文献精选
王庚新 1 ,张春玲 2* ,赵 伟 2 ,陈 露 2 ,邸铁涛 2 ,张 云 1 ,王艳辉 1 ,刘海艳 1
- 贵州中医药大学,贵州 550002;
- 贵州中医药大学第二附属医院
基金项目 国家自然科学基金资助项目,编号:81960805;贵州省研究生教育创新计划项目,编号:黔教合 YJSCXJH(2020)161
作者简介 王庚新,硕士研究生在读
邓蕙妍 肖峰 高爱莉 李润祥 朱慧兰 万苗坚
DOI:10.3969/g.issn.0253-9802.2013.08.012
基金项目:广东省自然科学基金($2011010005956),广州市医药卫生科技项目(20131A011130)
作者单位:510095广州,广州市皮肤病防治所(邓蕙妍,高爱莉。李润祥,朱慧兰);510630广州,中山大学附属第三医院(肖峰,万苗坚)
通讯作者。朱慧兰,E.mail:zhlhuilan@hotmail.com;万苗坚,E-mail:w13725313465@163.oom
【摘要】
目的探讨长波紫外线(UVA)和中波紫外线(UVB)对人永生化角质形成细胞(HaCaT细胞)造成急性损伤所需要的最小剂量,为构建人表皮细胞急性光损伤模型提供科学依据。方法用不同剂量的UVA或UVB照射HaCaT细胞。观察细胞形态学改变,检测细胞增殖活性(吸光度)和凋亡率。结果2.5—10 J/era2UVA照射对HaCaT细胞无损伤,20~40 J/cm2可致细胞出现形态学改变,与空白对照组相比增殖活性降低,凋亡率增加(P<0.01);11.4~34.2 mJ/cm2UVB照射对HaCaT细胞无损伤,随照射剂量增加,细胞出现不同程度损伤,与空白对照组相比增殖活性降低,凋亡率增加(P<0.01)。结论UVA和UVB照射均可构造急性光损伤模型。HaCaT细胞对UVB敏感性更高,引起急性光损伤所需的最小剂量更低。
【关键词】
长波紫外线;中波紫外线;角质形成细胞;光损伤
Construction of acute light damage model with human epidermal keratinocytes
DENG Hui—yan.XIAO
Feng,GAO Ai—li.LI Run—xiang,ZHU Hui—lan,WAN Miao-jia,L Guangzhou Dermatosis Preventing&Curing
Institute,Guangzhou 510095,China
Corresponding
author:ZHU
Hui—lan,E—mail:zhlhuilan@hotmaiL COrn;WAN Miao-jian,E—mail:
【Abstract】
Objective
To explore a minimum dose of ultraviolet A(UVA)and ultraviolet B(UVB) that could cause immortalized keratinocytes(HaCaT cells)acute injury,and provide a scientific basis for building human epidermal cell acute light damage model.
Methods HaCaT cells were treated with different dose of UVA/UVB.The morphological changes,as well as proliferation activity and apoptosis rate were ob— served.
Result No injury changes were onservd with radiating dose of low radiation dose as 2.5—1 0 J/cm2 UVA.Yet 20-40 J/cm2 caused cellular morphological changes,with decreased proliferative activity and in—creased apoptosis rate(P<0.01).No injury changes were observed with radiating dose of 1 1.4~34.2 mJ/ cm2 UVB.However,ceils manifested with varied morphological changes,activity and apoptosis rate with te in— vrease of UVB dosage(P<0.01).
Conclusion Both UVA and UVB radiation can be used as construction to make acute light damage model.HaCaT ceils presented with more sensitivity with UVB,showing lower mini—mum required dose to cause acute light damage.As a dose-dependent model,type and degree of radiations were alternative in different experimental settings.
【Key words】 UVA;UVB;HaCaT cells;Photodamage
郭 璇 1 ,解 军 1 ,索金荣 2 ,李英蕊 1 ,黄 磊 1 ,马牧南 1 ,李静静 3 ,傅松涛 1,2,3
1 山西医科大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,山西省太原市 030001;2 山西宾大干细胞科技有限公司,山西省太原市 030001;3 山西省生物医药健康研究生教育创新中心,山西省太原市 030001 第一作者:郭璇,男,1994 年生,陕西省延安市人,汉族,2020 年山西医科大学毕业,硕士,主要从事干细胞与组织再生研究。
通讯作者:傅松涛,硕士,教授,山西医科大学基础医学院,山西省太原市 030001;山西宾大干细胞科技有限公司,山西省太原市 030001;山西省生物医药健康研究生教育创新中心,山西省太原市 030001 https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7907-0316( 郭璇 )
基金资助:山西省‘1331 工程’重点学科建设计划经费,项目负责人:解军;山西省国际科技合作基金 (201703d421022),项目负责人:解军;山西省重点研发计划 ( 国际科技合作 )(201903D421023),项目负责人:解军
引用本文:郭璇,解军,索金荣,李英蕊,黄磊,马牧南,李静静,傅松涛 . 人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞不同途径移植治疗 1 型糖尿病鼠 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):78-83.
https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.
2095-4344.2144
投稿日期:2020-01-04
送审日期:2020-01-10
采用日期:2020-02-19
在线日期:2020-08-10
中图分类号:R459. 9;R394.2;R587.1
文章编号:
2095-4344(2021)01-00078-06
文献标识码:B
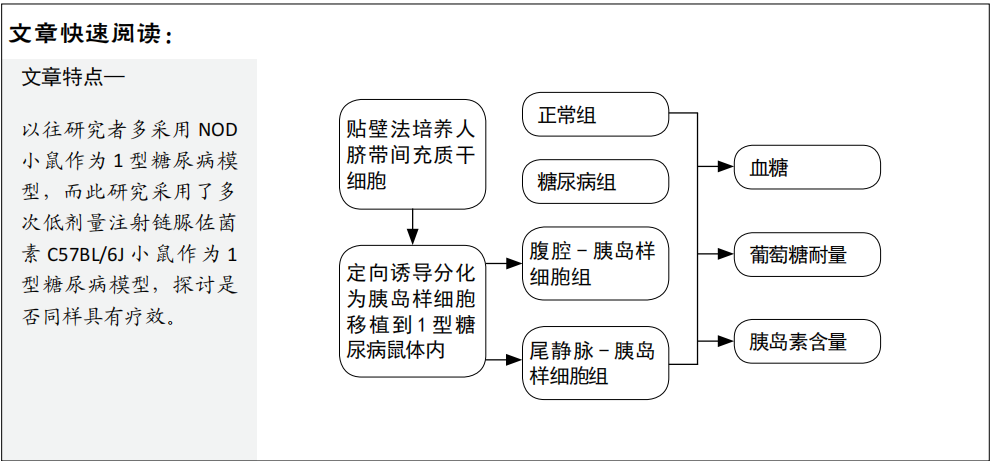
文题释义:
人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样细胞:人脐带间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能,可分化为骨细胞、脂肪细胞、胰岛细胞等,在相关因子作用下,可使其分化为分泌胰岛素的细胞,称为胰岛样细胞。
葡萄糖耐量:检测胰岛样细胞移植后糖尿病鼠是否可以更好地响应外周血糖浓度变化,释放胰岛素,降低血糖。
摘要
背景:人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞移植于1型糖尿病鼠体内,会使血糖降低,糖尿病症状有所改善,但腹腔移植的方式少有报道。
目的:观察不同途径移植人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞对于1型糖尿病小鼠的治疗效果。
方法:选采用组织块贴壁法分离培养人脐带间充质干细胞,然后将其定向分化为胰岛样细胞。从15只雄性C57BL/6J小鼠中随机取3只小鼠做正常组,其余12只小鼠腹腔注射链脲佐菌素制备1型糖尿病模型。造模成功9只小鼠随机分为糖尿病组、尾静脉-胰岛样细胞组、腹腔-胰岛样细胞组,每组3只。造模10 d后,正常组和糖尿病组不予处理,尾静脉-胰岛样细胞组经尾静脉注射0.4 mL胰岛样细胞悬液(含5×105个细胞),腹腔-胰岛样细胞组经腹腔注射0.4 mL胰岛样细胞悬液(含5×105 个细胞)。移植后每周检测2次血糖,移植后28 d进行葡萄糖耐量实验,移植后42 d检测胰岛素水平。
结果与结论:①与糖尿组相比,尾静脉-胰岛样细胞组在移植后第10天开始血糖明显下降,一直维持到31 d,胰岛素水平升高,葡萄糖耐量改善,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);腹腔-胰岛样细胞组血糖、胰岛素水平、葡萄糖耐量未见明显改善;②结果提示,应用人脐带间充质干细胞诱导的胰岛样细胞治疗1型糖尿病鼠,尾静脉注射是一种比较理想的移植方式,腹腔注射的效果不佳。
关键词:人脐带间充质干细胞;1型糖尿病;胰岛样细胞;腹腔;静脉;移植;鼠;实验
Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice Guo Xuan1 , Xie Jun1 , Suo Jinrong2 , Li Yingrui1 , Huang Lei1 , Ma Munan1 , Li Jingjing3 , Fu Songtao1, 2, 3
1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China;
2 Shanxi Binda Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Provincial Biomedical Health Graduate Education Innovation Center, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China Guo Xuan, Master, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province,China
Corresponding author: Fu Songtao, Master, Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Binda Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Provincial Biomedical Health Graduate Education Innovation Center, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Transplanting islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) into type 1 diabetic mice can reduce blood glucose level and improve the symptoms of diabetes mellitus. However, there are few reports on intraperitoneal transplantation.
OBJECTIVE: To study the therapeutic effect of transplantation of islet-like cells induced by hUC-MSCs in different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice.
METHODS: The hUC-MSCs were isolated and cultured by tissue explants adherent method and differentiated into islet-like cells. The 3 of 15 male C57BL/6J mice were used as normal group, and the remaining mice were taken to prepare a mouse model of type 1 diabetes using intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin. After successful modeling, nine model mice were randomly divided into diabetes group, tail vein-islet-like cells group, and abdomen-islet-like cells group, with three mice in each group. After 10 days of modeling, the normal group and diabetic group were not treated. The tail vein-islet-like cells group was injected with 5×105 cells/0.4 mL islet-like cells via the tail vein and the abdomen-islet-like cells group was intraperitoneally injected with 5×105 cells/0.4 mL islet-like cells. During the treatment, the blood glucose and insulin levels were measured twice a week; glucose tolerance test was performed at 28 days after cell transplantation; and fasting insulin level was detected at 42 days after cell transplantation.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSION: (1) Compared with the diabetic group, in the tail vein-islet-like cells group, the blood glucose level began to decrease on the 10th day after transplantation and maintained until the 31st day, and the insulin level and glucose tolerance significantly improved (P < 0.05). However, there was no significant improvement in blood glucose level, insulin level and glucose tolerance in the abdomen-islet-like cells group. (2) To conclude, transplantation of hUCMSCs induced islet-like cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice via tail vein is an ideal transplantation method, and the effect of intraperitoneal injection is unsatisfactory.
Key words: human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; type 1 diabetes mellitus; islet-like cells; abdomen; vein; transplantation; mouse; experiment
Funding: the Fund for Shanxi “1331 Project” Key Subject Construction (to XJ); The International Scientific and Technological Cooperative Foundation of Shanxi
Province, No. 201703d421022 (to XJ); Key R&D Program of Shanxi Province (International Cooperation), No. 201903D421023 (to XJ)
How to cite this article: GUO X, XIE J, SUO JR, LI YR, HUANG L, MA MN, LI JJ, FU ST. Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2021;25(1):78-83.
黎俏洁
(海南医学院第二附属医院内分泌科,海南海口570100)
[摘要]目的:探讨达格列净与吡格列酮联合二甲双胍治疗2型糖尿病(T2DM)的疗效及对胰岛素敏感性和胰岛a和β细胞功能的影响。方法:选取100例T2DM患者为研究对象,依据治疗方法不同分为达格列净组和吡格列酮组,每组各50例。达格列净组予以达格列净+二甲双胍治疗;吡格列酮组予以吡格列酮+二甲双胍治疗。比较两组患者血糖指标[空腹血糖(FPG) .餐后2 h血糖(2hPG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbAle)]、血脂指标[总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇( LDL-C)]、胰岛素抵抗指数( HOMA-IR)、胰岛素敏感性[葡萄糖输注率(GIR)]、胰岛a和β细胞功能指标[a:胰高血糖素曲线下面积( AUCglc);β:早相胰岛素分泌指数( I30/G30)、胰岛素分泌曲线下面积(AUCins)]及不良反应发生情况。结果:治疗后,两组患者FPG、2hPG、HbAle .TC、TG、LDL-C、HOMA-IR、AUCgle均降低(P<0.05),且达格列净组低于吡格列酮组(P <0.05) ;GIR、I30/G30、AUCins均升高(P<0.05),且达格列净组高于吡格列酮组(P<0.05)。两组患者不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:达格列净与吡格列酮联合二甲双胍治疗T2DM均可有效改善患者糖脂代谢,减轻IR并可提高胰岛素敏感性,保护胰岛a和β细胞功能,但达格列净联合二甲双胍的作用相对更好。
[关键词]达格列净;吡格列酮;二甲双胍;2型糖尿病;胰岛素敏感性;胰岛细胞功能[中图分类号] R587.1
[文献标志码] A
Effect of daglitazone and pioglitazone combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its influence on insulin sensitivity and islet a and β cell function
LI Qiao-jie
( Department of Endocrinology , the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College , Haikou 570100 , Hainan ,China)
[ Abstract] Objective: To investigate the effect of dapagliflozin and pioglitazone combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus ( T2DM) and its effect on insulin sensitivity and islet a and β cell function.
Methods : 100 patients with T2DM were selected and divided into daglitazone group and pioglitazone group according to different treatment methods, with 50 cases in each group. The daglitazone group was treated with daglitazone + metformin , and the pioglitazone group was treated with pioglitazone + met-formin. The blood glucose [ fasting plasma glucose ( FPG), 2 h postprandial blood glucose ( 2hPG ),glycosy lated hemoglobin ( HbAlc) ] , blood lipids [ total cholesterol ( TC),triglyceride ( TG ) , low density lipoprotein cholesterol ( LDL-C)] , insulin resistance[ insulin resistance index ( HOMA-IR )], insulin sensitivity [ glucose infusion rate ( GIR) ] and islet a and β cell function [ a :area under the curve of glucagon ( AUCglc),β: early phase insulin secretion index ( I30/ G30) ,area under insulin secretion curve (AUCins) ] and adverse effects were compared between the two groups.
Results : After treatment , FPG ,2hPG, HbAlc , TC, TG, LDL-C, HOMA-IR and AUCglc in the two groups were signific antly dec reased , and daglitazone group was lower than the pioglitazone group
(P<0.05). GIR , I30/G30 and AUCins were significantly increased (P<0. 05) , and daglitazone group was higher than the pioglitazone group ( P < 0. 05). There was no significant difference in the total inlcidence of adverse reactions between the two groups (P >0.05).
Conclusion : Dagliptin and pioglitazone combined with metformin in the treatment of T2DM can effectively improve glucose and lipid metabolism ,reduce IR , improve insulin sensitivity, and protect the function of islet a and β cells , and the efficacy of dagliptin is relatively better.
[Key words] Type 2 diabetes ;Dapagliflozin ;Pioglitazone ; Metformin; Insulin sensitivity; Islet cells function




