




This article is excerpted from the RSC Medicinal Chemistry by Wound World.
Zhenyuan Wang,ab Mi Wang, *a Qingsheng Tao,c Yufei Li, d Hao Wang,a Mei Zhang,c Xueli Liuc and Jiaheng Zhang *a
a Sauvage Laboratory for Smart Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518055, China. E-mail: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。, 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
b Shenzhen Shinehigh Innovation Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen 518055, China
c Advanced Research, L'Oreal Research & Innovation China, Shanghai 201206, China
d The Centre in Artificial Intelligence Driven Drug Discovery, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Macao Polytechnic University, Macao 999078, China
† Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 2101906. For ESI
and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.
org/10.1039/d5md00001g
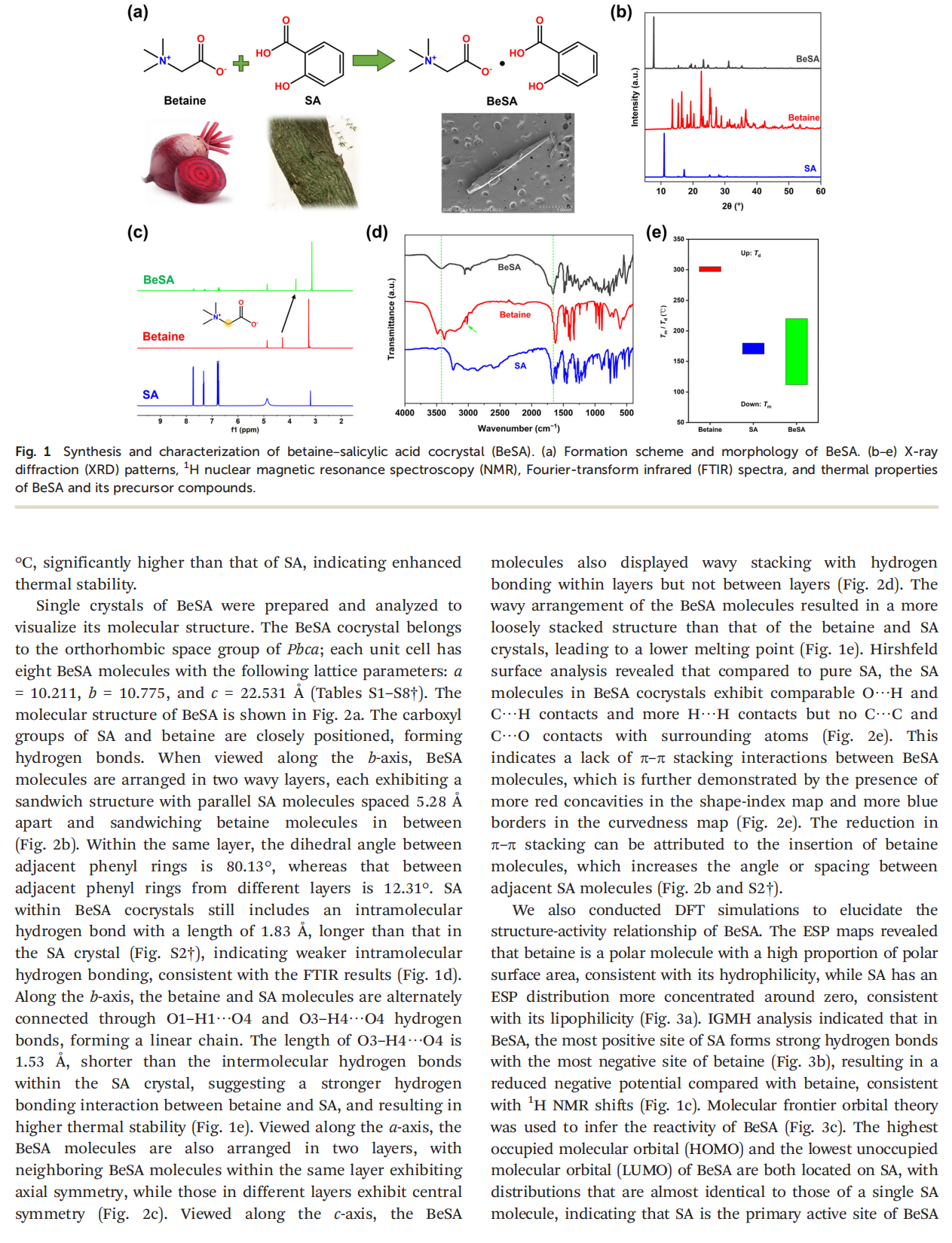
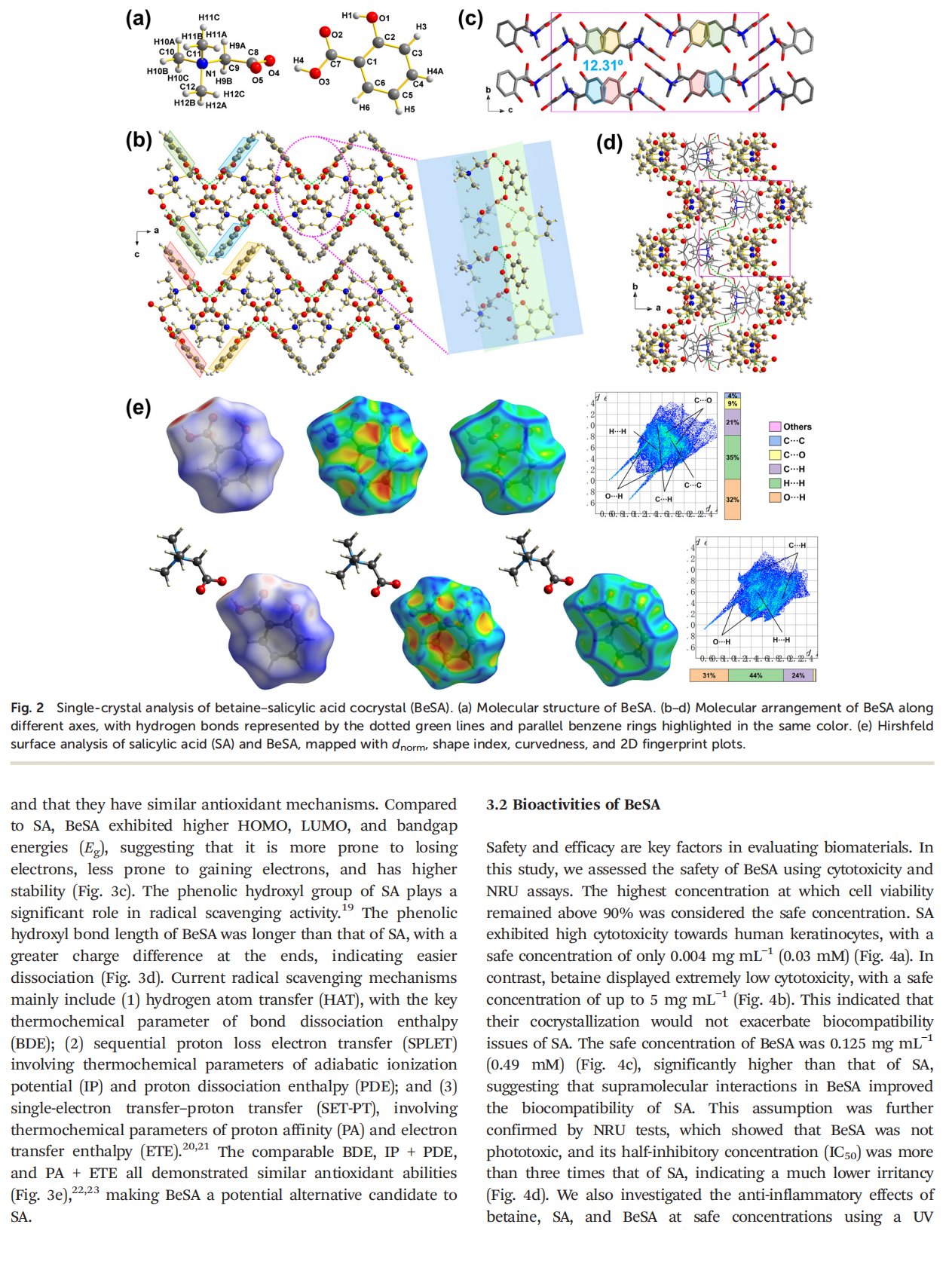
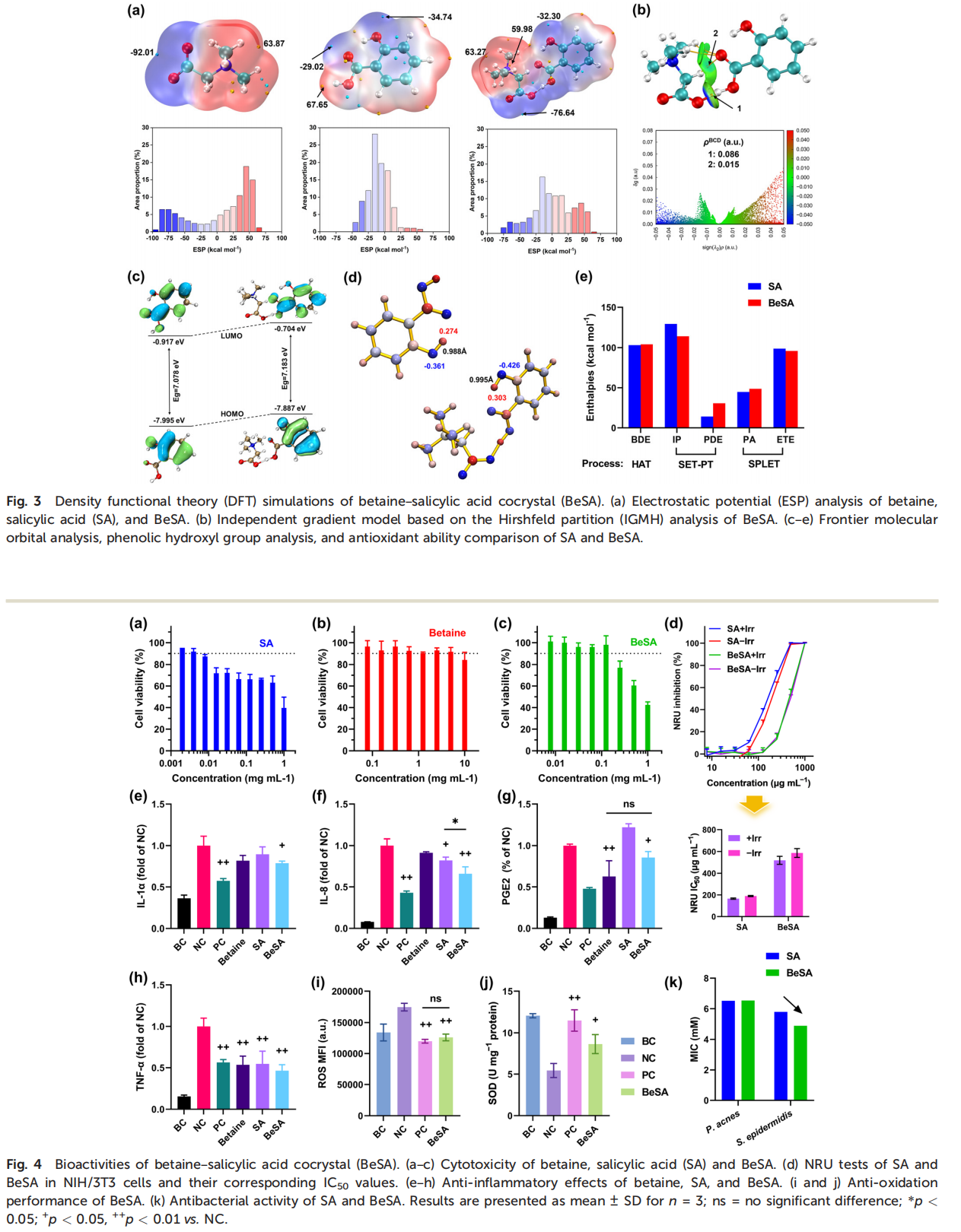
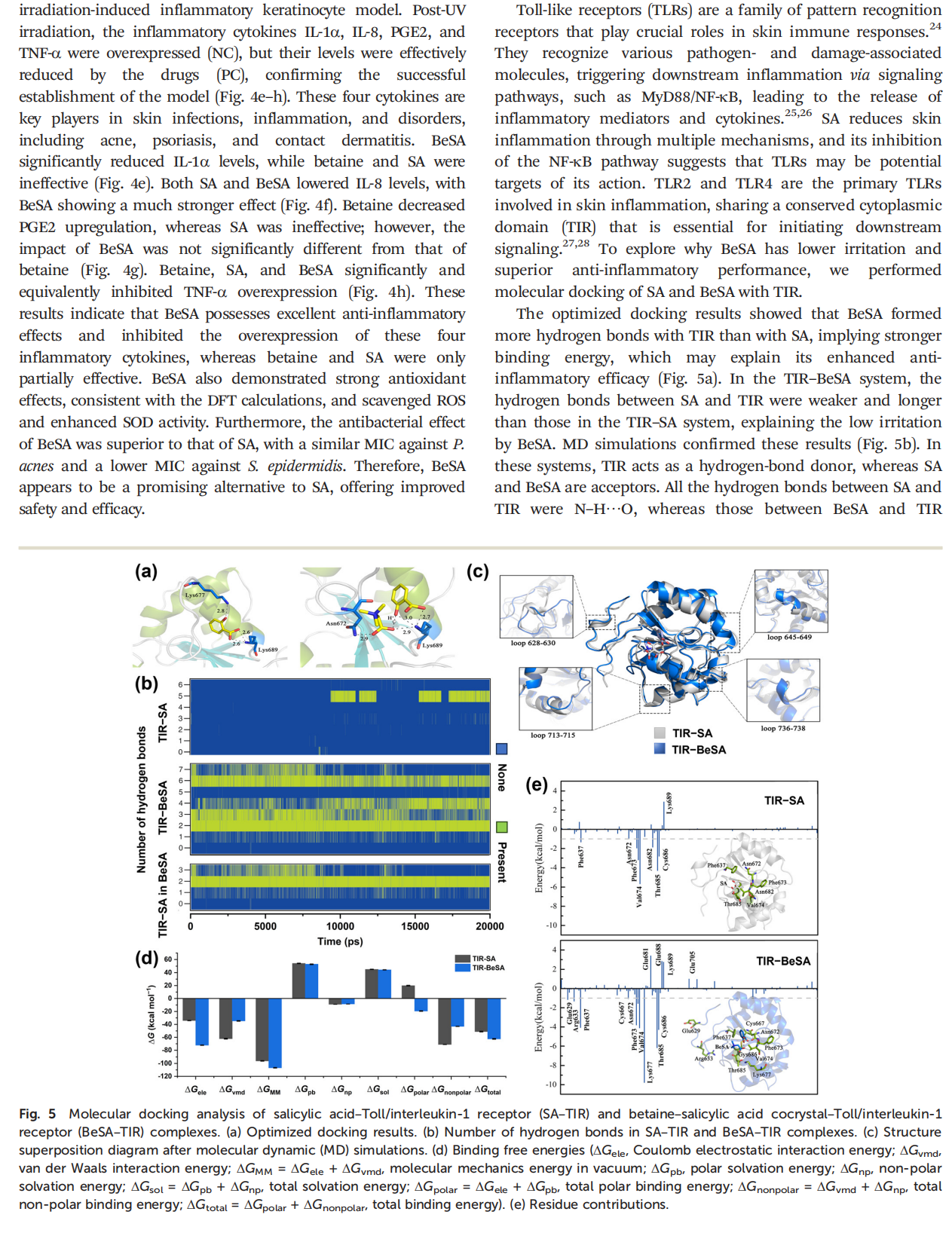
Salicylic acid (SA) is a natural lipophilic active ingredient commonly used in cosmetics and skin disease treatments, offering benefits such as exfoliation, anti-inflammation effects, antibacterial properties, oil control, and acne alleviation. However, its poor water solubility, low bioavailability, and potential side effects, such as allergies, irritation, and dryness, hinder its widespread application. In this study, we prepared a betaine–salicylic acid (BeSA) cocrystal and systematically characterized its crystal structure, biological activity, and clinical efficacy. The results showed that BeSA has significantly lower irritancy and cytotoxicity than SA, but exhibits excellent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties as well as high moisturizing and anti-acne efficacy, making it a potential alternative to SA. Further, quantum chemical calculations and molecular docking simulations were conducted to investigate the intrinsic mechanisms underlying the excellent bioactivity of BeSA cocrystals. This study introduces an innovative solution for safer and more effective skincare formulations based on SA and offers theoretical guidance regarding material engineering and further material optimization, which has crucial implications for both industry and academia.
Received 1st January 2025,
Accepted 4th February 2025
DOI: 10.1039/d5md00001g rsc.li/medchem










This article is excerpted from the RSC Medicinal Chemistry by Wound World.
