
伤口世界
电子邮件地址: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。

- 星期五, 19 12月 2025
Thematic analyses of participant survey responses following dermatology ECHO programs with dermoscopy: Practical tips and lessons learned


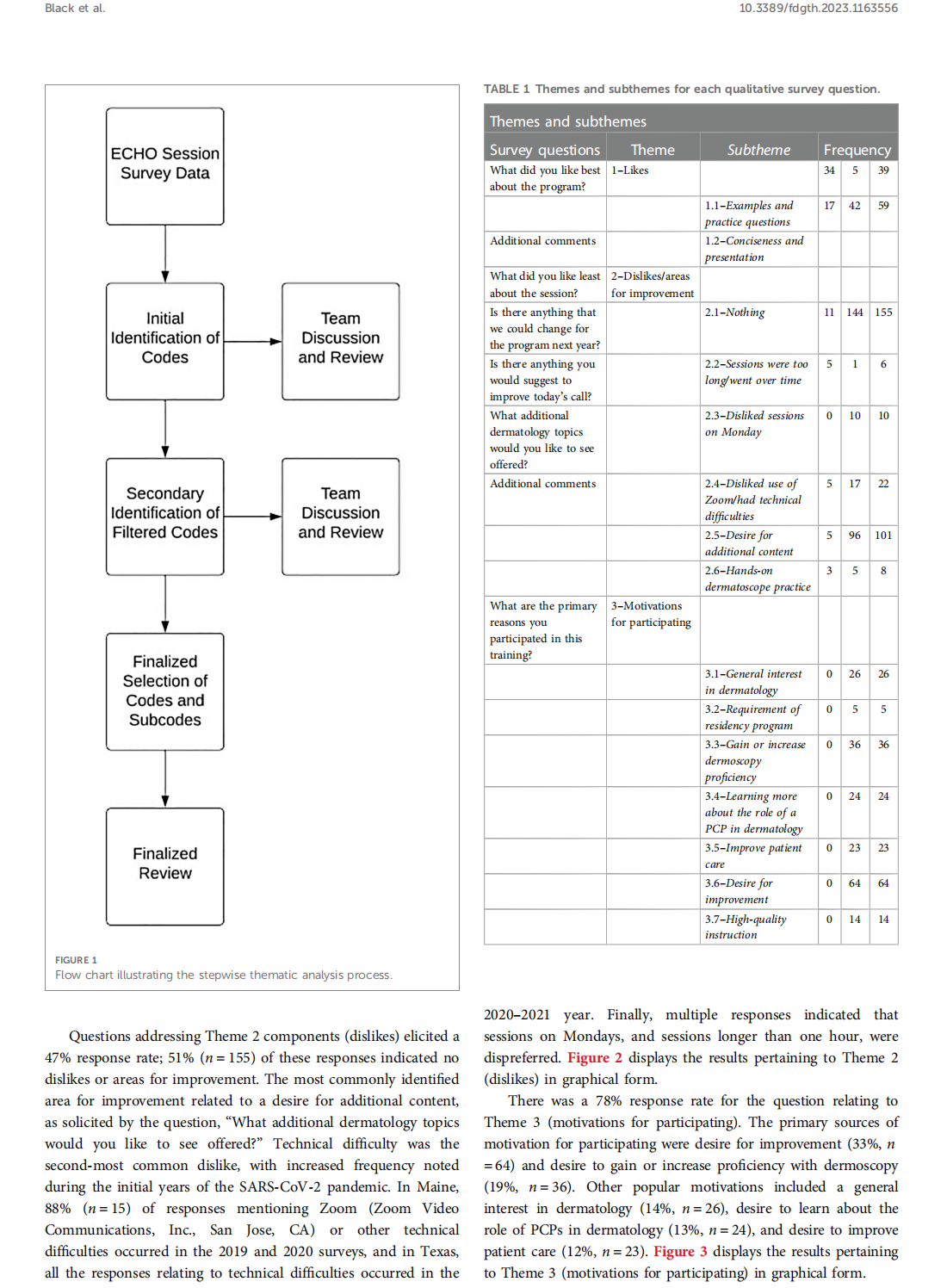

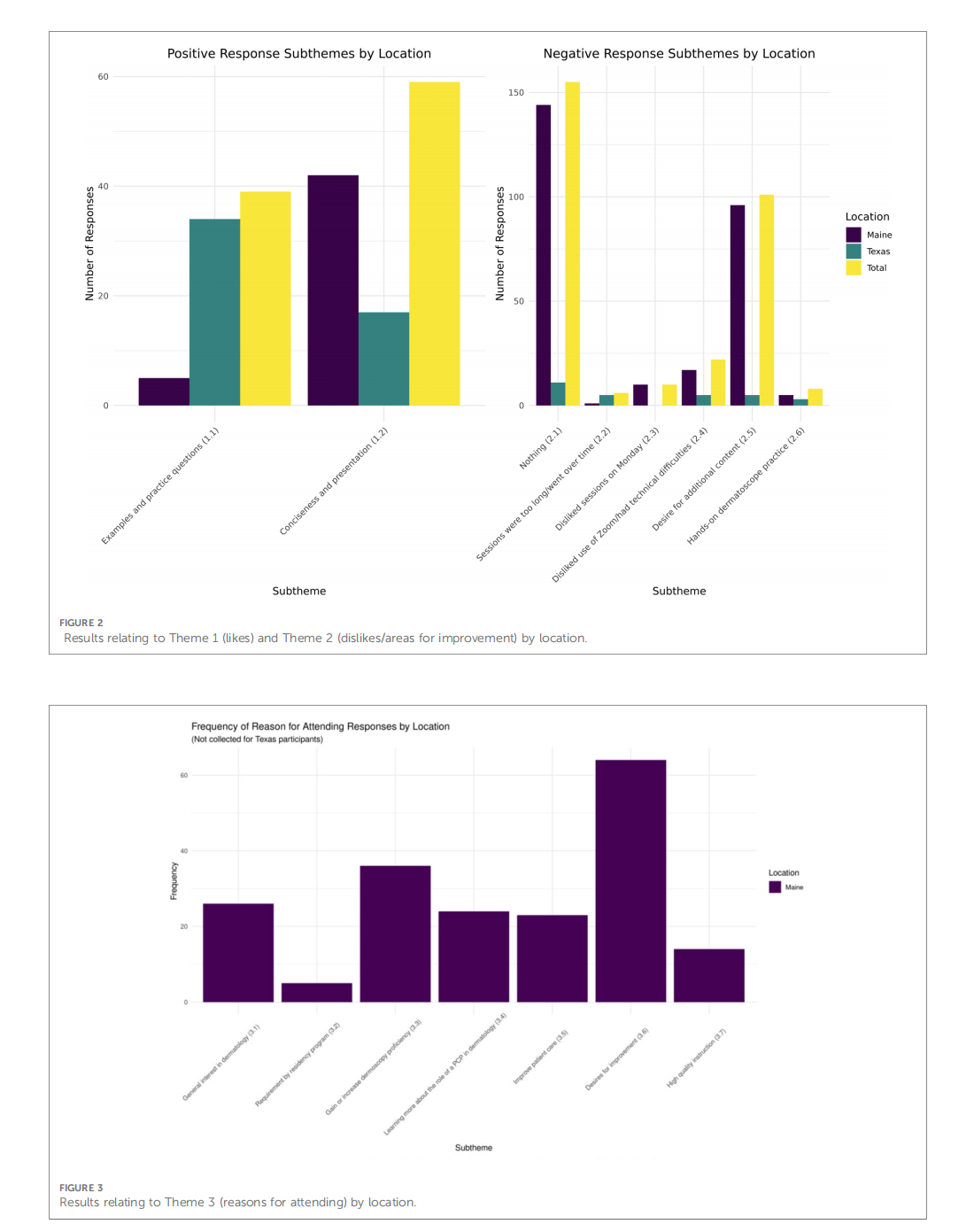


This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Digital Health》 by Wound World

- 星期四, 18 12月 2025
Betaine: a promising novel anti-aging substance as an exercise mimetic

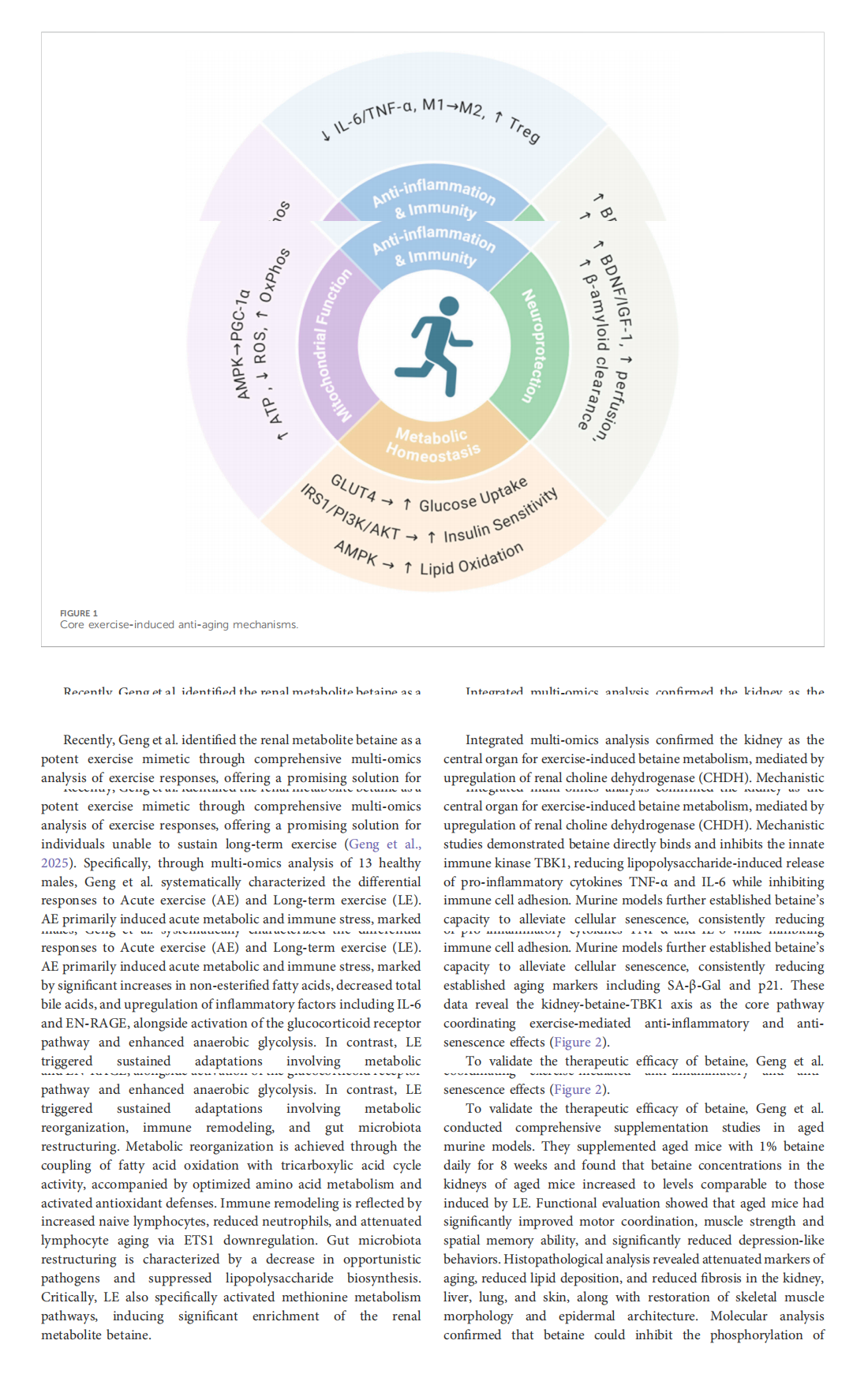
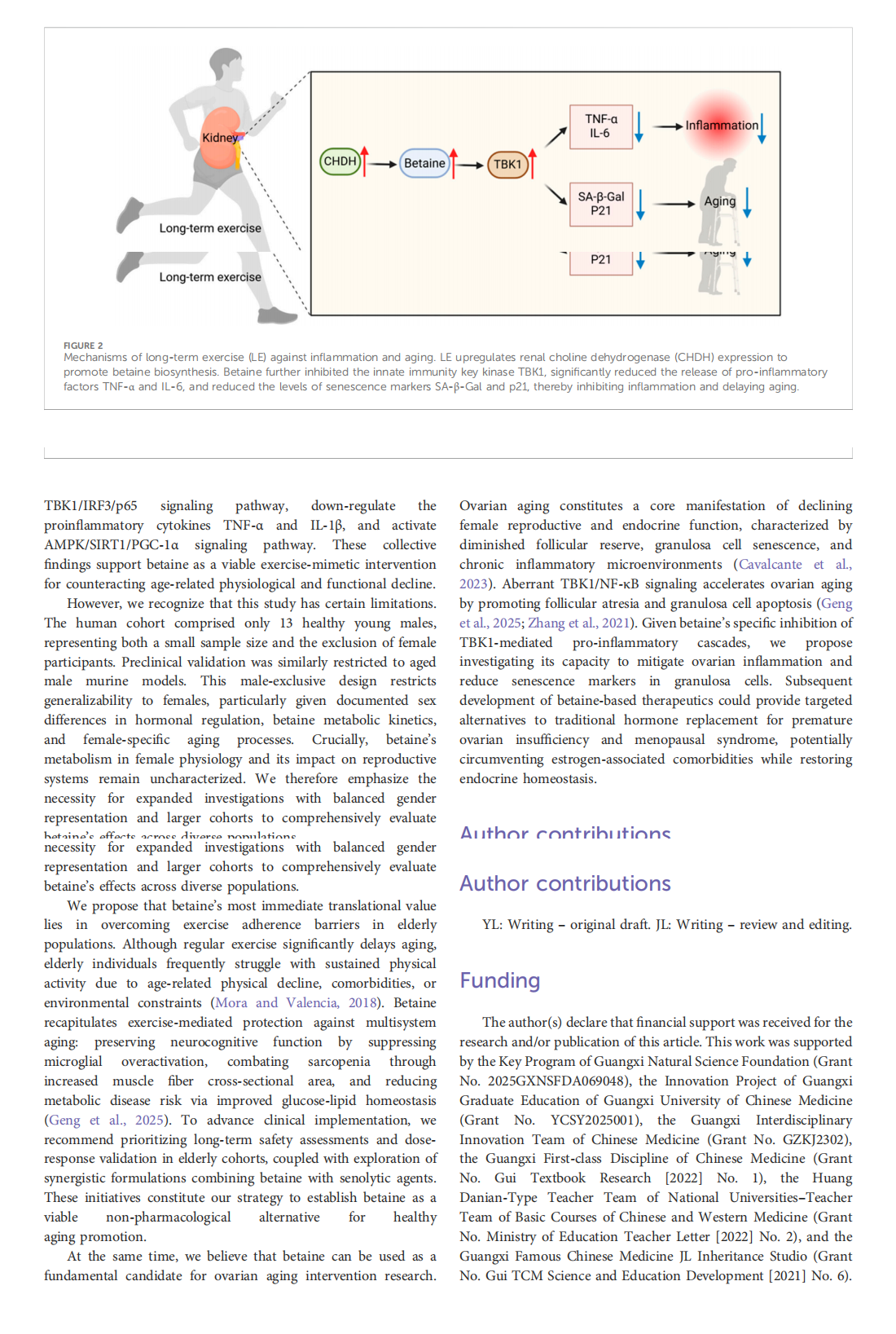

This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Pharmacology》 by Wound World

- 星期三, 17 12月 2025
Single domain Camelid antibody fragments for molecular imaging and therapy of cancer






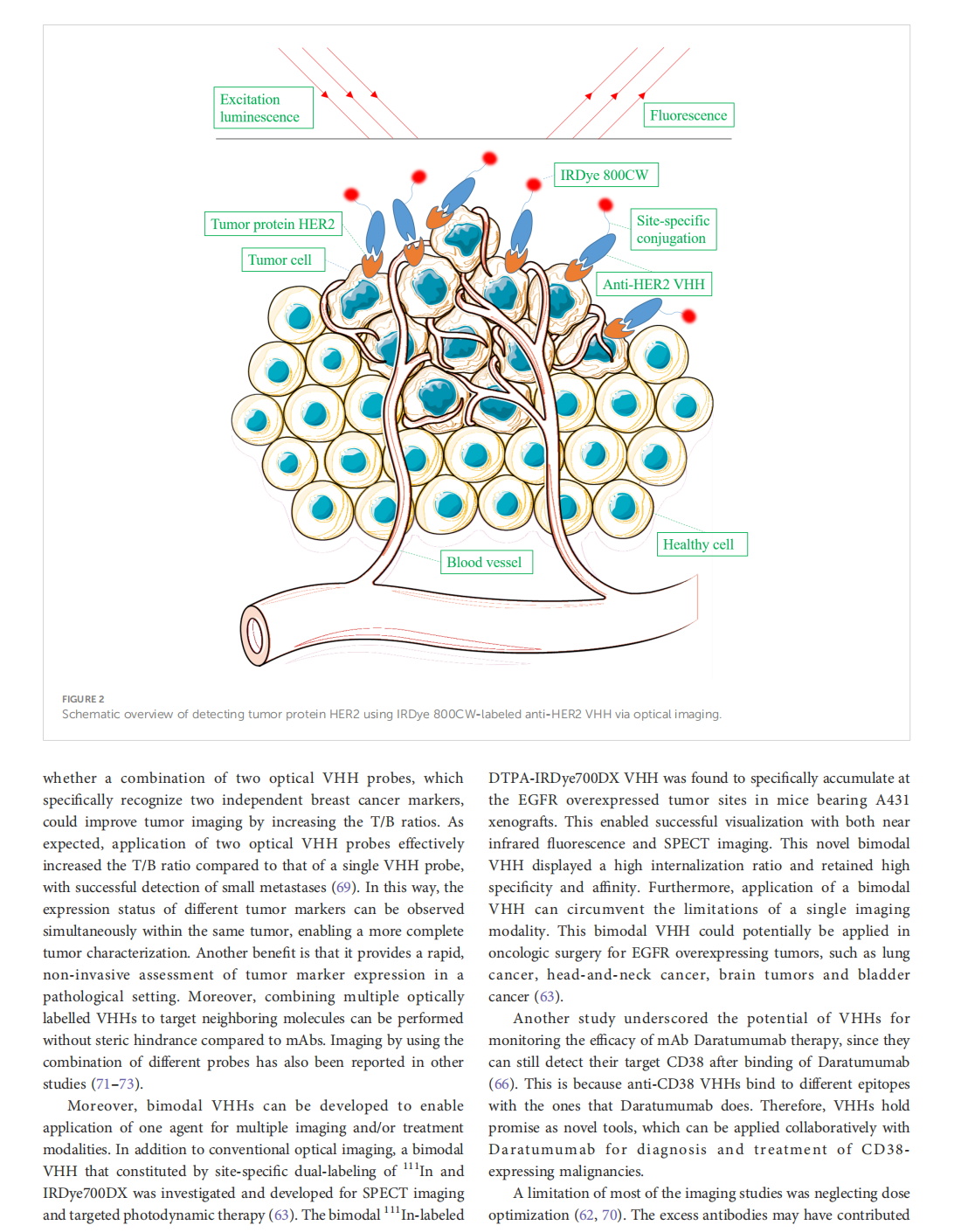

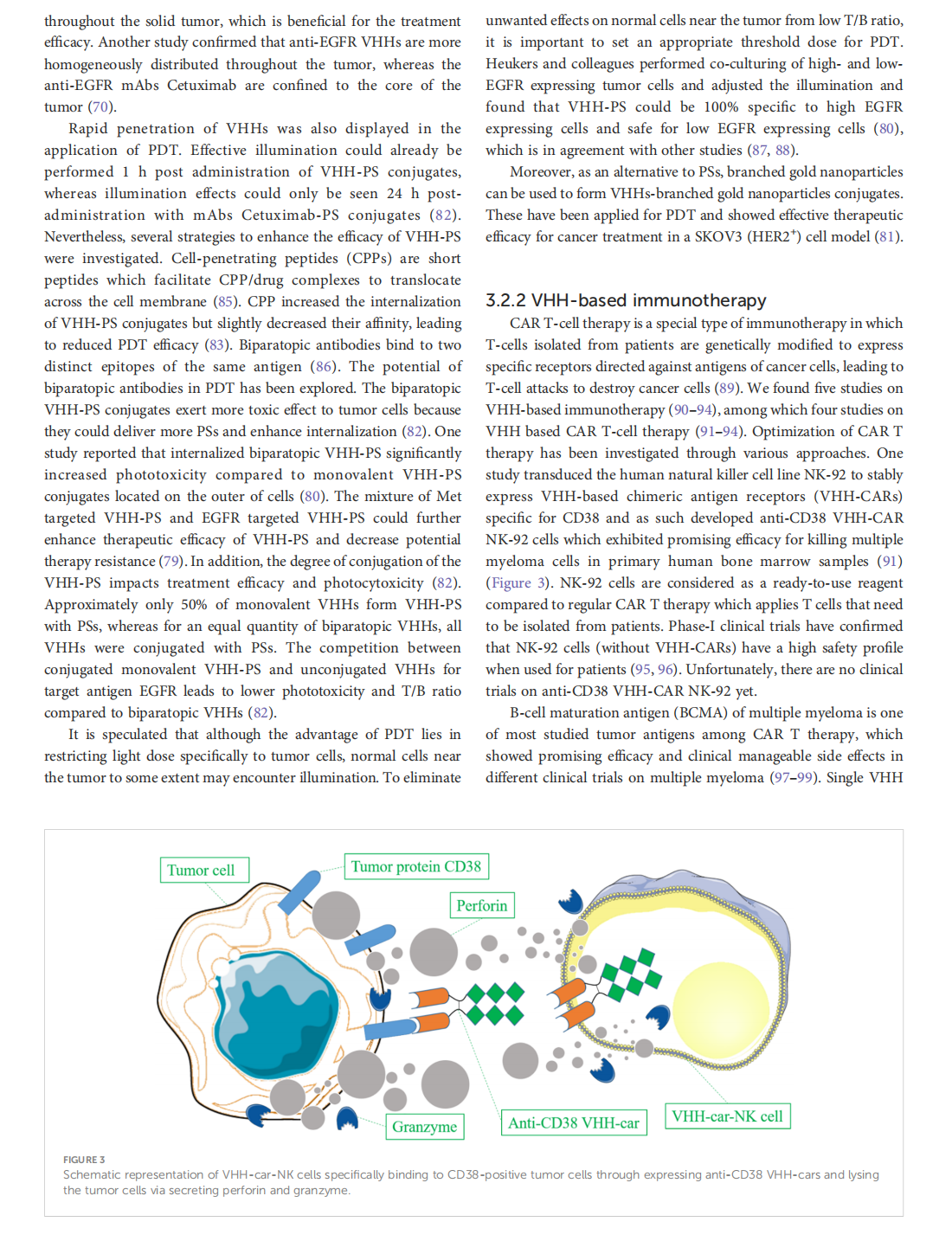









This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Oncology》 by Wound World

- 星期二, 16 12月 2025
The Effects of the Anti-aging Protein Klotho on Mucociliary Clearance


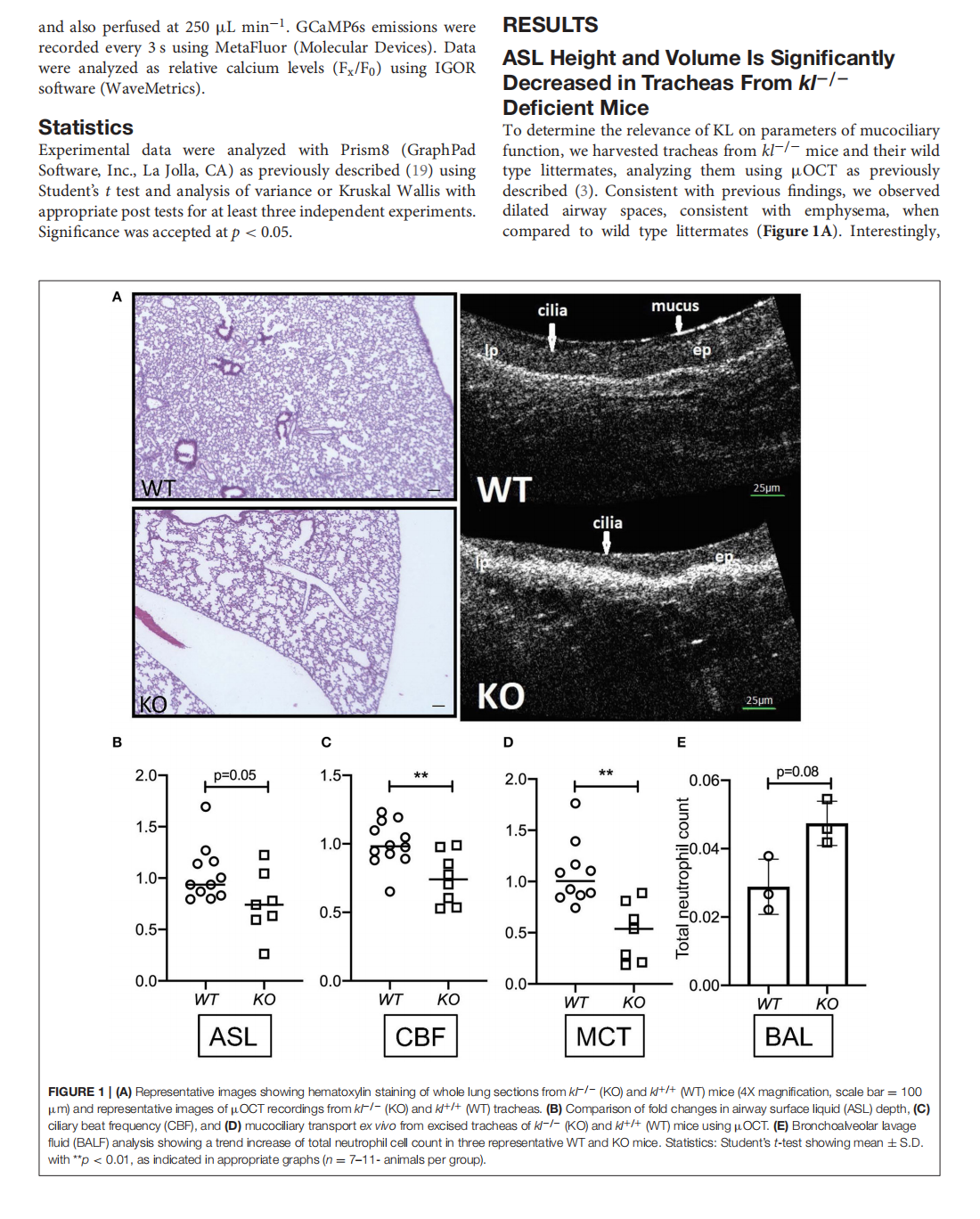
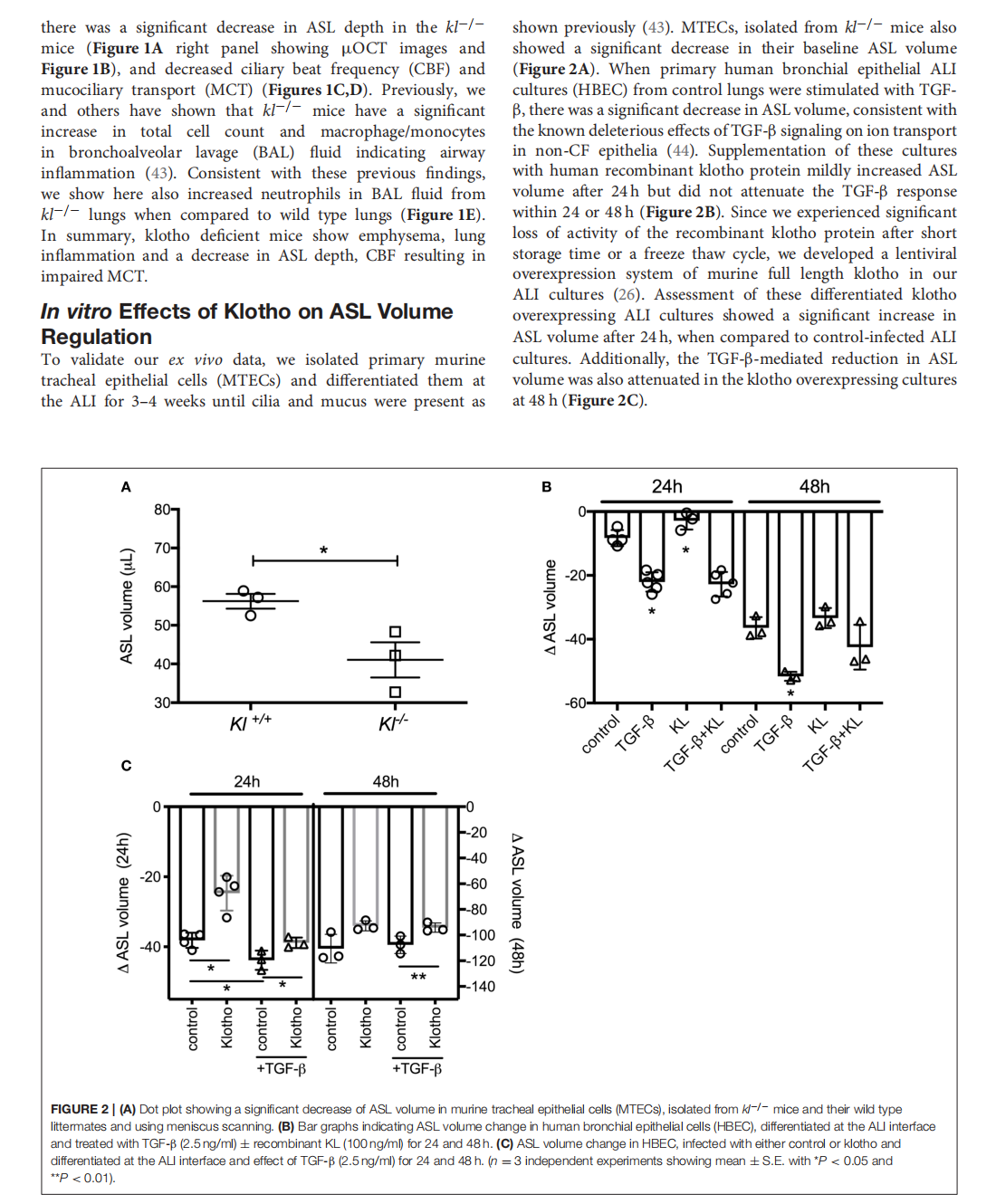
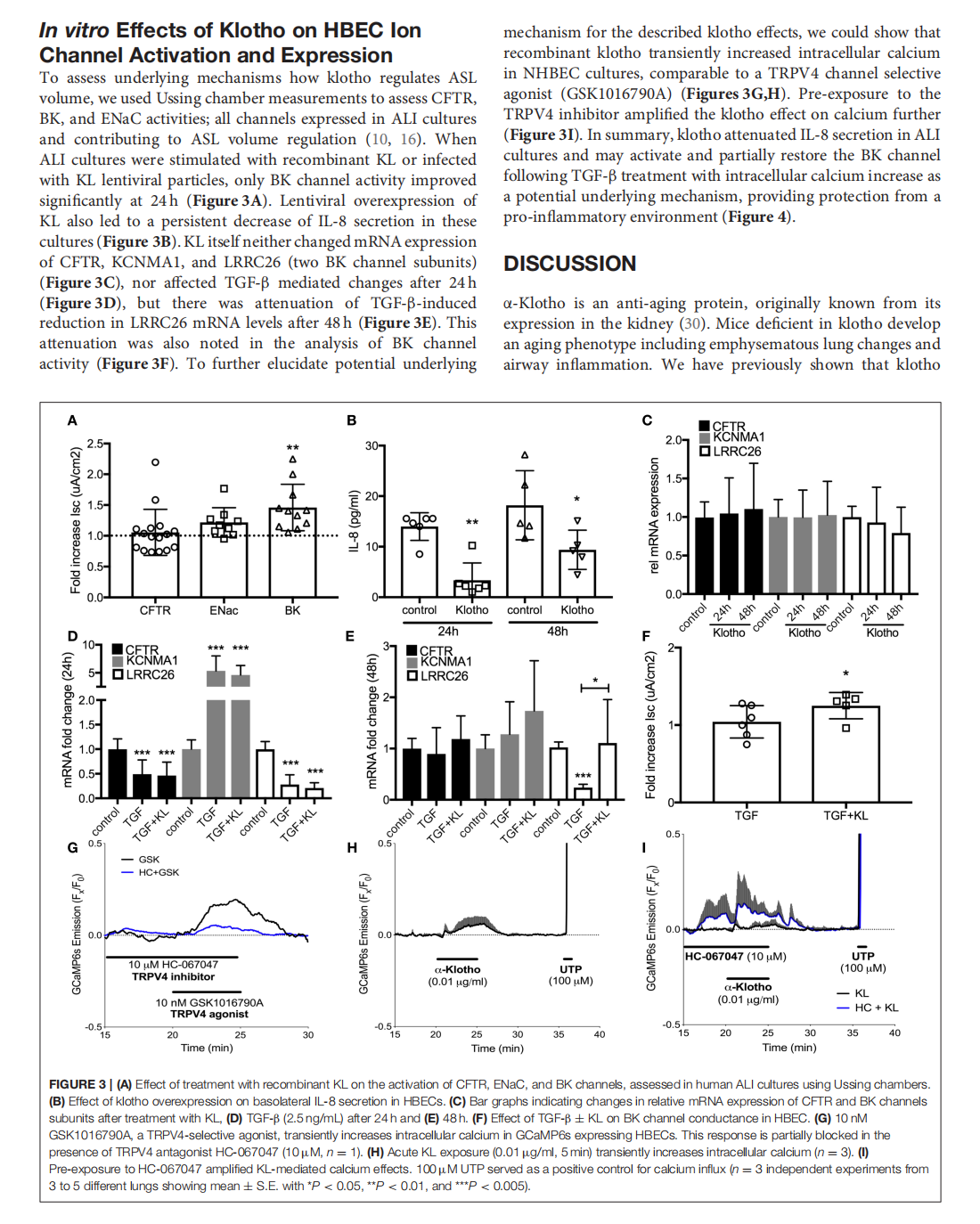
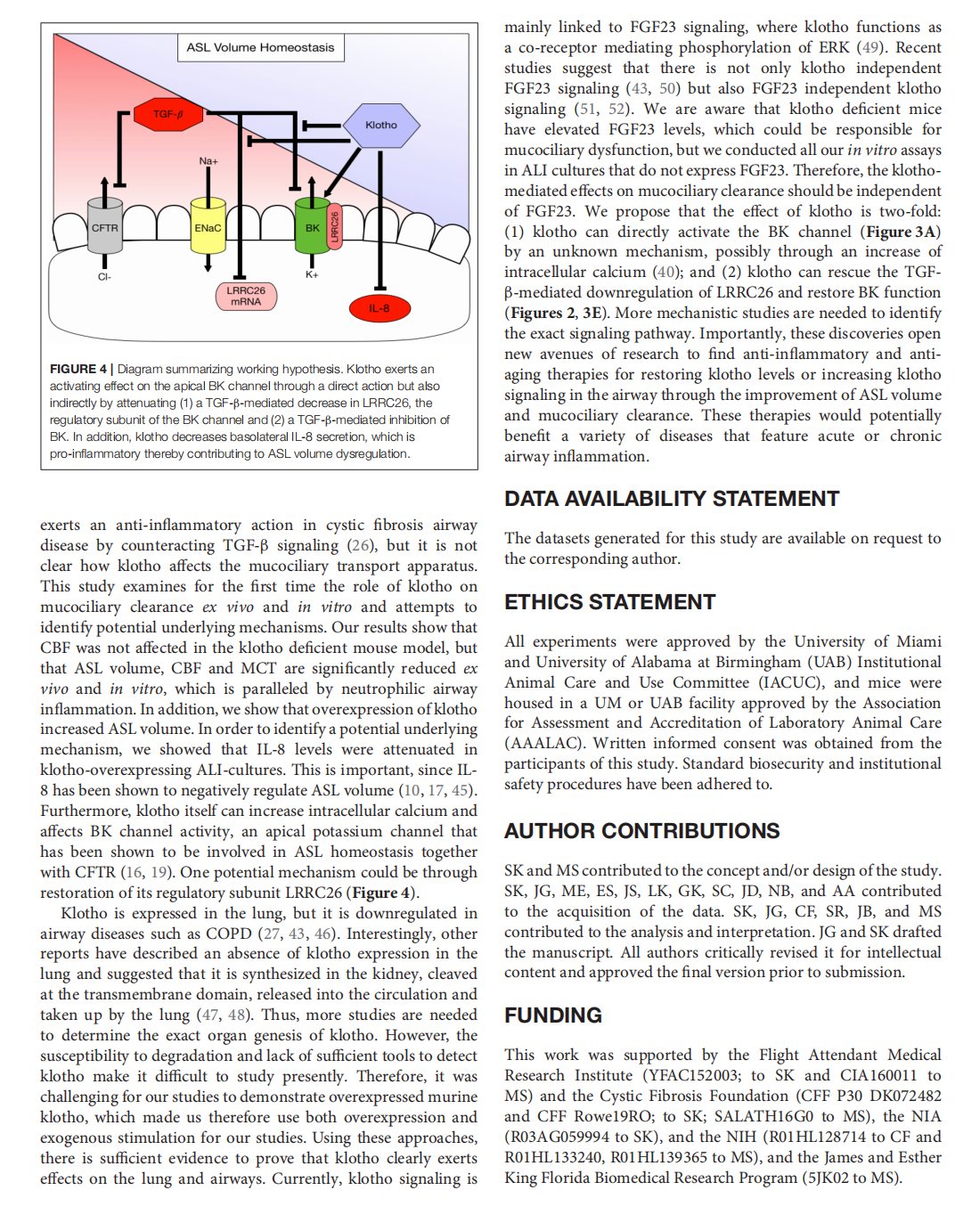


This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Medicine》 by Wound World

- 星期一, 15 12月 2025
The role of anti-aging approaches in managing hypogonadism in sedentary older males






This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Aging》 by Wound World

- 星期五, 12 12月 2025
Prediction of Subtle Cognitive Decline in Normal Aging: Added Value of Quantitative MRI and PET Imaging


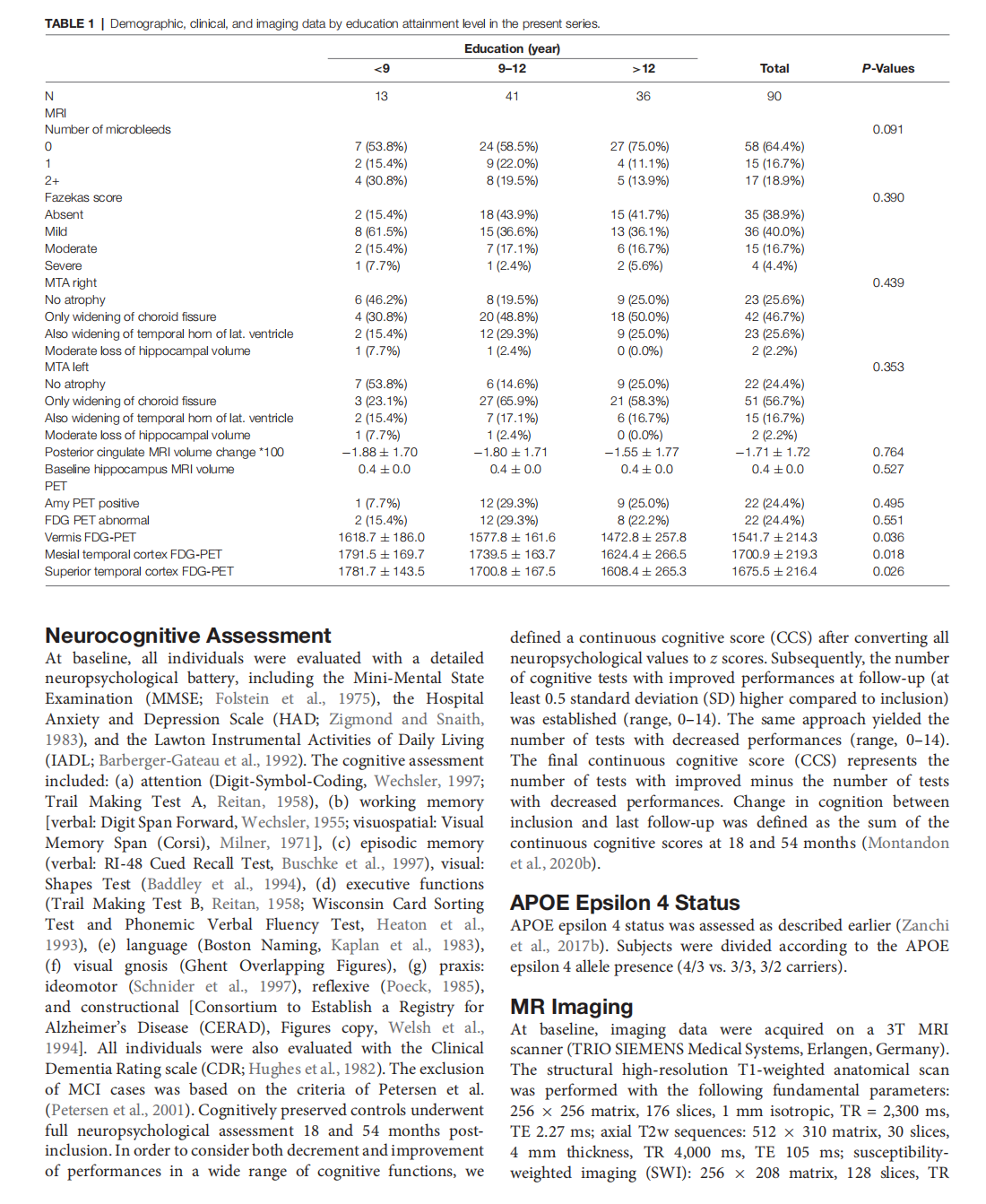








This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience》 by Wound World
