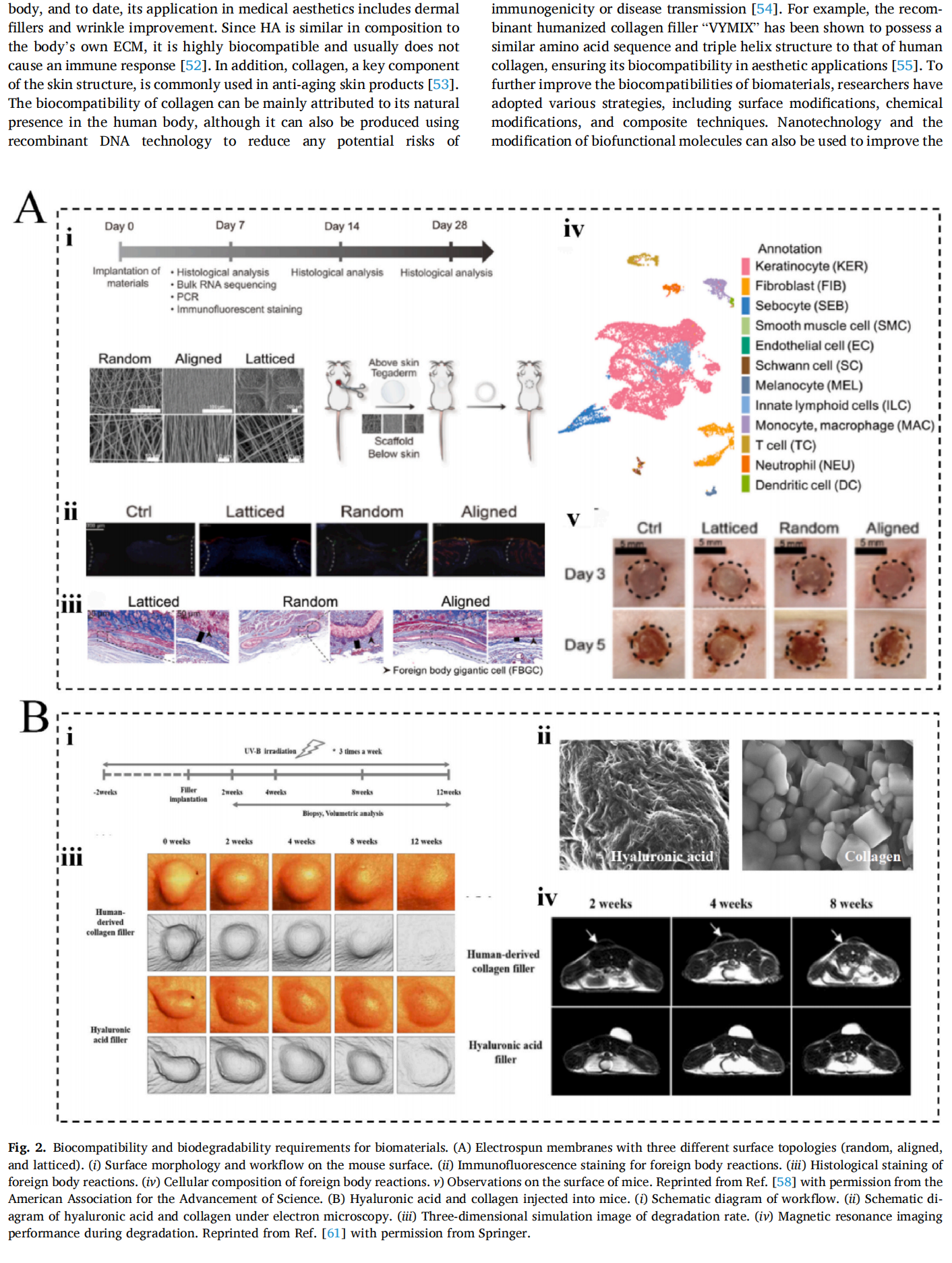

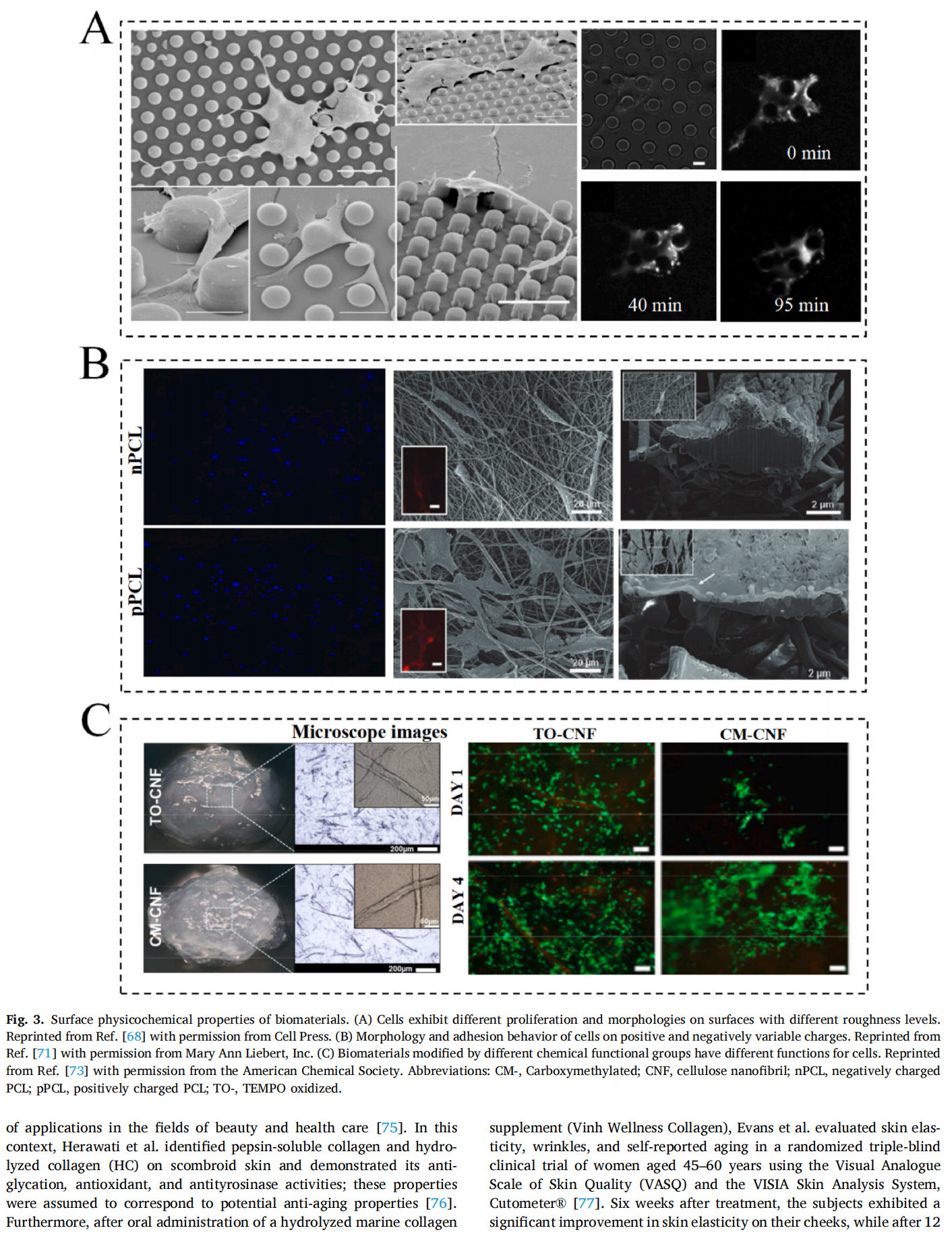
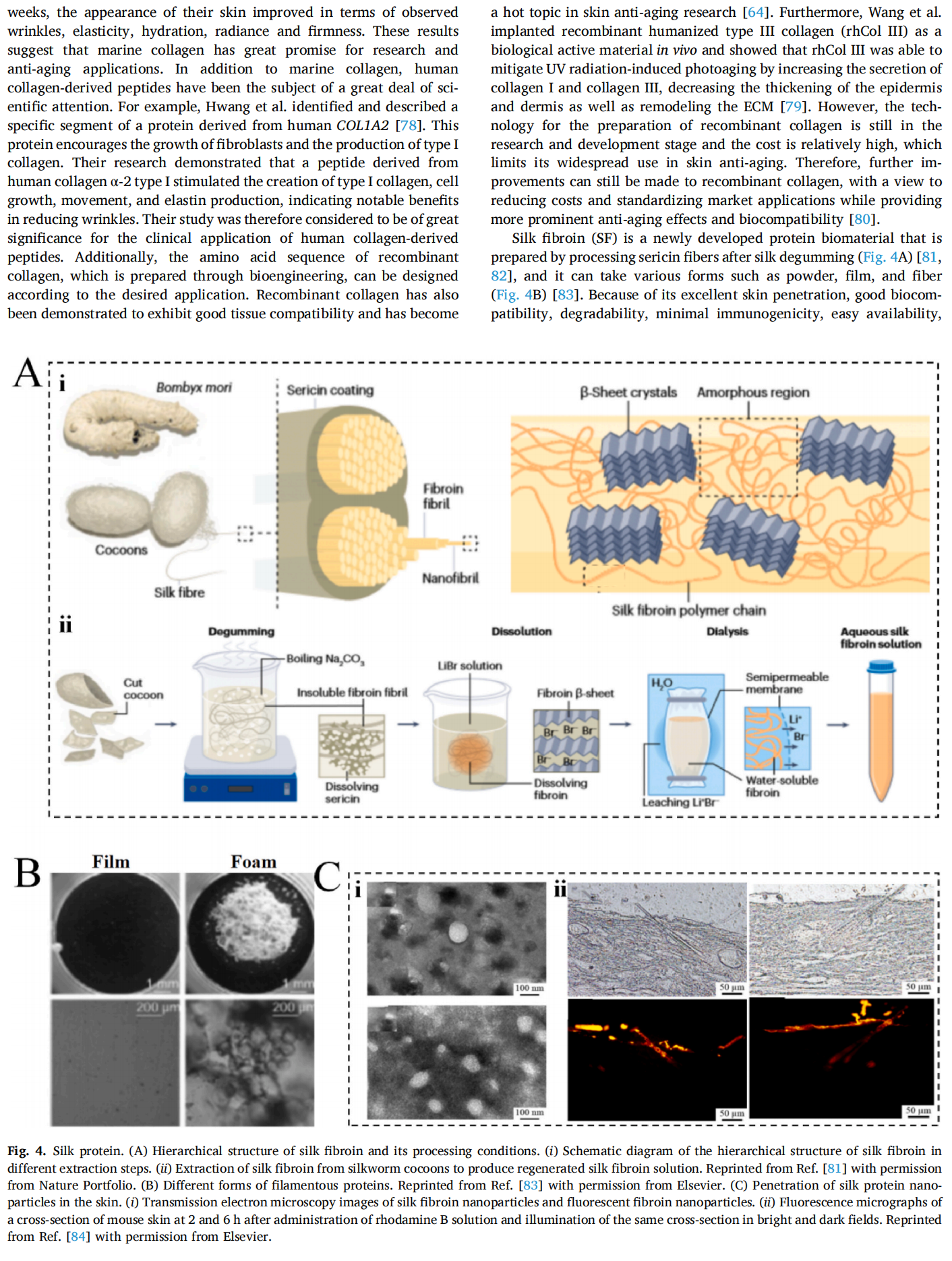
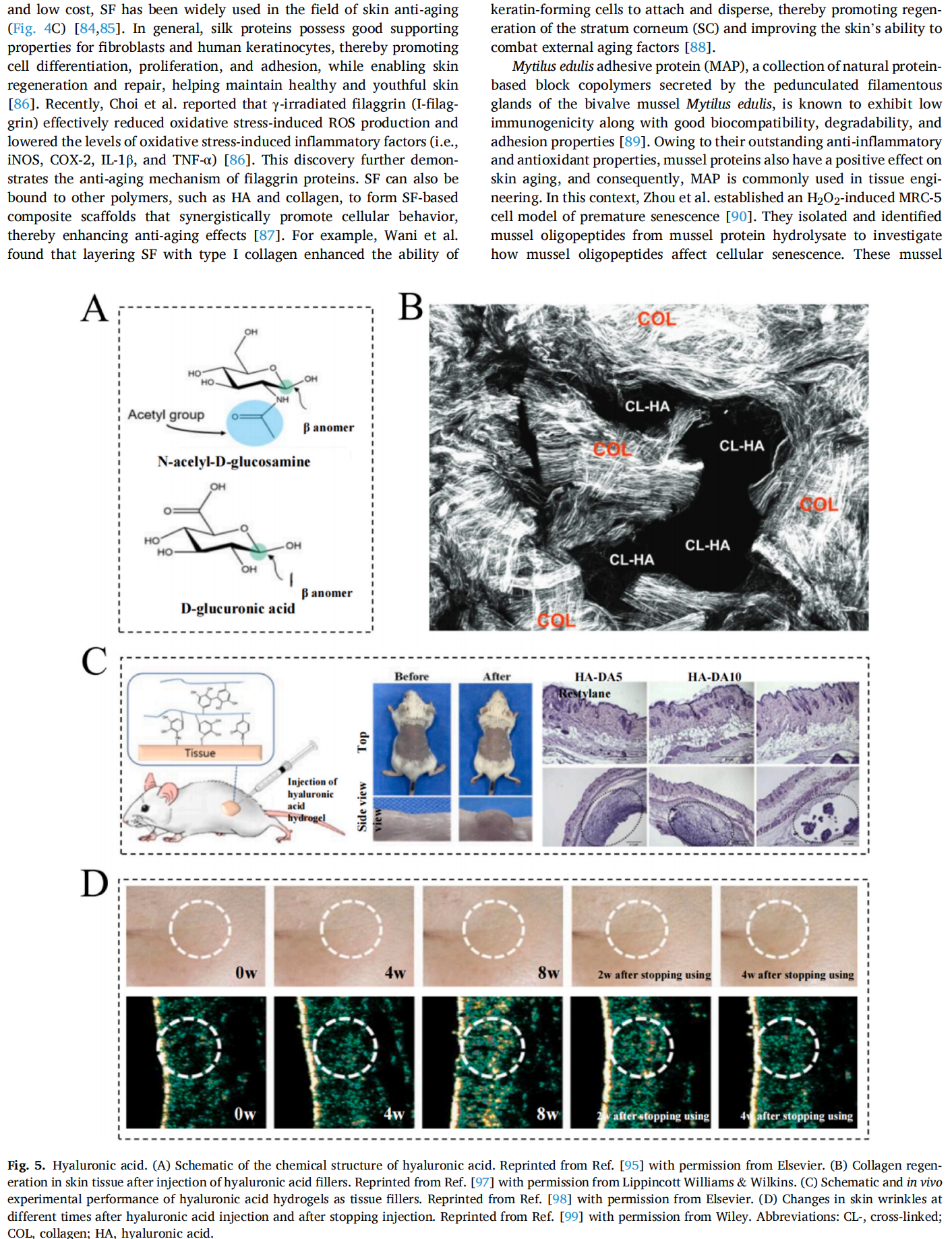





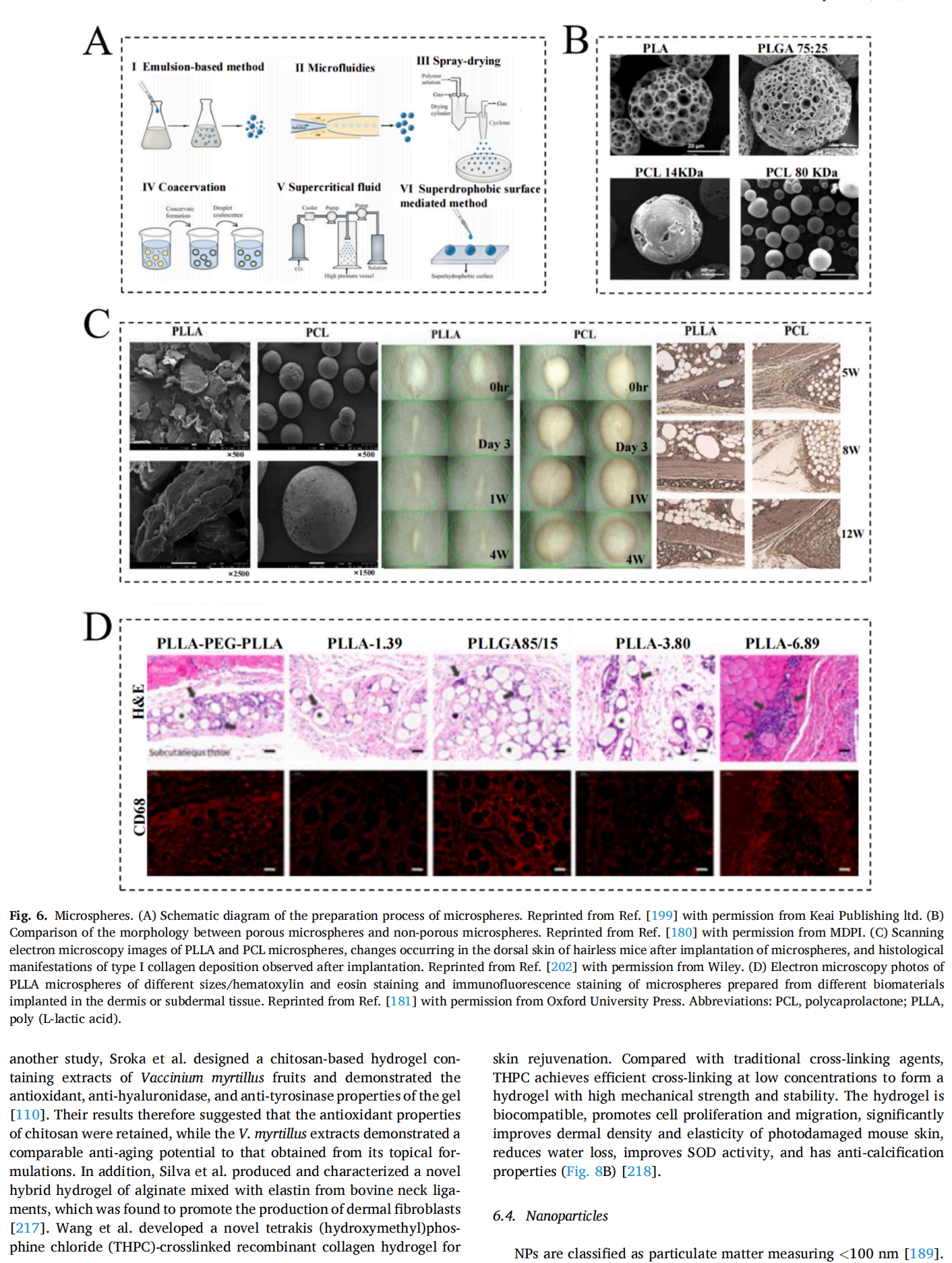
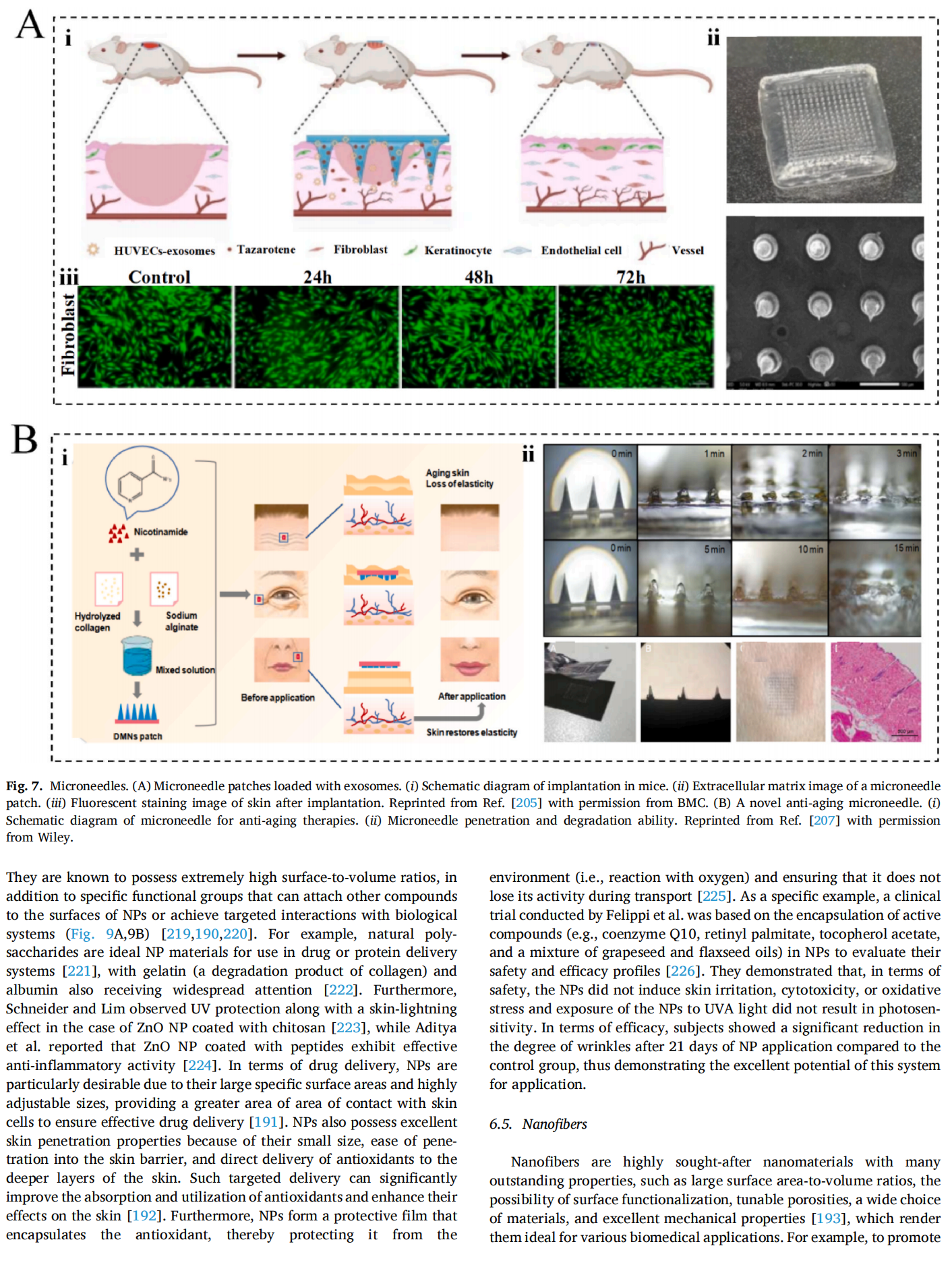







This article is excerpted from the Materials Today Bio 28 (2024) 101210 by Wound World.
Xin Dan a,1 , Songjie Li a,1 , Han Chen a , Ping Xue a , Bo Liu a , Yikun Ju b , Lanjie Lei c,**,
Yang Li a,***, Xing Fan a,*
a Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, 710032, China
b Department of Plastic and Aesthetic (Burn) Surgery, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, 410011, China
c Key Laboratory of Artificial Organs and Computational Medicine in Zhejiang Province, Institute of Translational Medicine, Zhejiang Shuren University, Hangzhou, 310015, China
* Corresponding author.
** Corresponding author.
*** Corresponding author.
E-mail addresses: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。 (L. Lei), 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。 (Y. Li), 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。 (X. Fan).
1 These authors contributed equally to this work and shared the first authorship.
ARTICLE INFO
Keywords:
Biomaterials、Skin anti-aging、Plastic surgery、Tissue regeneration、Medical aesthetics
ABSTRACT
Skin aging is the phenomenon of degenerative changes in the structure and function of skin tissues over time and is manifested by a gradual loss of skin elasticity and firmness, an increased number of wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. Skin anti-aging refers to a reduction in the skin aging phenomenon through medical cosmetic technologies. In recent years, new biomaterials have been continuously developed for improving the appearance of the skin through mechanical tissue filling, regulating collagen synthesis and degradation, inhibiting pigmentation, and repairing the skin barrier. This review summarizes the mechanisms associated with skin aging, describes the biomaterials that are commonly used in medical aesthetics and their possible modes of action, and discusses the application strategies of biomaterials in this area. Moreover, the synergistic effects of such biomaterials and other active ingredients, such as stem cells, exosomes, growth factors, and antioxidants, on tissue regeneration and anti-aging are evaluated. Finally, the possible challenges and development prospects of biomaterials in the field of anti-aging are discussed, and novel ideas for future innovations in this area are summarized.


























This article is excerpted from the Materials Today Bio 28 (2024) 101210 by Wound World.
