










This article is excerpted from the from Skin Res Technol. 2024;30:e13679 by Wound World.
Nguyen Ngan Giang1,2 Hyun Ji Kim3 Pham Ngoc Chien2,3 Han Jin Kwon4 Jung Ryul Ham4 Won Ku Lee4 Yeon Ju Gu4 Shou Yi Zhou2,5 Xin Rui Zhang2,5 Sun Young Nam2 Chan Yeong Heo1,2,3,5
1 Department of Medical Device Development, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, South Korea
3 Korea Institute of Nonclinical Study, H&Bio. co. Ltd., Seongnam, Republic of Korea
4 UltraV Co., Ltd. R&D Center, Seoul, South Korea
5 Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Correspondence Sun Young Nam and Chan Yeong Heo, Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
Email: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。 and 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。
Abstract
Background: Injectable filler, a nonsurgical beauty method, has gained popularity in rejuvenating sagging skin. In this study, polydioxanone (PDO) was utilized as the main component of the ULTRACOL200 filler that helps stimulate collagenesis and provide skin radiant effects. The study aimed to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of ULTRACOL200 with other commercialized products in visually improving dermatological problems.
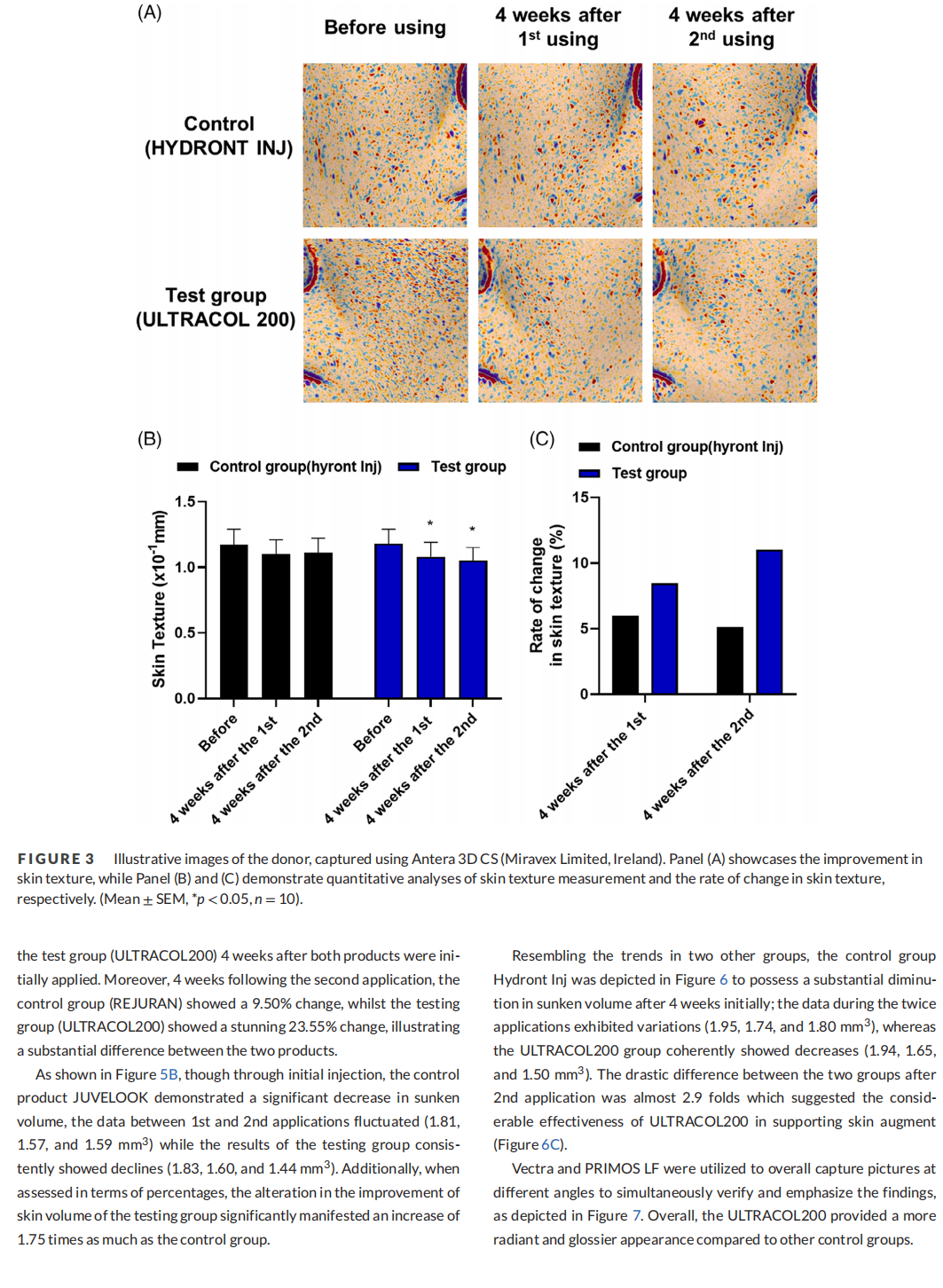
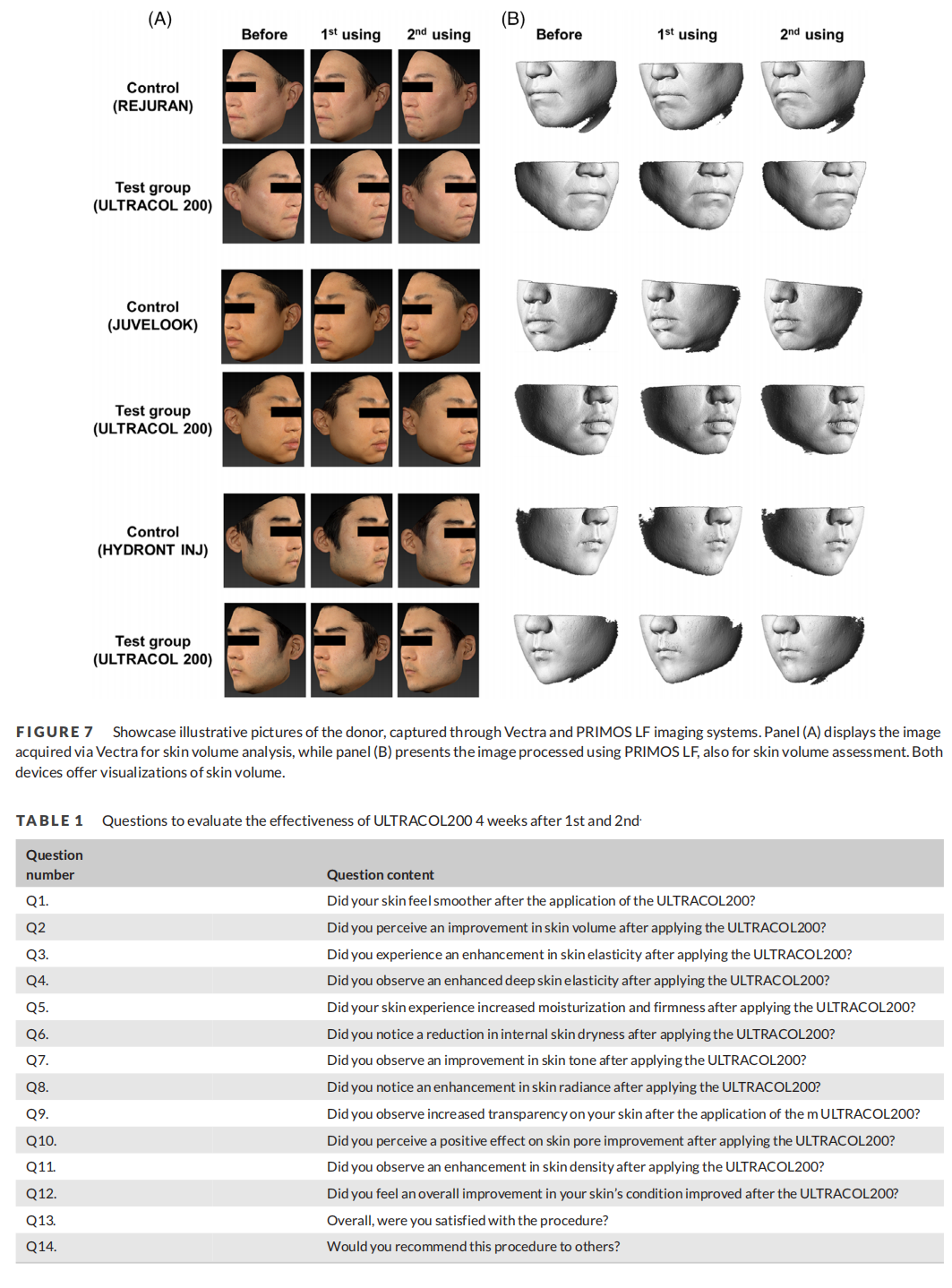
Methods: Herein, 31 participants aged between 20 and 59 years were enrolled in the study. 1 mL of the testing product, as well as the quantity for the compared groups was injected into each participants face side individually. Subsequently, skin texture and sunken volume of skin were measured using ANTERA 3D CS imaging technology at three periods: before the application, 4 weeks after the initial application, and 4 weeks after the 2nd application of ULTRACOL200.
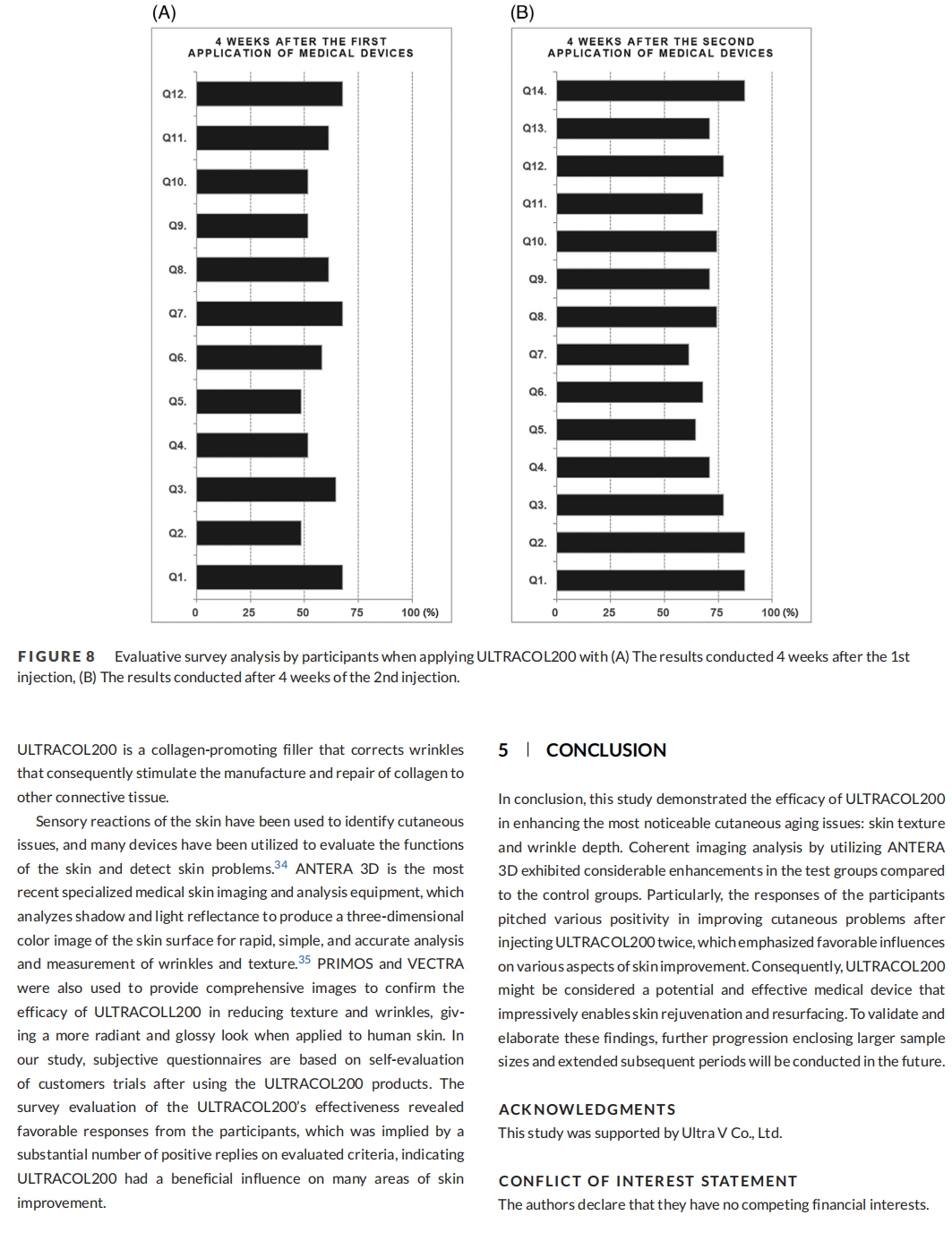
Results: The final results of skin texture and wrinkle volume evaluation consistently demonstrated significant enhancement. Consequently, subjective questionnaires were provided to the participants to evaluate the efficacy of the testing product, illustrating satisfactory responses after the twice applications.
Conclusion: The investigation has contributed substantially to the comprehension of a PDO-based filler (ULTRACOL200) for skin enhancement and provided profound insight for future clinical trials.
KEYWORDS collagen formation, filler, polydioxanone, skin enhancement, Ultracol200














This article is excerpted from the from Skin Res Technol. 2024;30:e13679 by Wound World.
