

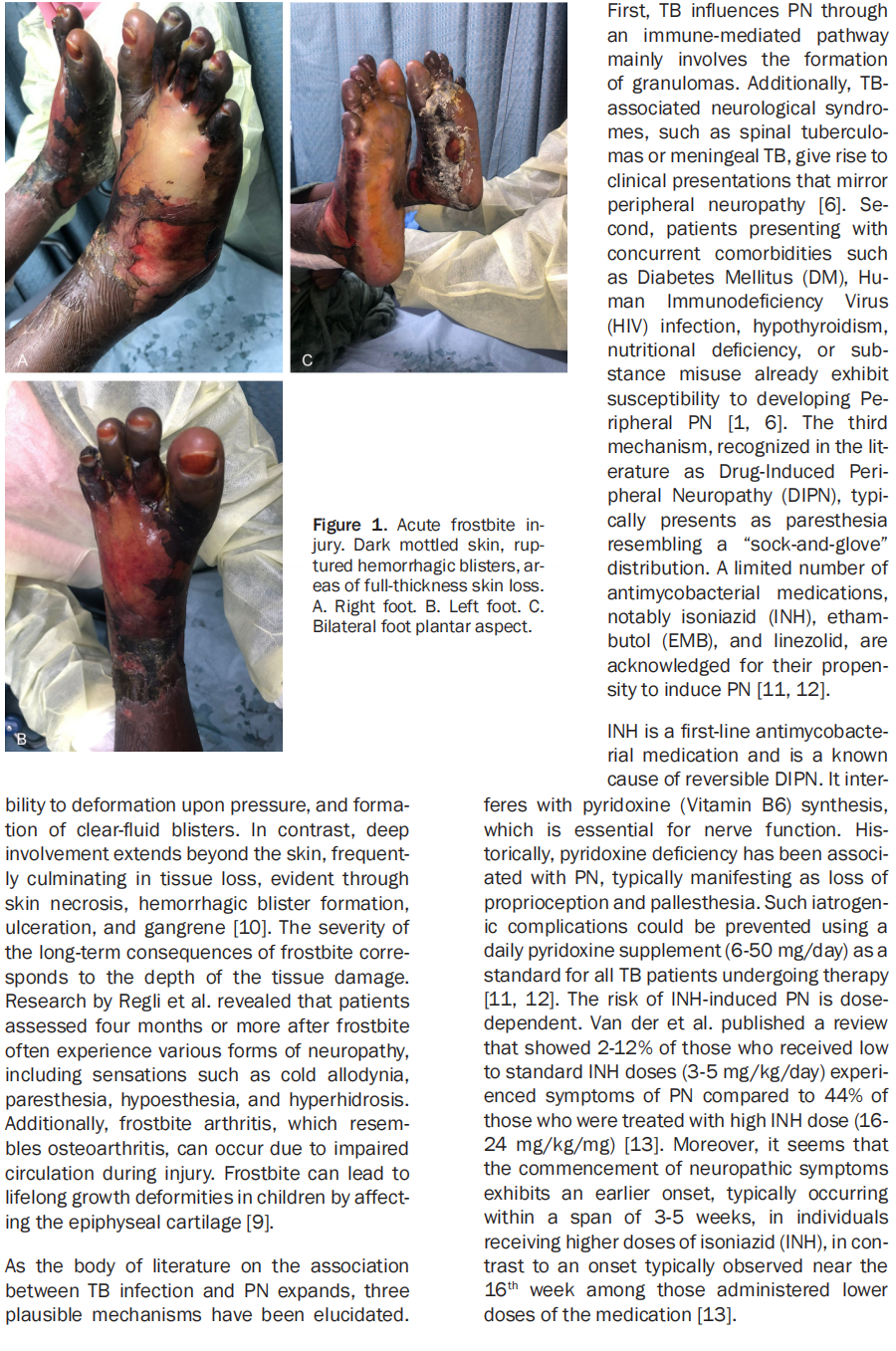
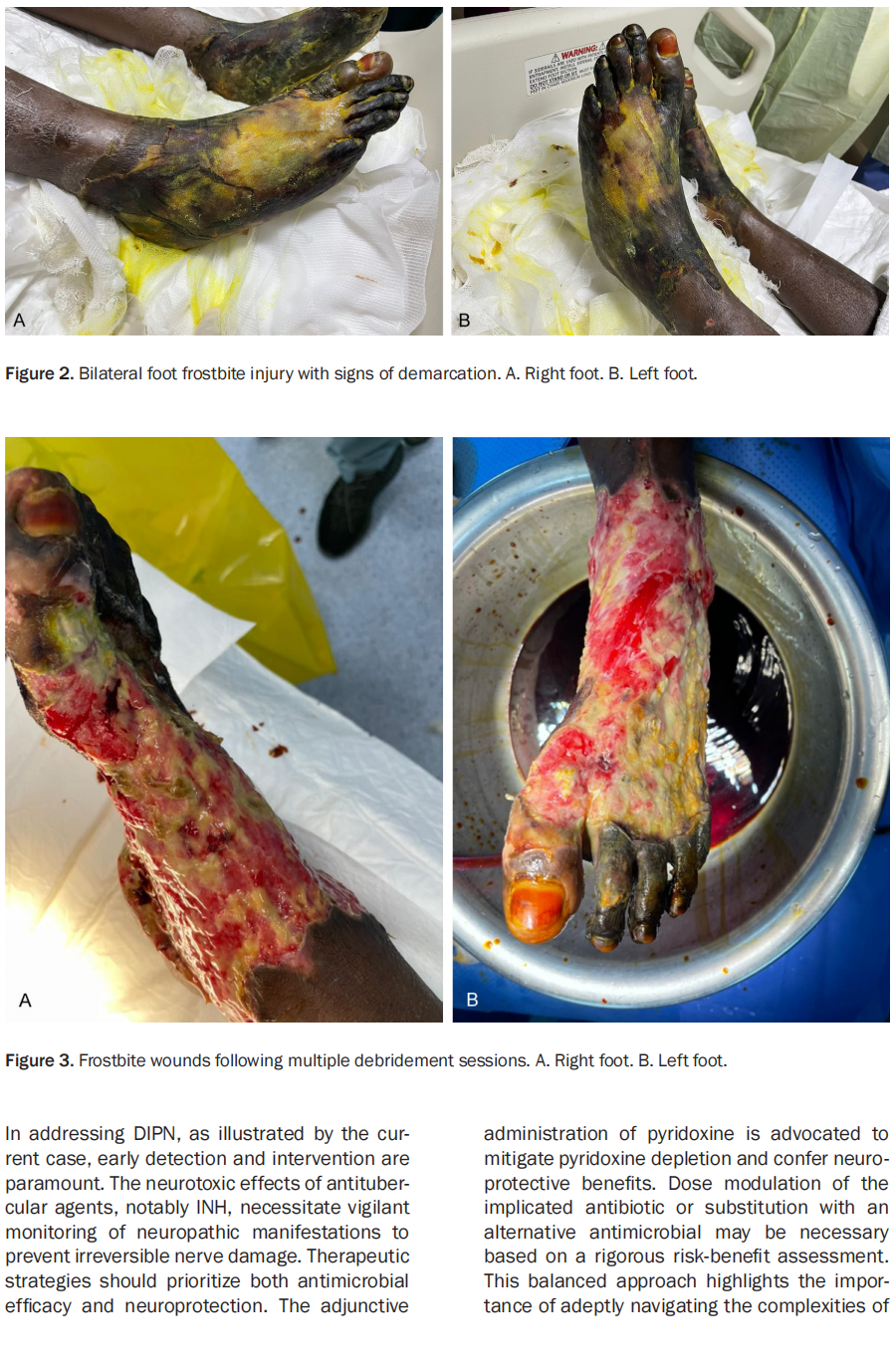
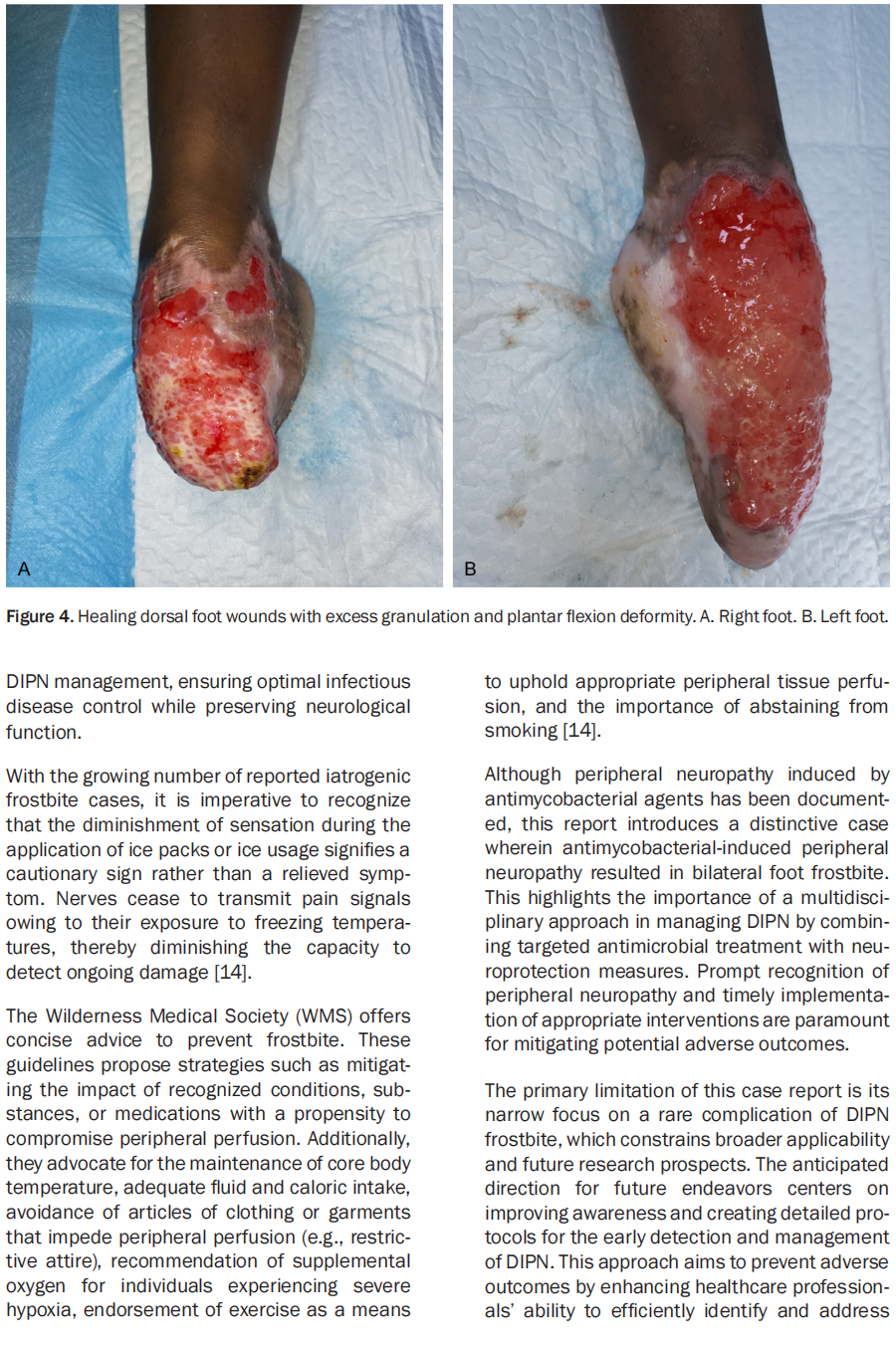

This article is excerpted from the Int J Burn Trauma 2024;14(2):32-37 by Wound World.
Shahad N Alanazi1 , Dana A Bali1 , Nawaf M Alwagdani2 , Youssof Mal3 , Maram T Alkhatieb4 , Hattan A AlJaaly1 , Zahir T Fadel1
1 Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; 3Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine in Rabigh, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; 4Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Received October 24, 2023; Accepted March 13, 2024; Epub April 15, 2024; Published April 30, 2024
Abstract: This case report describes a unique scenario in which antimycobacterial-induced peripheral neuropathy (PN) culminates in severe bilateral foot frostbite. Drug-induced peripheral neuropathy (DIPN) is explored in the context of TB treatment, highlighting the role of medications such as isoniazid (INH) and their potential to cause PN. The report highlights the importance of identifying PN in patients undergoing antimycobacterial treatment. Early recognition and proper management of PN is crucial to prevent complications. Notably, the report advocates for patient education regarding medication side effects and avoiding harmful practices, such as ice immersion, to alliviate neuropathic pain. Emphasis is directed towards the need for a multidisciplinary approach to patient care and a focus on preventative strategies to improve patient outcomes and avoid severe debilitating complications.
Keywords: Frostbite, peripheral neuropathy, isoniazid (INH), drug-induced peripheral neuropathy (DIPN)






This article is excerpted from the Int J Burn Trauma 2024;14(2):32-37 by Wound World.
