
伤口世界
电子邮件地址: 该Email地址已收到反垃圾邮件插件保护。要显示它您需要在浏览器中启用JavaScript。

- 星期二, 06 1月 2026
Genetic profiling and precision skin care: a review


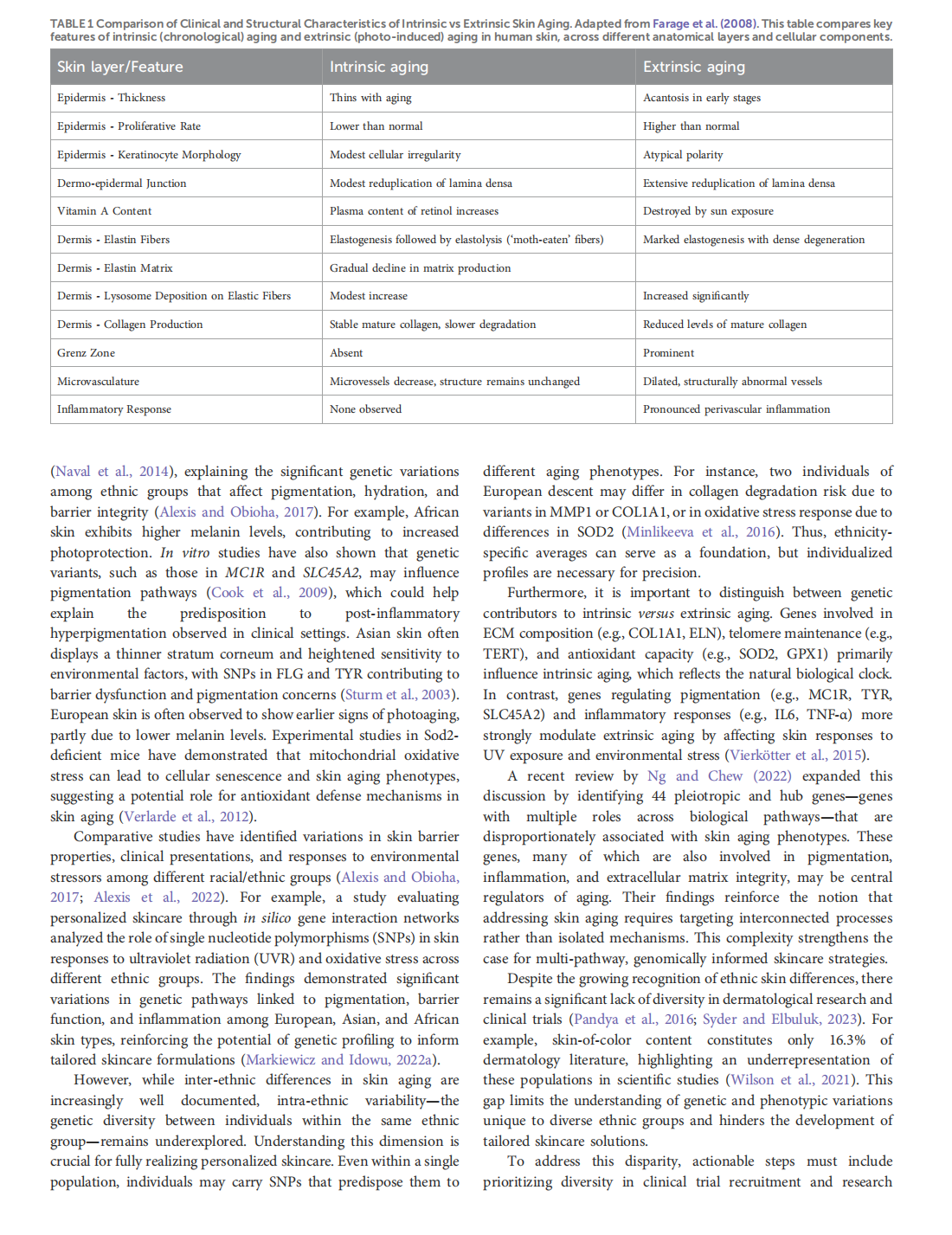




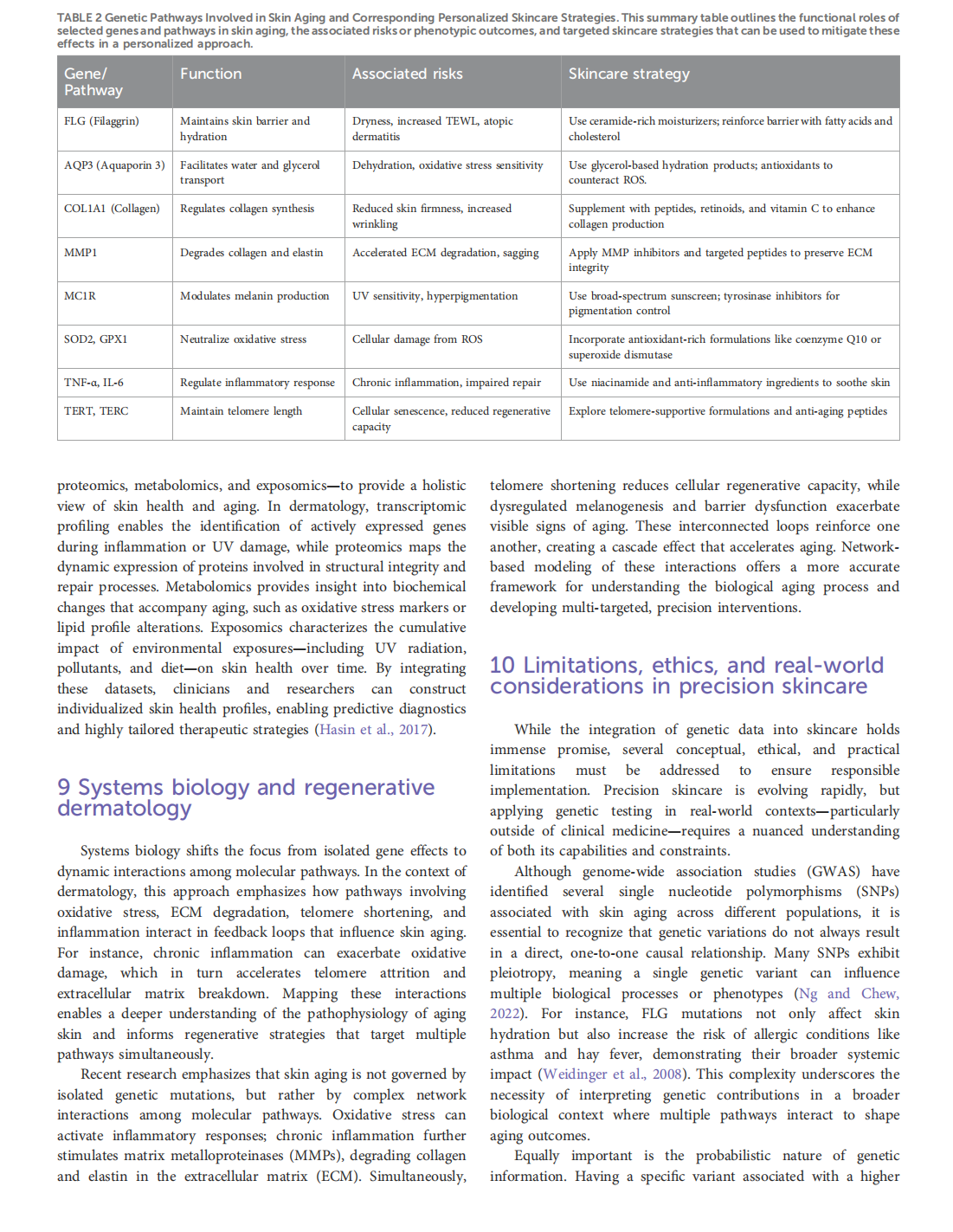




This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Genetics》by Wound World

- 星期一, 05 1月 2026
Medical ozone treatment for pain, fatigue, anxiety, and depression in cancer patients: a scoping review



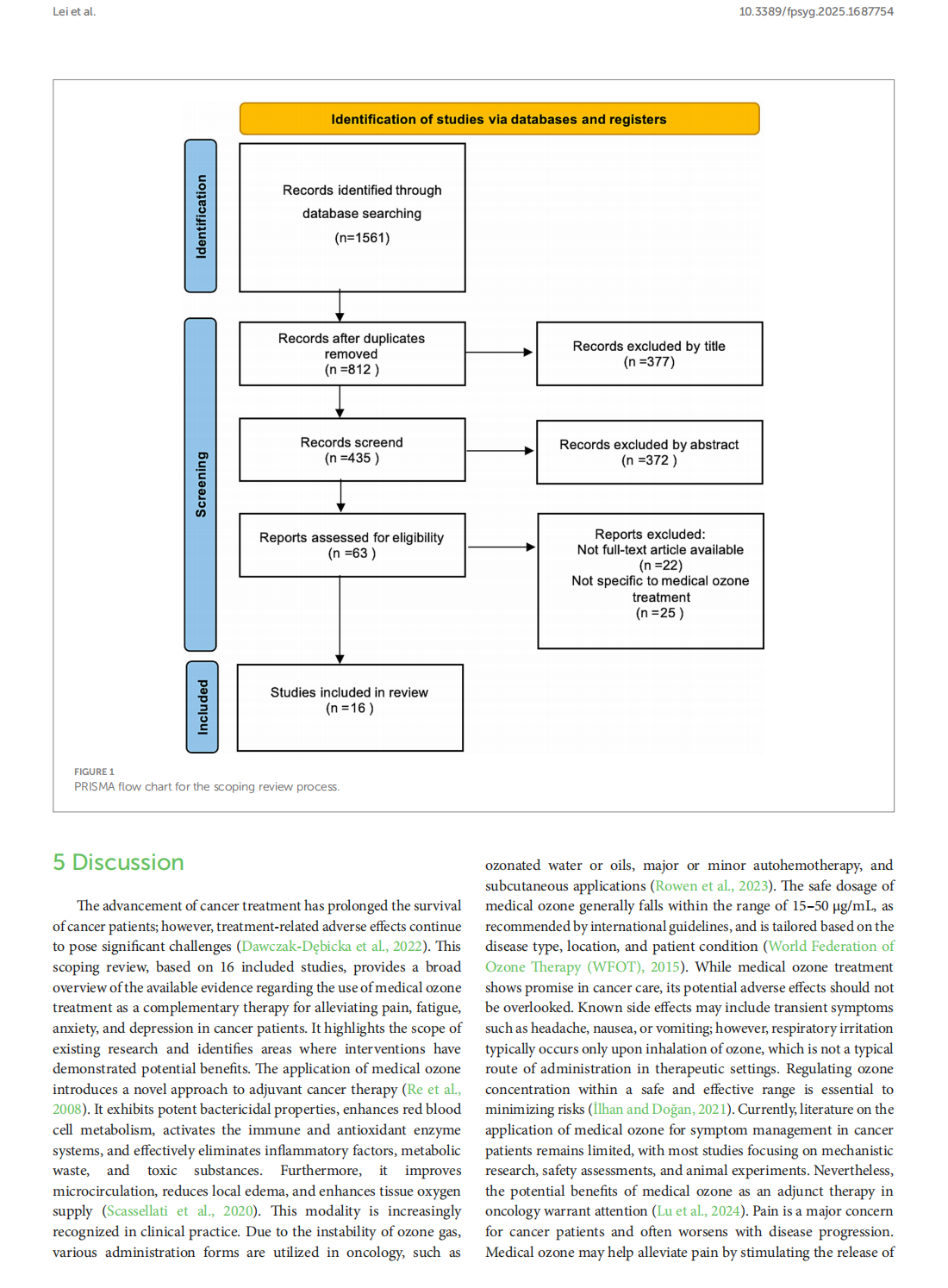
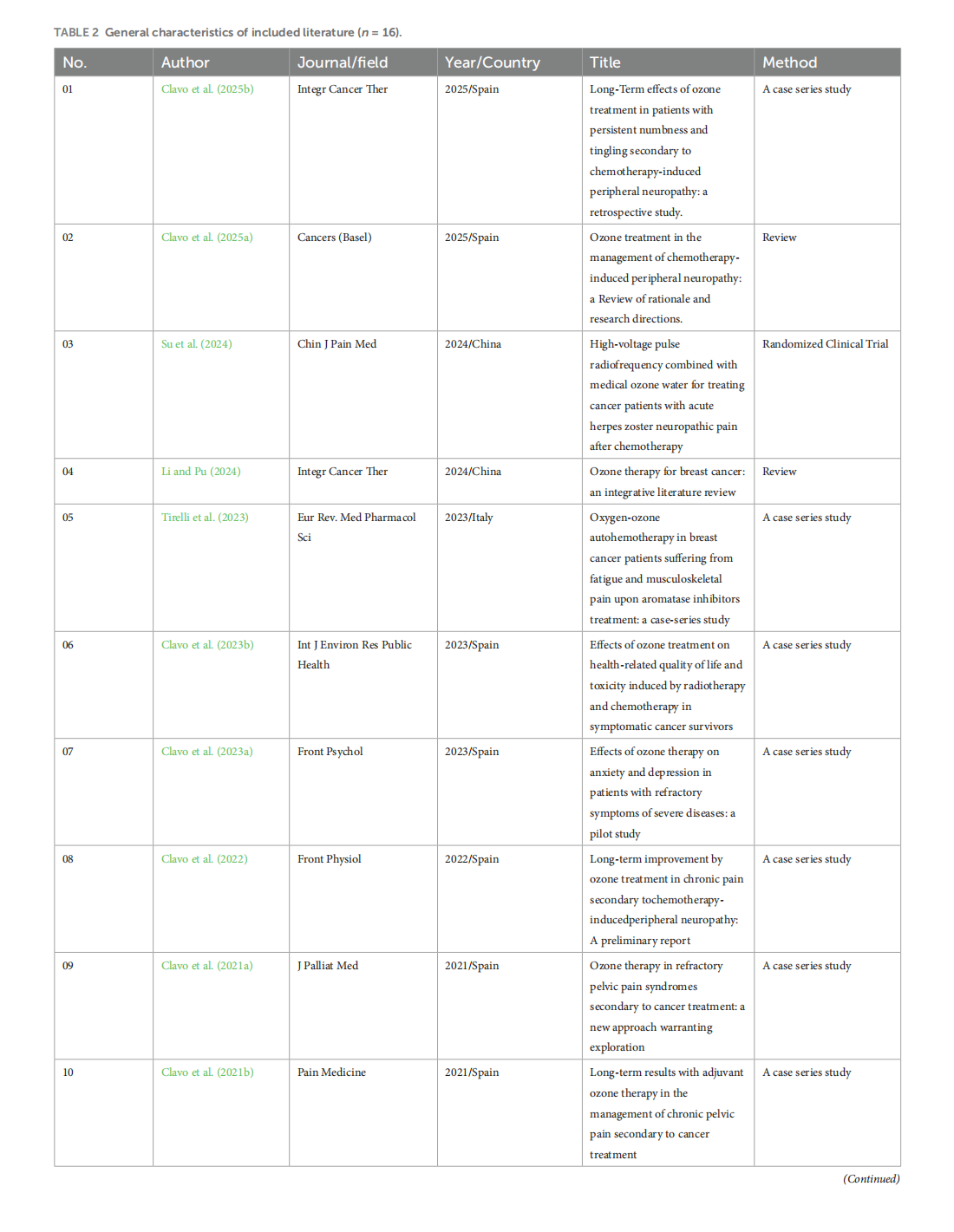
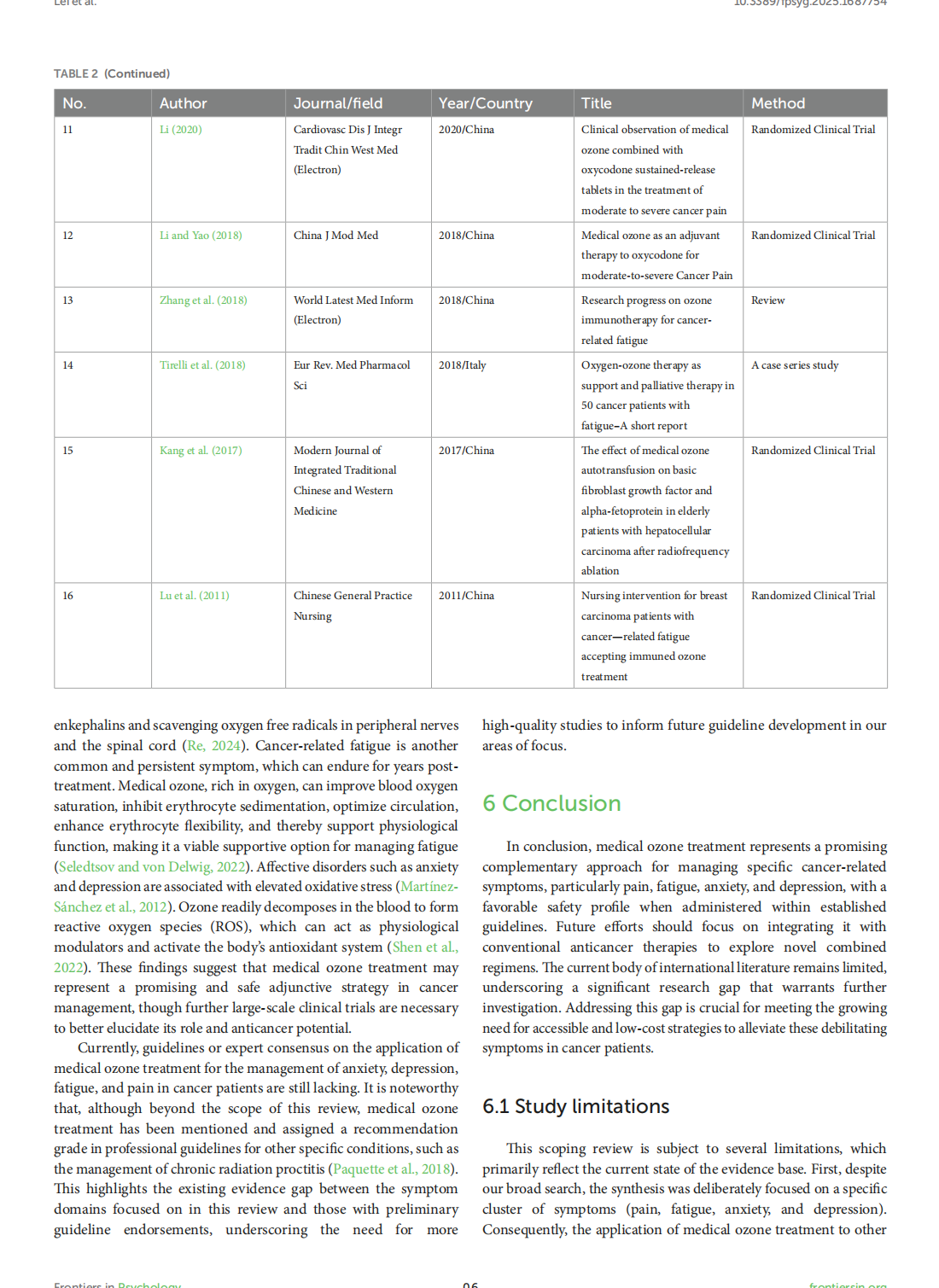
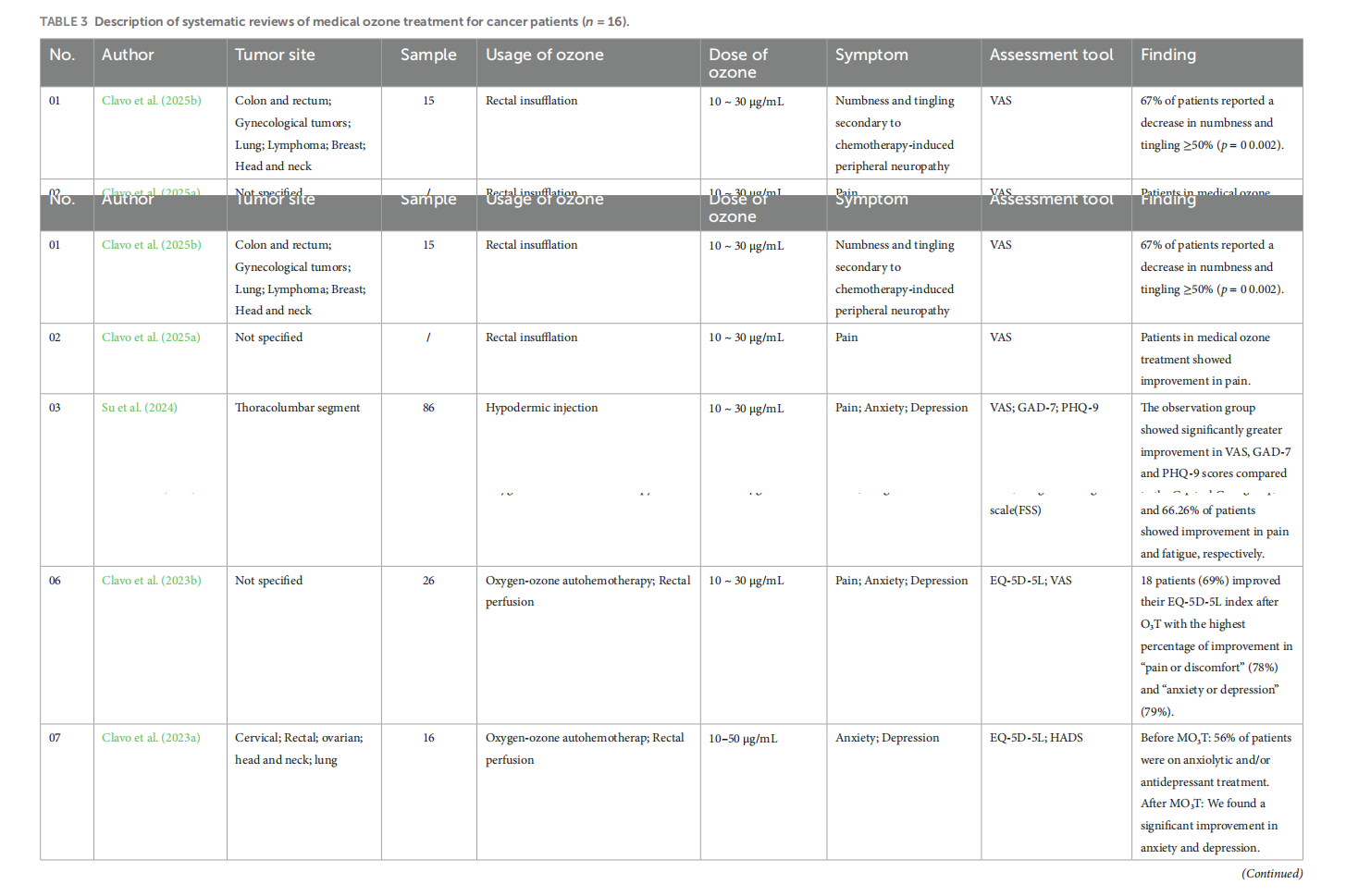
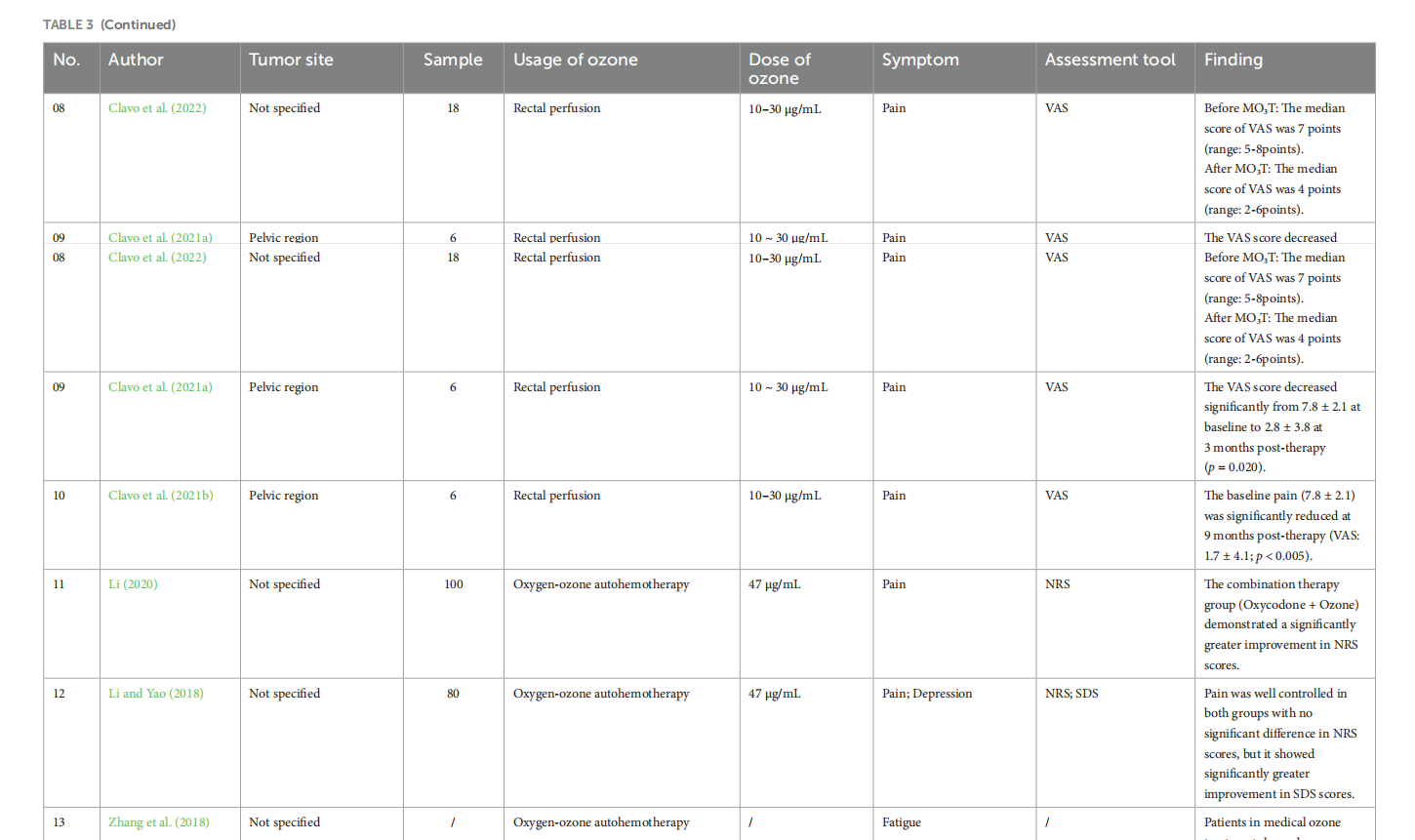


This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Psychology》by Wound World

- 星期日, 04 1月 2026
Great challenges in molecular medicine: toward personalized medicine




This article is excerpted from the 《Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology》 by Wound World

- 星期三, 31 12月 2025
The potential interaction between medical treatment and radioiodine treatment success: A systematic review




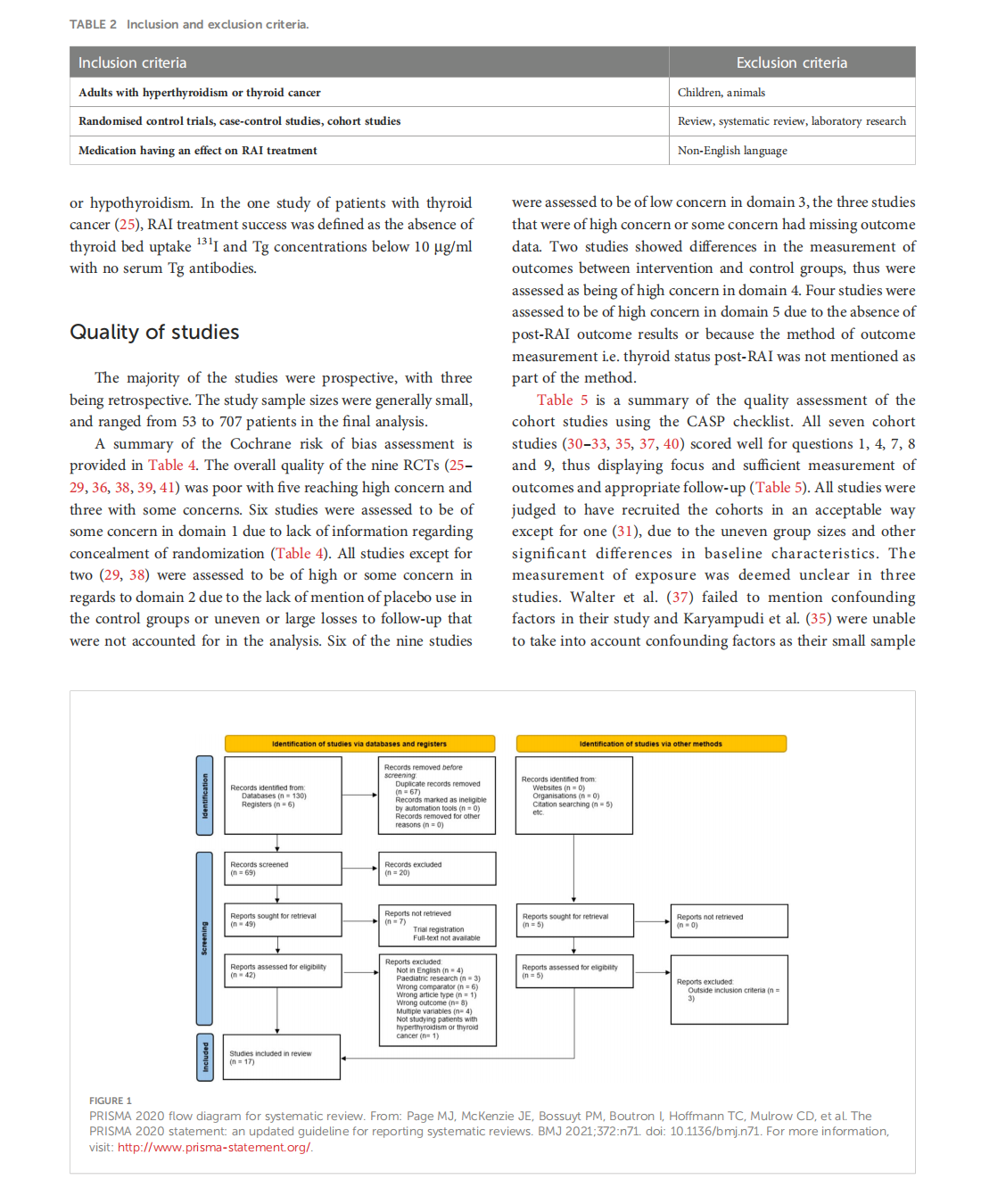
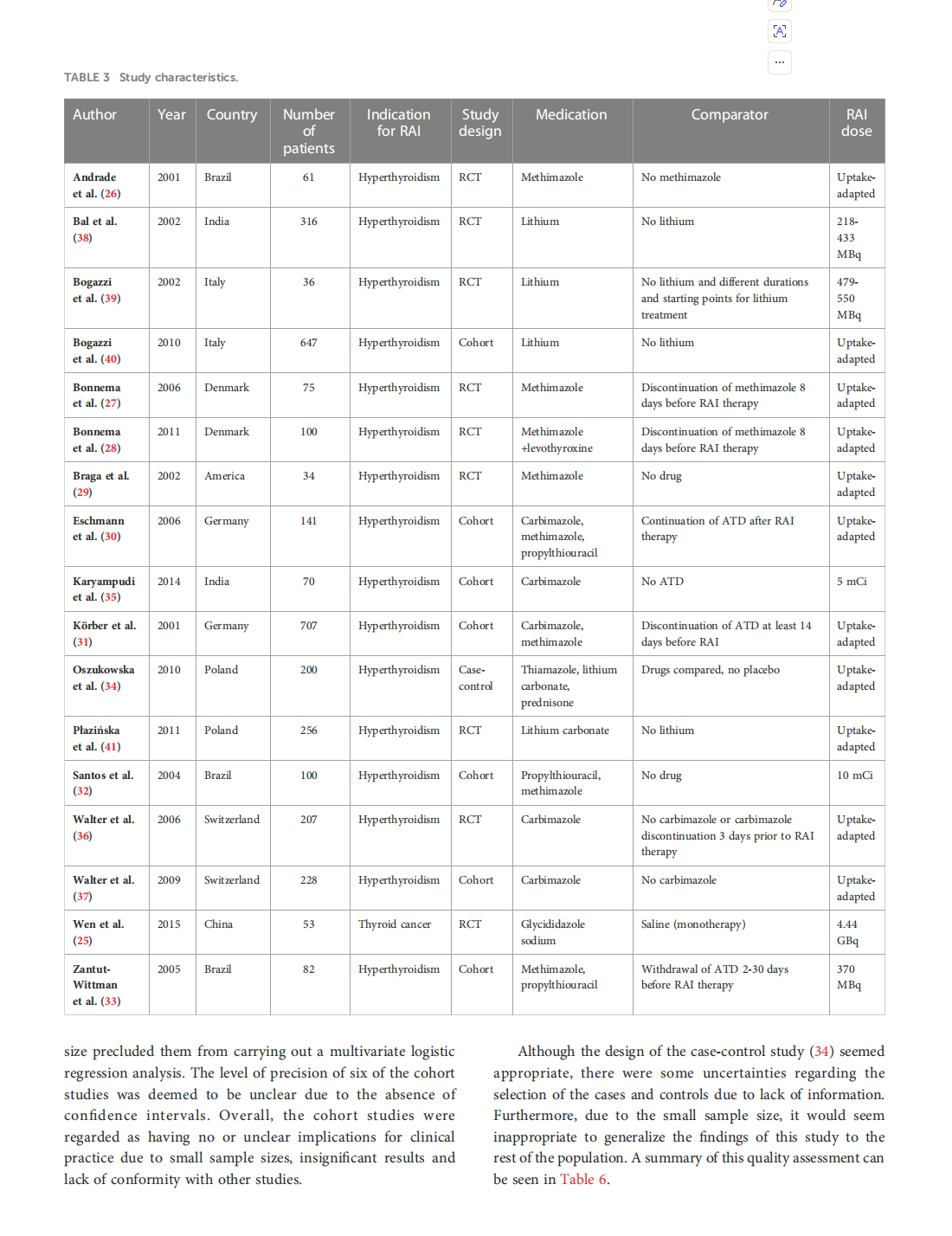






This article is excerpted from the《Frontiers in Endocrinology》 by Wound World

- 星期二, 30 12月 2025
A systematic review of treatment of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy by Pain Phenotype versus treatment Based on Medical comorbidities



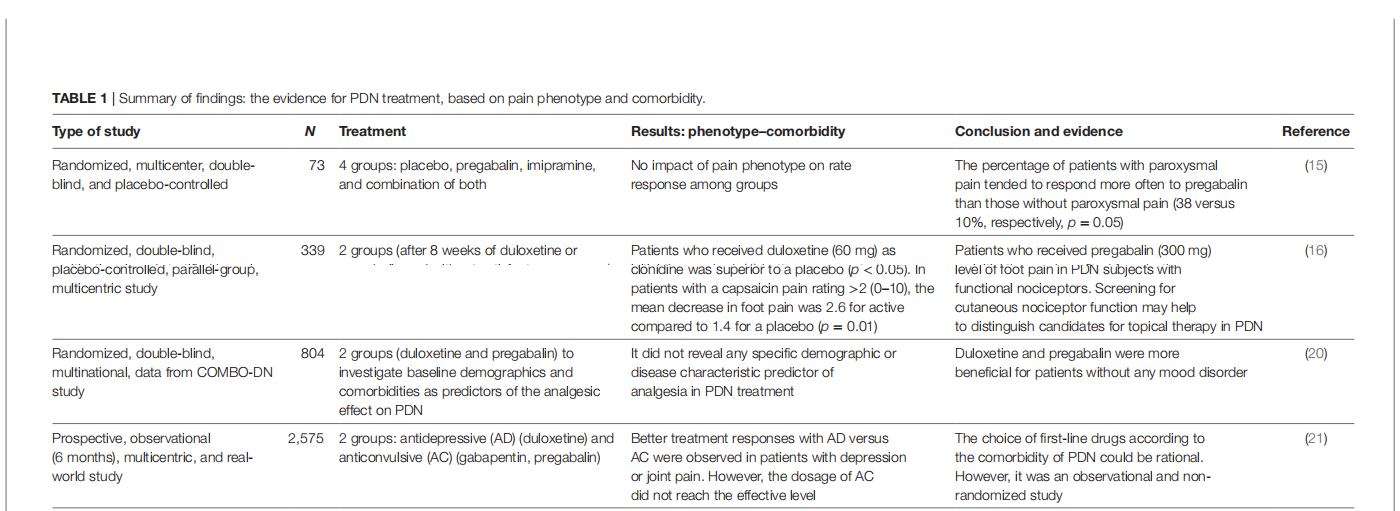
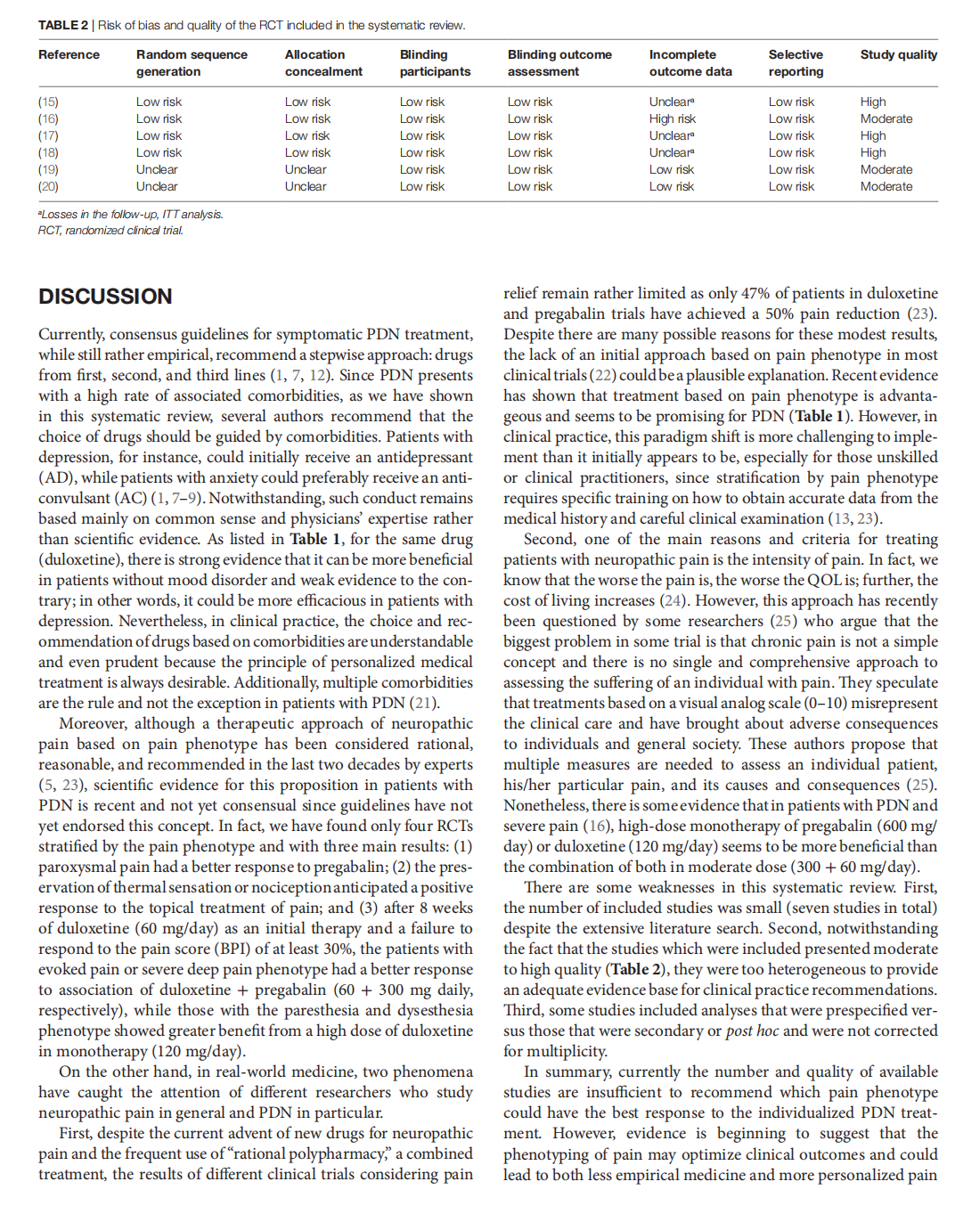

This article is excerpted from the 《Pain Research and Management》 by Wound World

- 星期一, 29 12月 2025
Medical treatment cost for Chinese inpatients with colorectal cancer by sites


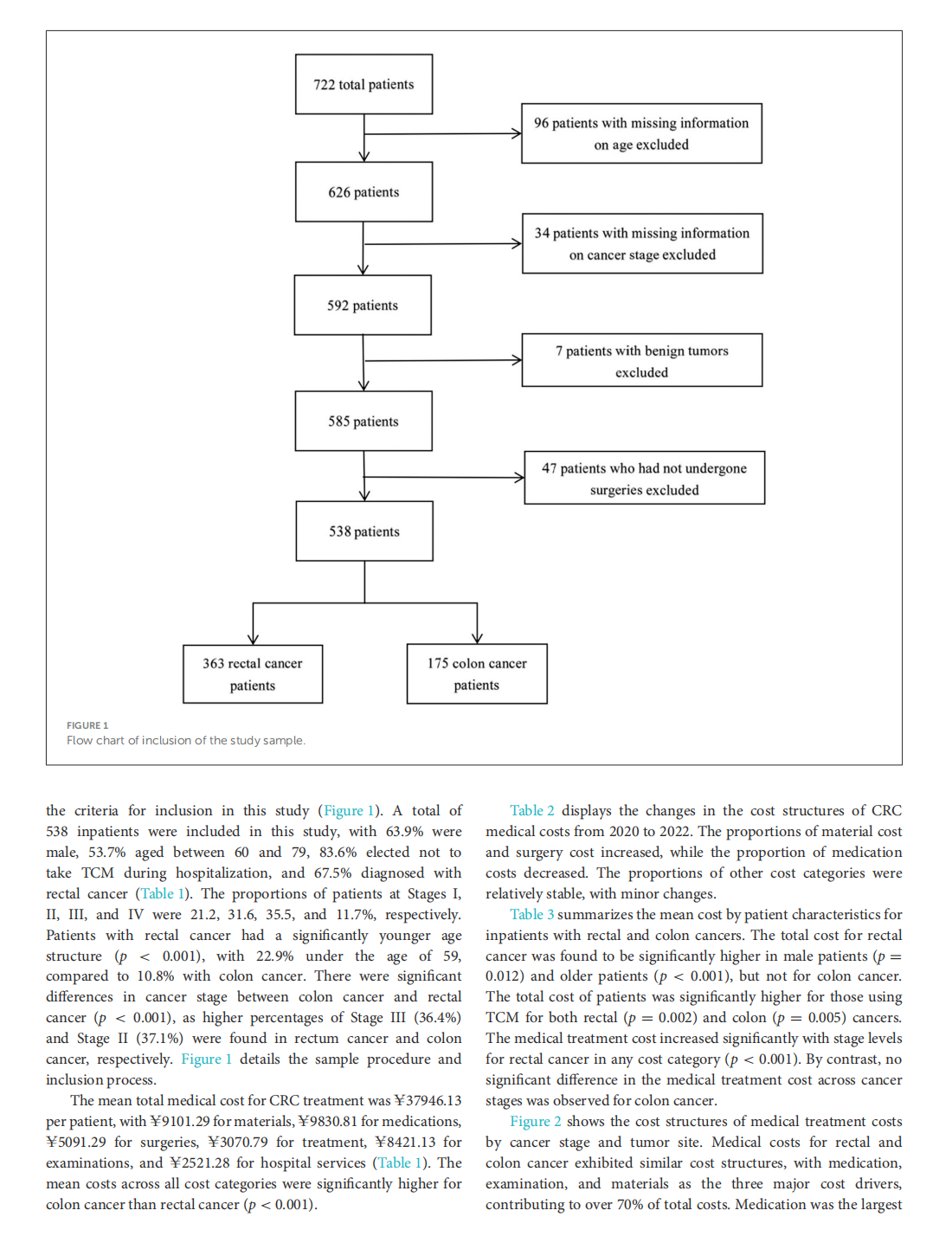
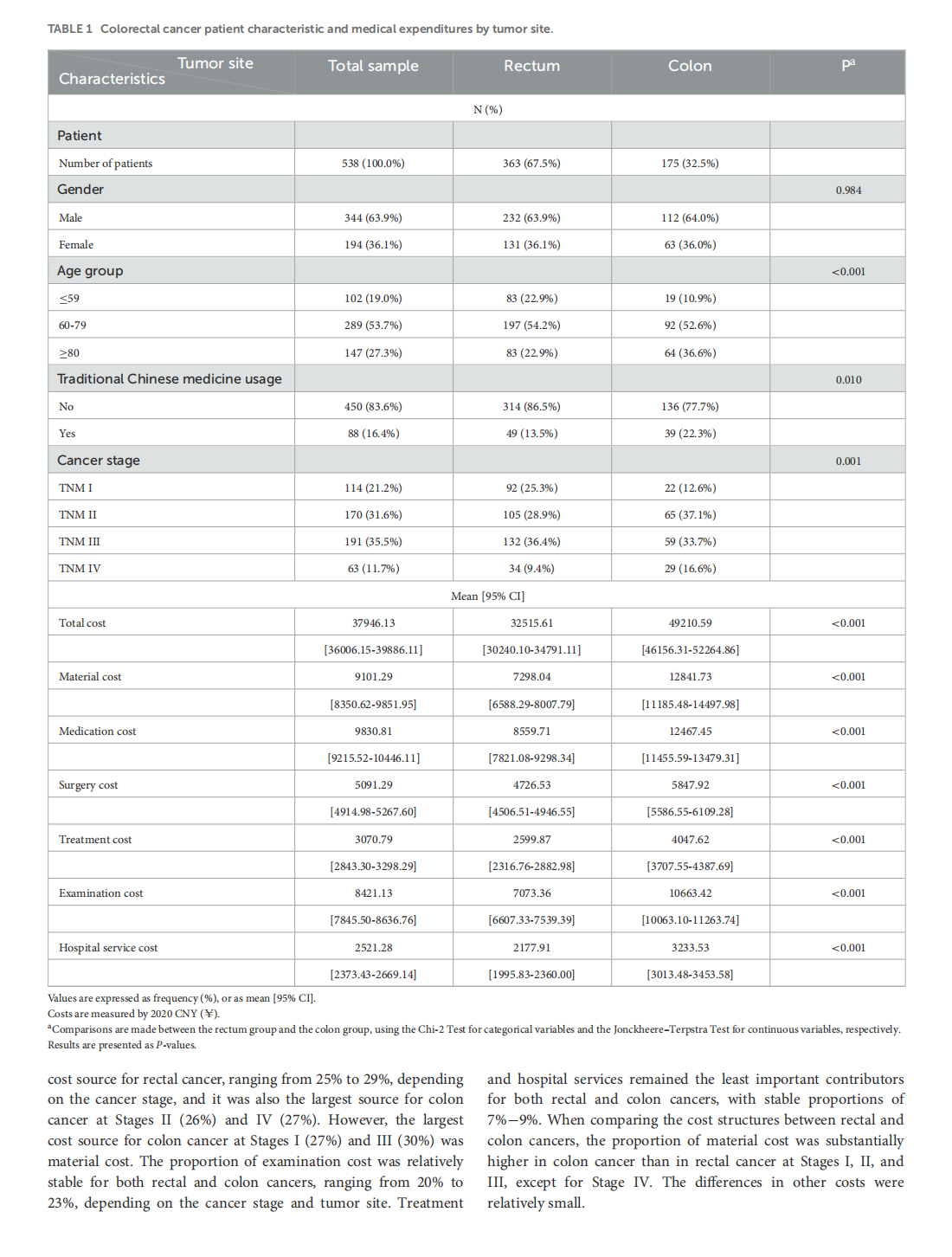
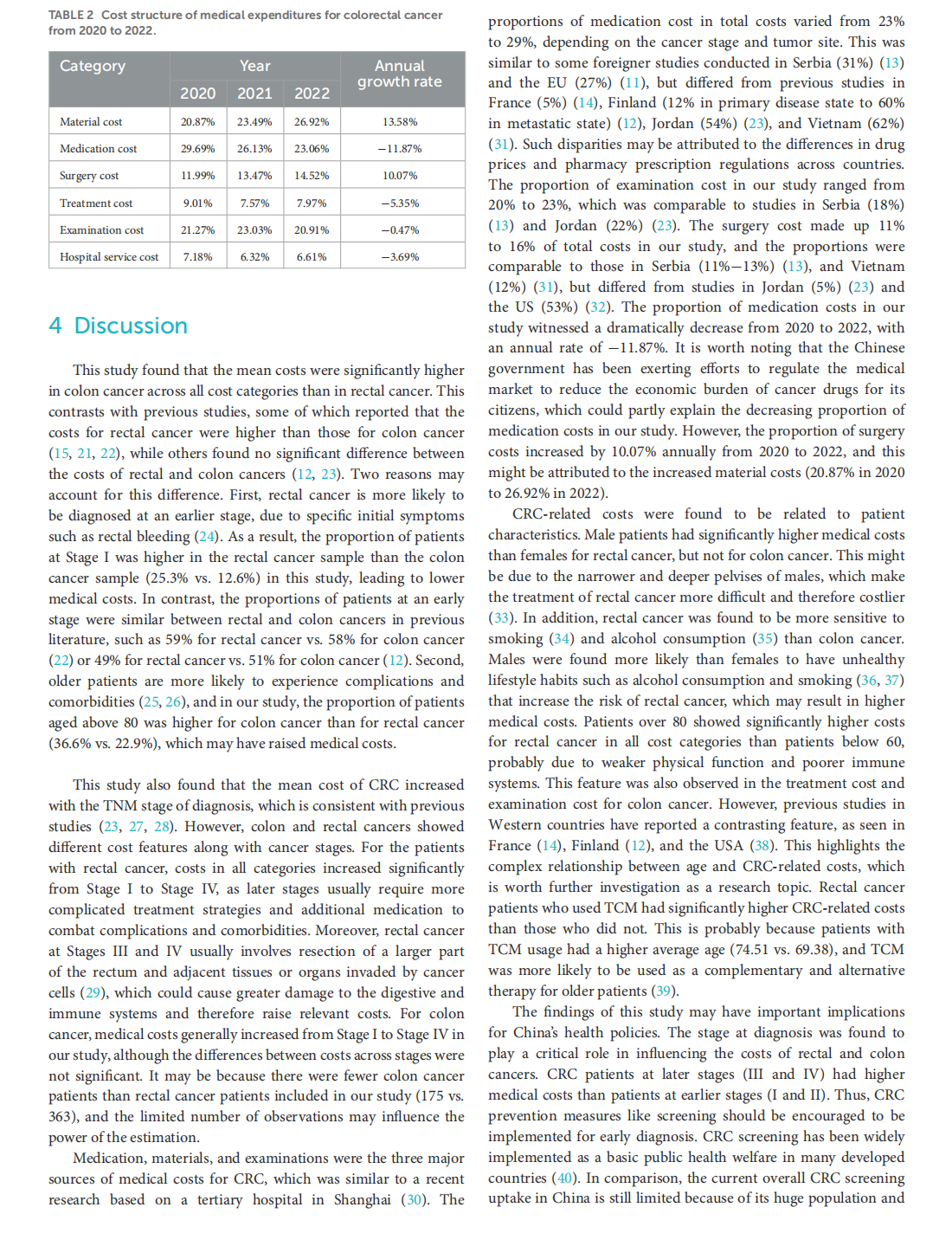
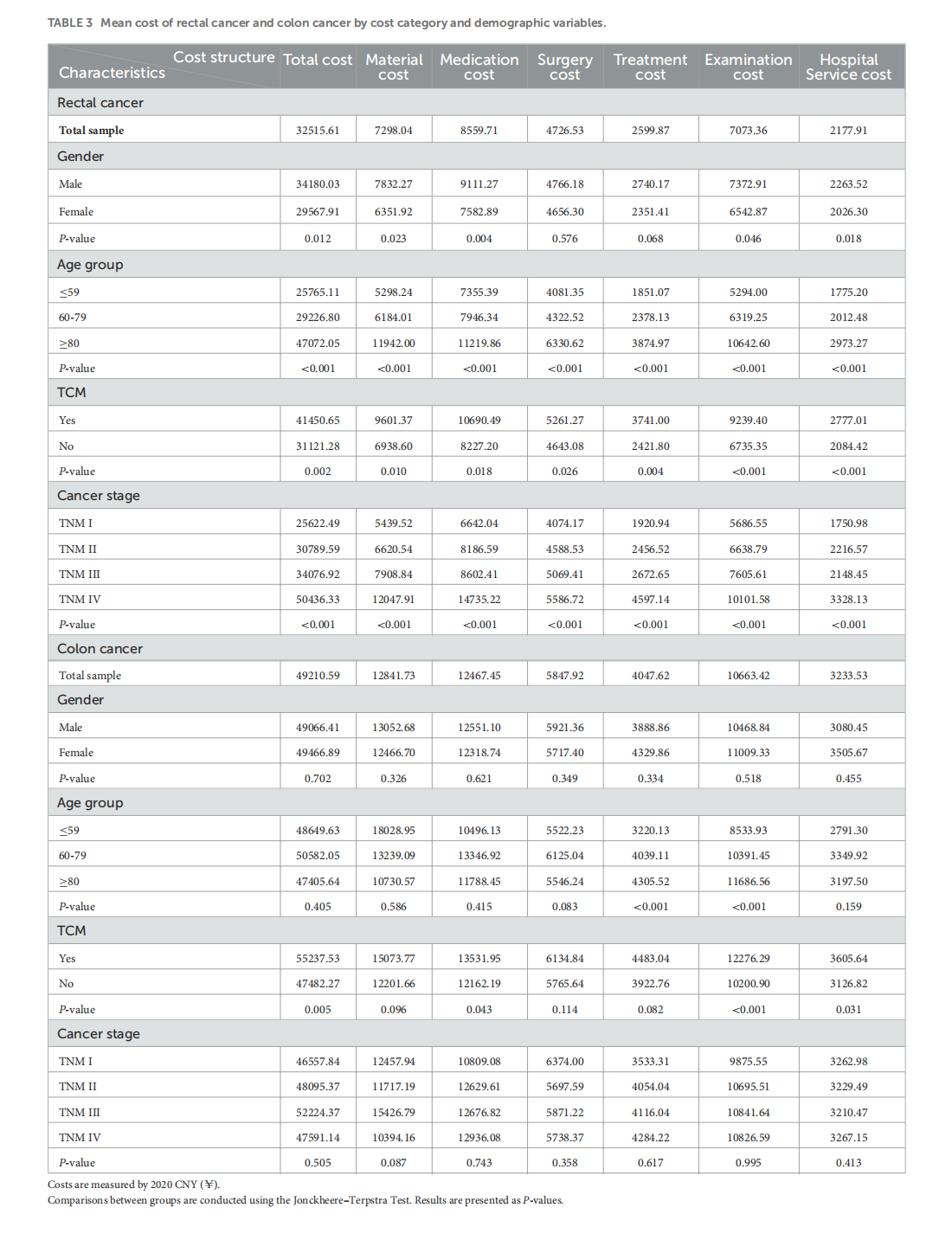
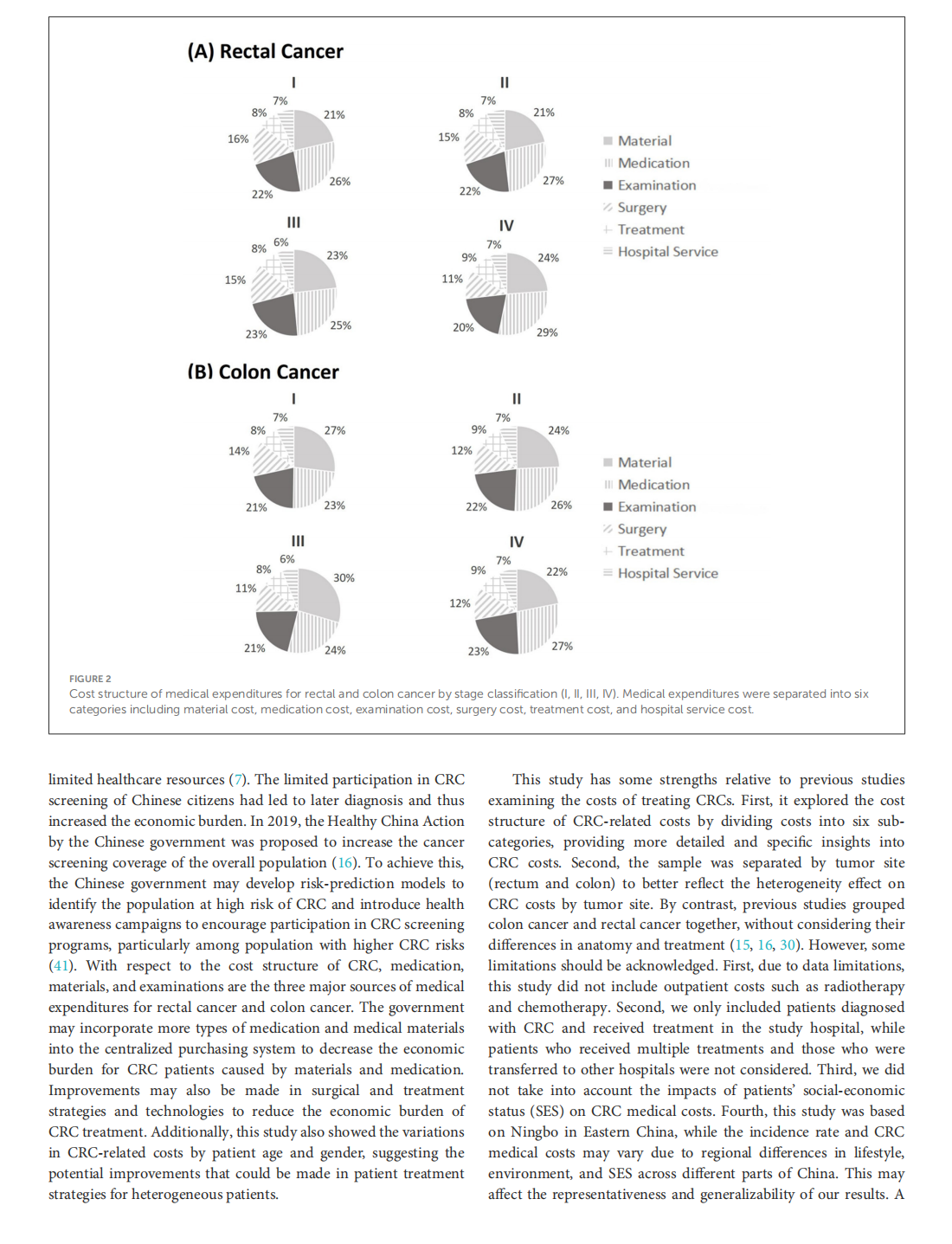


This article is excerpted from the 《Chinese Journal of Cancer》 by Wound World
