Until 2022, there were no definite guidelines for the screening of vitamin B12 deficiency in patients taking metformin. Thus, vitamin B12 deficiency frequently remains unrecognised in such individuals.
According to the MHRA, up to one in ten people taking metformin have low vitamin B12. This is now regarded as a common adverse effect, particularly when taking metformin at high doses or for an extended period. In June 2022, the Department of Health and Social Care recommended screening for B12 deficiency in those using metformin (MRHA, 2022).
Studies allude to detection rates of 6%–7%. In order to assess how our four rural primary care practices were performing, we conducted a pilot study. Patients on metformin were screened with a single blood test at random during the year. Of the 672 people screened, 20 were found to be deficient in vitamin B12 – a baseline detection rate of ~3%.
The average time between initiation of metformin and detection of the deficiency was 24 months. There was a greater risk with doses above 2 g/day and with the sustained-release formulation.
Those with the deficiency were tested for intrinsic factor antibodies to rule out pernicious anaemia. None screened positive, confirming this was an adverse drug-related effect due to metformin
Based on our findings, we decided to initiate a quality improvement programme (QIP) to screen patients appropriately for vitamin B12 deficiency and to ensure consistency of care.
What did we do, and what were the outcomes?
The existing screening pathway was mapped (see Figure 1a). It revealed a process whereby an ad hoc blood-testing programme was delivered by the practice nurses 6 weeks before a patient’s scheduled annual diabetes review.
Patient awareness of the symptoms of B12 deficiency and their importance was poor, while a clinical survey found a lack of clinical awareness about its prevalence. Testing intervals and protocols varied considerably. Blood testing focused on glycaemic and lipid control, with no formal B12 screening being offered.
Across the four practices, 692 patients with diabetes and being treated with metformin were enrolled on the QIP (Figure 1b). Participants were scheduled for blood tests in April, August and December, and provided with forms that included a request for B12 testing. Patients and clinicians were also educated on the effects and iatrogenic risk of developing metformin deficiency.
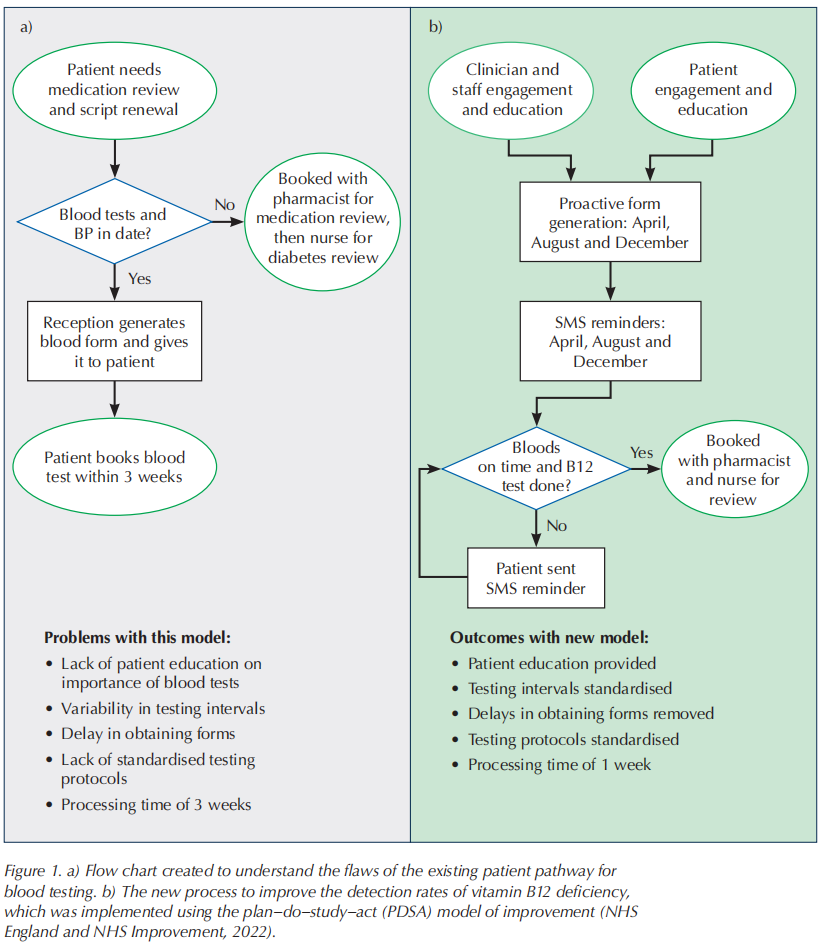
Blood-testing attendance was boosted by sending SMS reminders a week before scheduled blood tests, to remind patients to book their appointments. A further reminder was sent to those who did not attend. Patients were subsequently booked for reviews with the pharmacist and with a nurse.
Following implementation of the QIP methodology, processing times were reduced from 3 weeks to 1 week. Vitamin B12 deficiency detection rose to ~10% (67/692 patients) from the baseline 3%. There were also improvements in glycaemic and lipid control, as the regular testing reduced therapeutic inertia.
We concluded that patient education and empowerment were key to timely blood-testing attendance, while staff engagement and training ensured commitment to the pathway.
Our programme may serve as a guide to help other practices identify those at high risk, and who may require vitamin B12 supplementation, along with periodic testing. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of this deficiency can help prevent it and its clinical consequences, particularly anaemia and peripheral neuropathy, from worsening.
“Prompt diagnosis and treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency can help prevent it and its clinical consequences, particularly anaemia and peripheral neuropathy, from worsening.”
Treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency
To prevent these complications, treating patients appropriately by adequate repletion is pivotal. Patients using metformin with concomitant vitamin B12 deficiency should receive cobalamin supplementation to correct it and to prevent the related risk of peripheral nerve damage and/or other clinical consequences.
Although treatment may be cost-effective, the most appropriate regimen has not yet been clearly defined. Further studies are warranted to establish the most convenient route for treating vitamin B12 deficiency in metformin-treated patients.
References
1. MHRA (2022) Metformin and reduced vitamin B12 levels: new advice for monitoring patients at risk . MHRA, London. Available at: https://bit.ly/3BlGkhJ (accessed 30.11.23)
2. NHS England, NHS Improvement (2022) Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) cycles and the model for improvement. Available at: https://bit.ly/3uE5uZn (accessed 30.11.23)
This article is excerpted from the Journal of Diabetes Nursing by Wound World.


