
This article is excerpted from the Journal of Medical Ultrasound ¦ Volume 32 ¦ Issue 3 ¦ July-September 2024 by Wound World.
Hassan Nasreddine1 , Yehya Tlaiss2 *, Firas Hassan2 , Reina Ibrahim2
1 Department of Plastic Surgery, Specialized Hospital Haidar and Hajjar, Beirut, Lebanon,
2 Department of General Surgery, University of Balamand, Beirut, Lebanon
Abstract
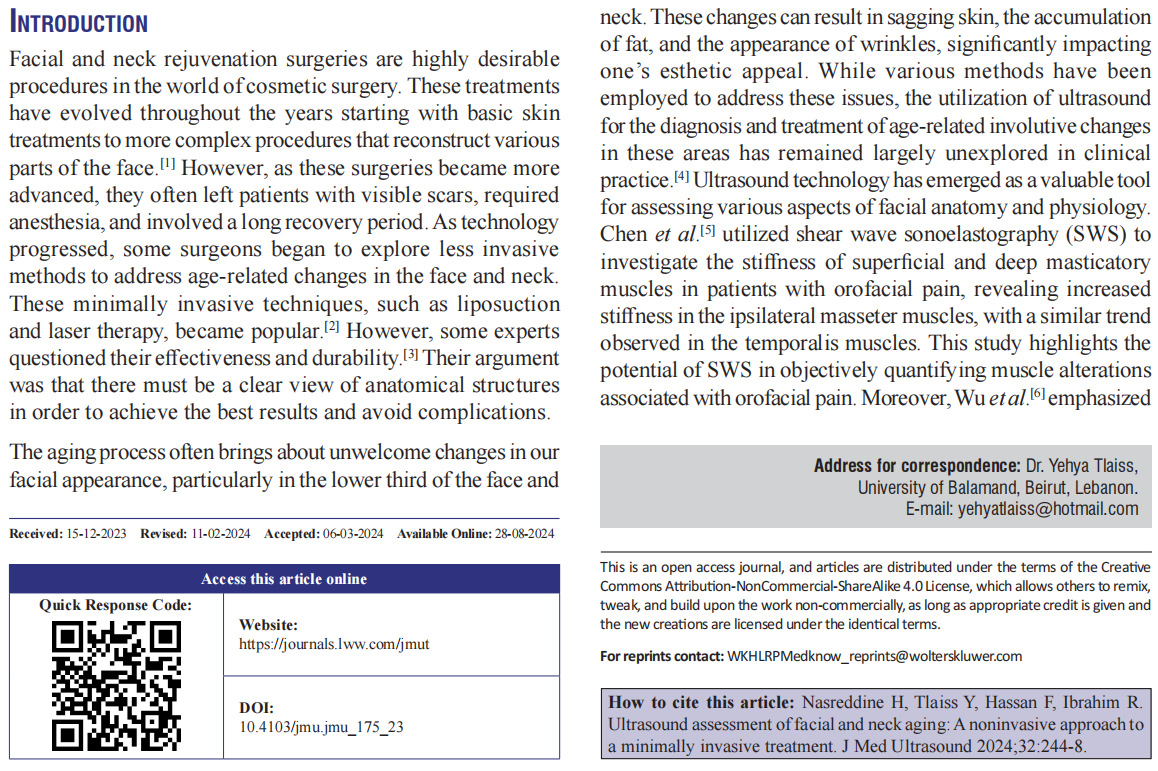
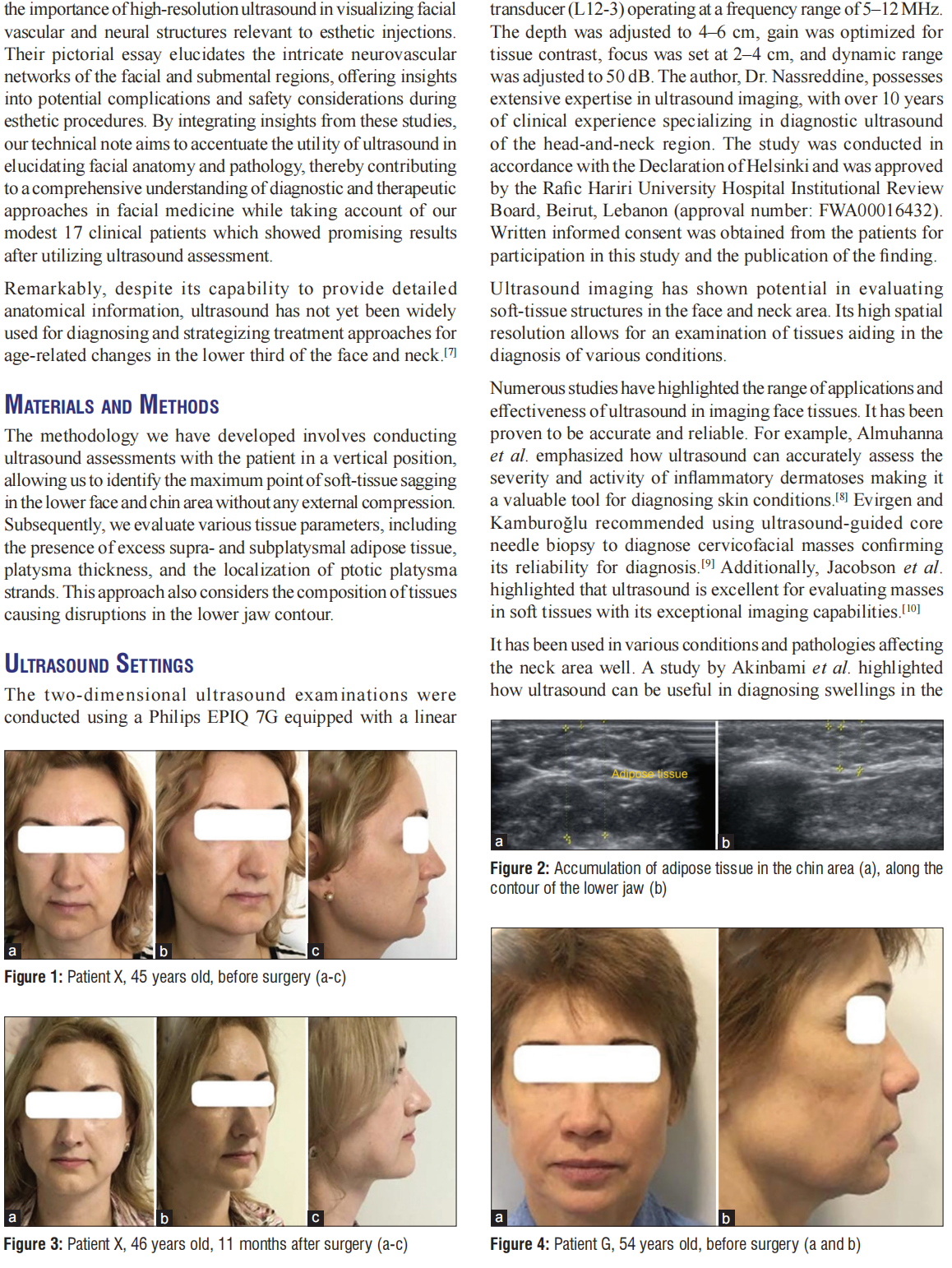
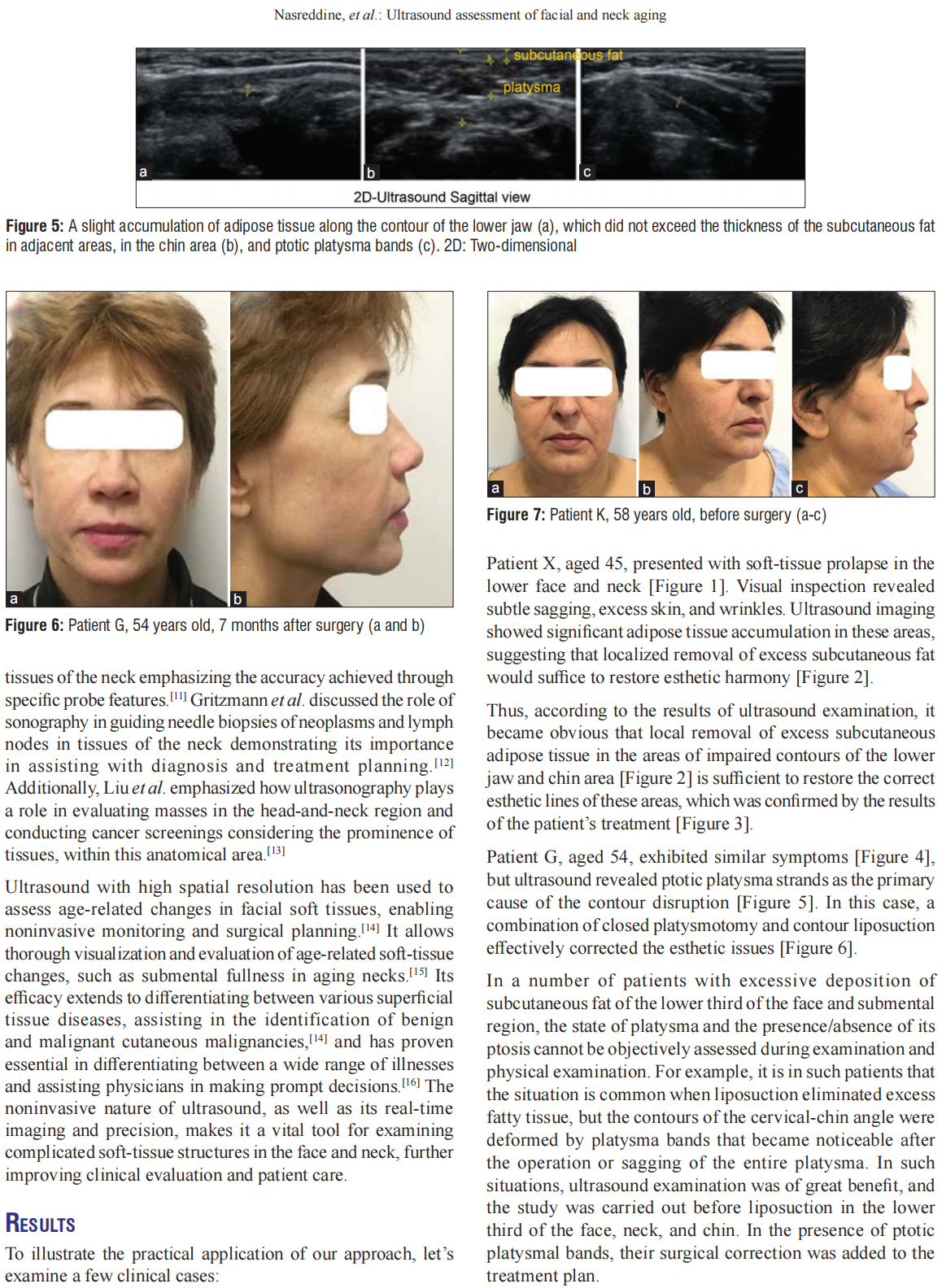
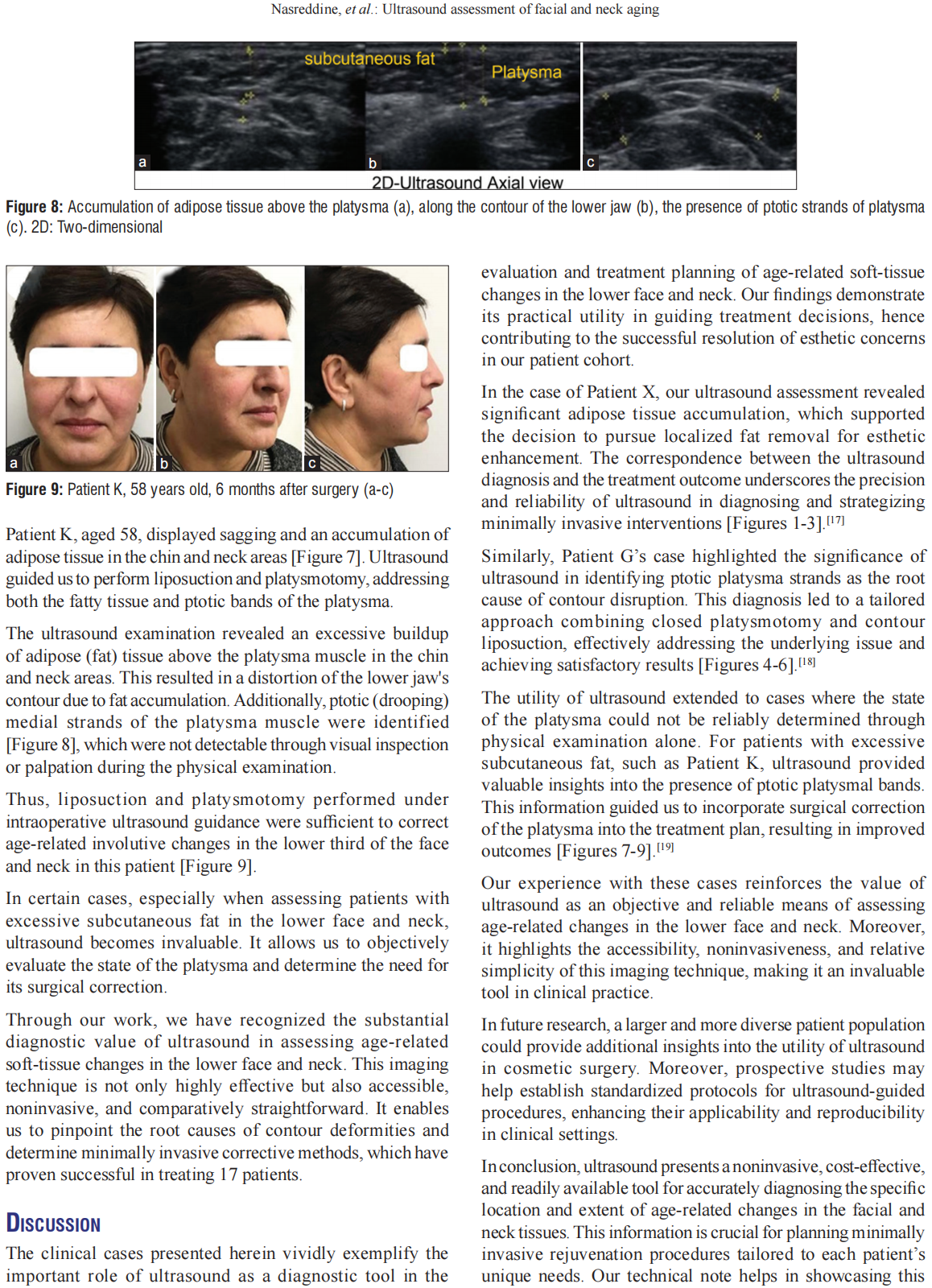
This technical note explores the diagnostic potential of ultrasound in assessing age‑related changes in the soft tissues of the lower face and neck, with a primary focus on identifying causes of contour deformities and guiding minimally invasive rejuvenation procedures. Seventeen clinical patients with various age‑related soft‑tissue changes were subjected to ultrasound assessments, targeting issues such as soft‑tissue sagging, supra‑ and subplatysmal adipose tissue excess, platysma thickness, and localization of ptotic platysma strands. The ultrasound examinations successfully identified specific anatomical features contributing to age‑related soft‑tissue changes in all 17 patients. This information guided tailored treatment plans, resulting in remarkable esthetic improvements in each case. The discussion emphasizes ultrasound’s invaluable role as a diagnostic tool for precisely identifying soft-tissue alterations in the lower face and neck. The noninvasive nature and high spatial resolution of ultrasound make it particularly effective for this purpose. The corrective methods guided by ultrasound findings proved to be minimally invasive and yielded successful outcomes in all cases, promoting high levels of patient satisfaction. The study highlights the underutilization of ultrasound’s diagnostic potential in clinical practice and highlights the importance of its incorporation into routine assessments. Ultrasound emerges as a cost‑effective, noninvasive, and accessible means of accurately diagnosing age‑related soft‑tissue changes, empowering clinicians to tailor rejuvenation procedures to each patient’s unique needs. The hope is that by emphasizing its utility, this study encourages the broader adoption of ultrasound in clinical practice.
Keywords: Face and neck, noninvasive, plastic surgery, ultrasound





This article is excerpted from the Journal of Medical Ultrasound ¦ Volume 32 ¦ Issue 3 ¦ July-September 2024 by Wound World.