
This article is excerpted from the J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024. 34(1): 65–73 by Wound World.
Kyung Min Kim, Ji-Won Song, Chang-Wan Lee, Du-Seong Kim, Johann Sohn, and Seunghun Lee*
Biohealthcare R&D Center, HYUNDAI BIOLAND Co., Ltd., Ansan 15407, Republic of Korea
Received: June 26, 2023
Accepted: September 19, 2023
First published online:
October 19, 2023
*Corresponding author
Phone: +82-31-8085-7514
Fax: +82-31-8085-7605
E-mail: shunlee@hyundaibioland.
co.kr
Supplementary data for this paper are available on-line only at http://jmb.or.kr.
pISSN 1017-7825
eISSN 1738-8872
Copyright © 2024 by the authors. Licensee KMB. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
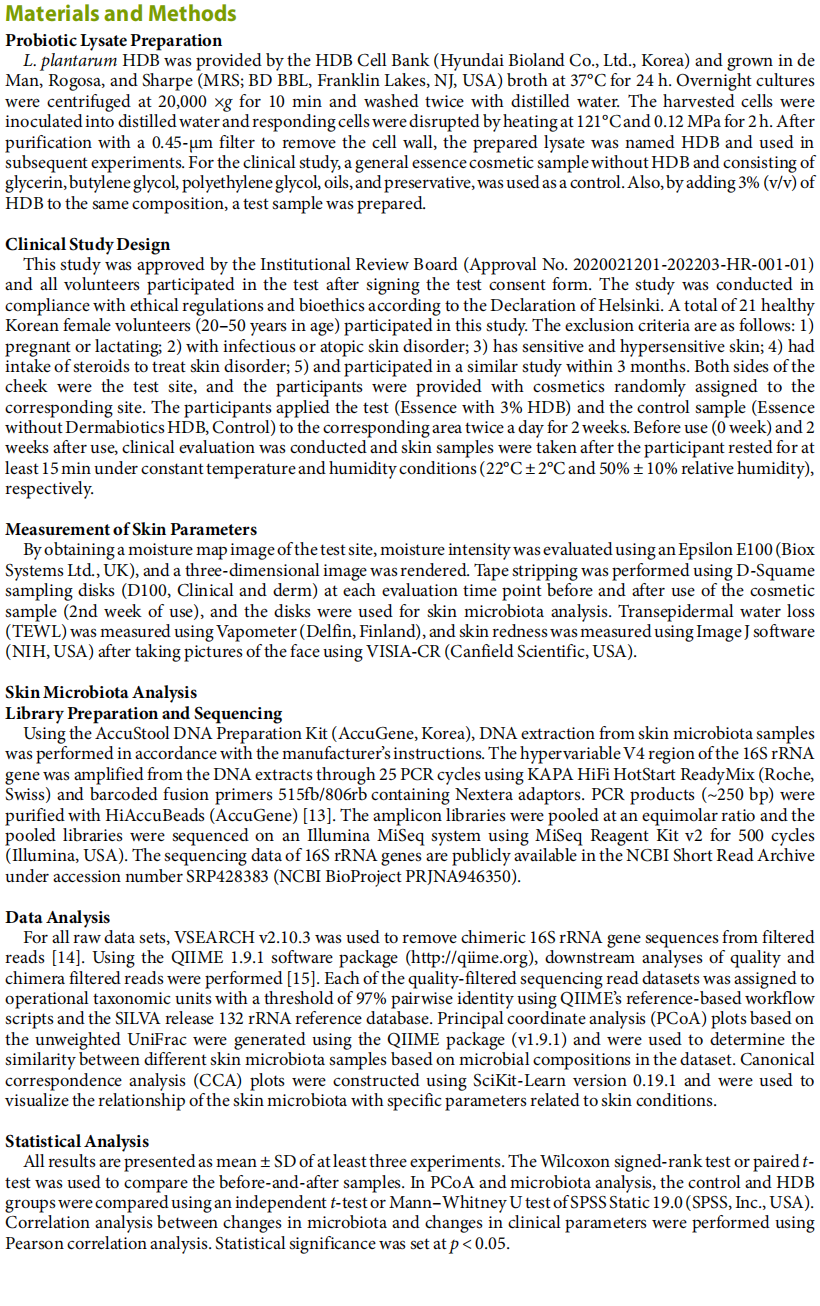
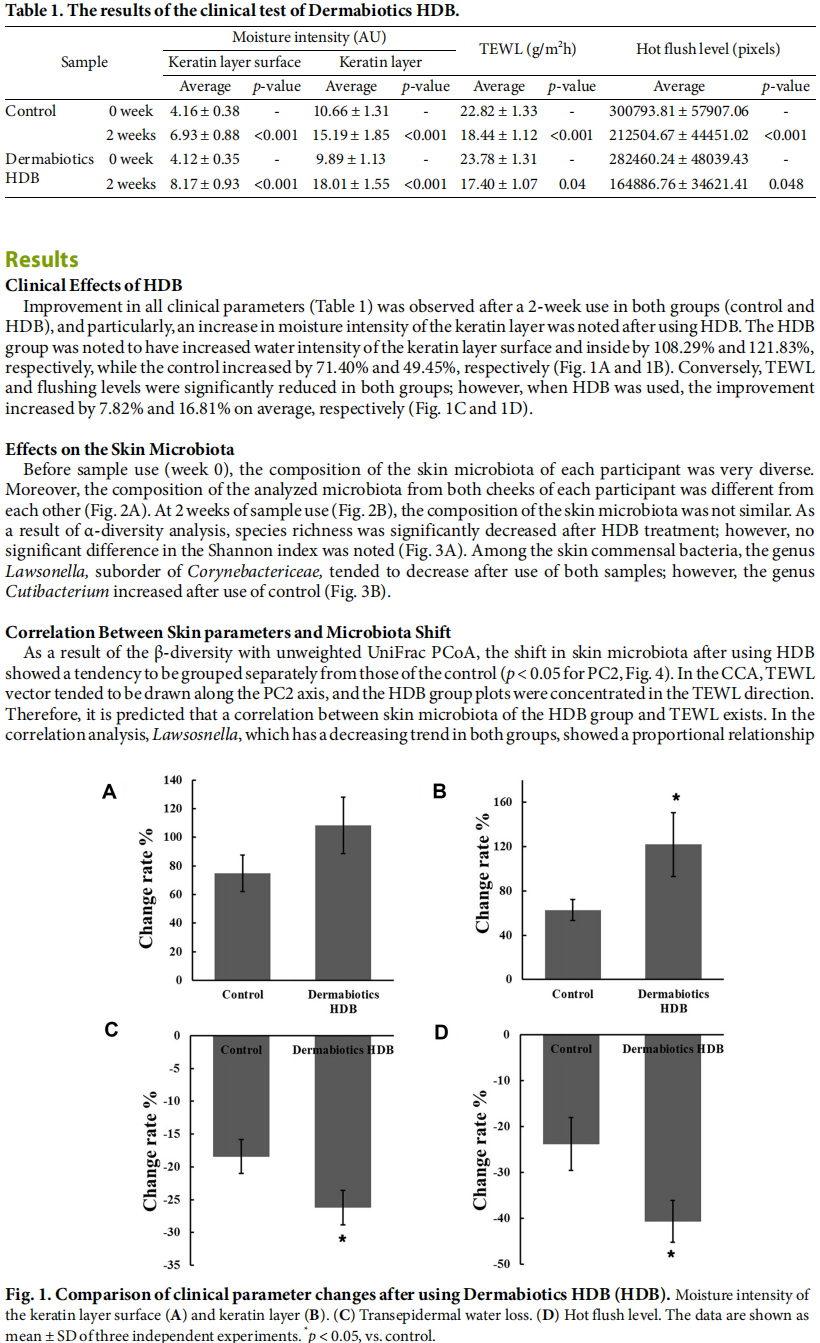
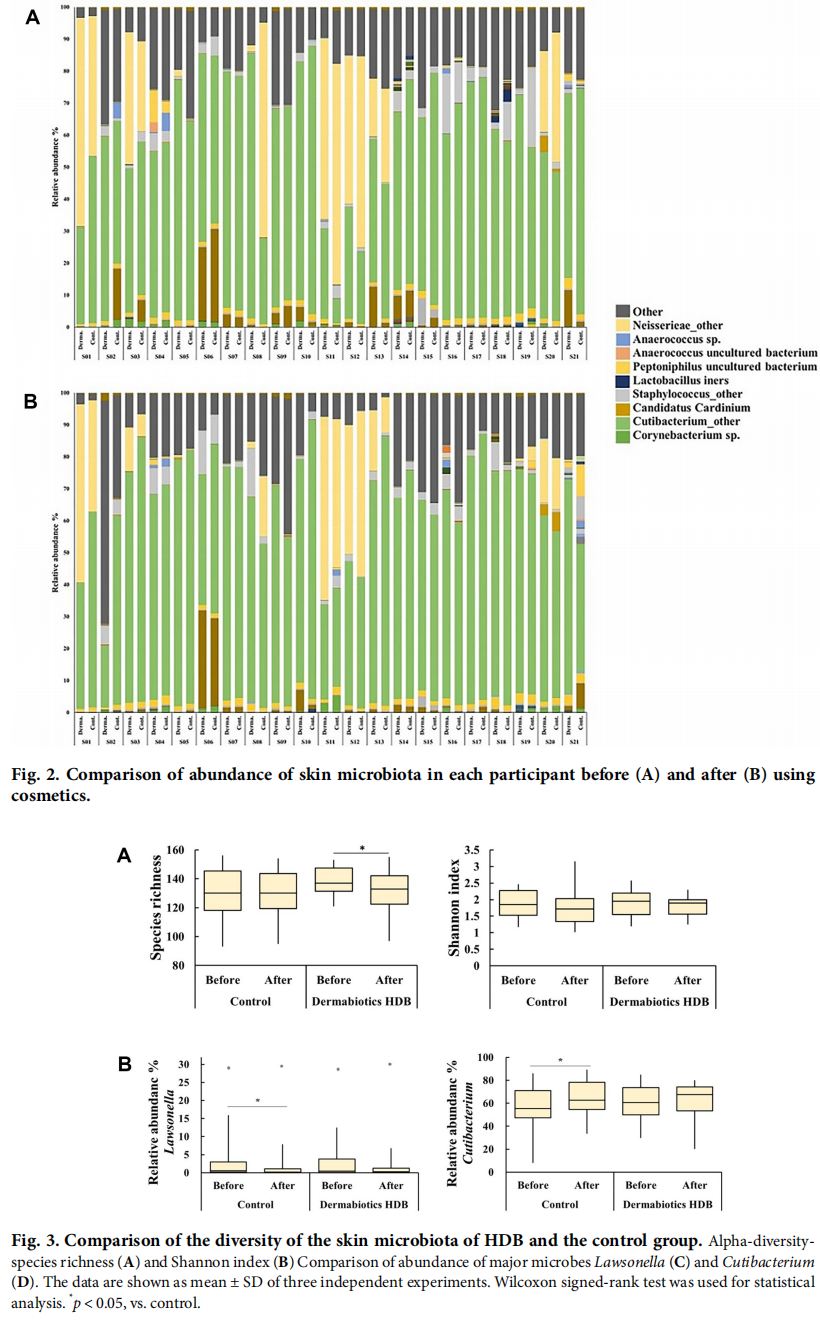
In the regulation of inflammatory responses and skin homeostasis, the skin and its microbiota are closely related. Studies have reported that lactic acid bacteria extracts can improve the skin condition and microbiota. In our previous study, we developed probiotic lysates, which are efficacious in improvement of human skin cells and the skin barrier. The skin-moisturizing effect of Dermabiotics HDB (HDB) prepared with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, and the correlation between changes in the skin microbiota and moisture contents, were evaluated and analyzed in clinical trials. The clinical parameters on the cheeks of 21 female participants were measured using biophysical tools before and after (2 weeks) using HDB or control. The skin microbes were collected and identified using 16s rRNA gene sequencing. HDB significantly improved moisture intensity, transepidermal water loss (TEWL), and hot flush level on the cheek. The beta-diversity of the skin microbiota was different from that of the control in the unweighted UniFrac principal coordinate analysis after using HDB. The genus Lawsonella demonstrated a positive correlation with TEWL and a negative correlation with the moisture contents of the keratin layer, regardless of the use of HDB and control. Conversely, after HDB use, the genus Staphylococcus was increased and associated with a lower hot flush level, while the genera of the phylum Proteobacteria tended to decrease, which is associated with an improved skin condition. Overall, HDB showed clinically proven effects, including skin moisturization with regulation of the skin microbiota.
Keywords: Probiotics, cell lysate, skin moisturizing, skin microbiota









This article is excerpted from the J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024. 34(1): 65–73 by Wound World.
